Abstract
With the smart speakers agent of Home Service Robot represented by voice interaction, tangible user interface interaction and somatosensory interaction are widely present in family environment and serve multiple family members, the trustworthy AI stimulates the transition of the interaction form from passive interaction to proactive interaction, finally into active interaction. However, with the personalization of family members’ needs, the improvement of emotional needs lead to user low patience and high expectations toward the home service robots, the traditional passive interaction has met the above changes of users. This paper proposes the active interaction design method to enhance the initiate of the intelligent agents to solve the user’s needs, improve Interaction performance and user experience. This paper uses questionnaire analysis, user interview, expert cognitive walkthrough, field survey, and comparative research to conduct research. Through the comparative study of passive interaction, proactive interaction and active interaction, the computational analysis, context awareness, consciousness awareness and emotion analysis, combined with the actual case of Baidu smart speakers project, the author put forward active interaction model and the active interaction design form of the family agent. Apply it to the family situation and gradually improve the active interaction research of the home service robot in the family environment.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
The Human-Agent Interaction (HAI) has experienced Command-Line Interface (CLI), Graphical User Interface (GUI), Voice User Interface (VUI) and Natural User Interface (NUI). The role of the agent transforms “no mind” machine to our family members, moves toward the interaction of human and machine integration.
Passive interaction is the main interaction form of the current home service robot which is from user to home service robot to user, but the home service robot lacks environmental awareness, mind awareness, emotion perception, knowledge graph and other factors, active interaction that predict user intent and initiate responses by intelligent systems begin to grow rapidly [1] and can effectively enhance the user experience. For the study of active interaction, DeepMind proposes to use meta-enhanced learning to achieve causal reasoning, so that the home service robot can actively interact [2]; Intel Labs China proposes to trigger active interaction through Confidence Interval(CI); Baidu proposes the NIRO system included active interaction model and put it into commercial use; Feng Yang et al. proposed an active interactive dialogue robot system and active dialogue method, and applied to the service industry. To some extent, active interaction solves technical problems such as system robustness, poor causal reasoning, and learning sample limitations.
This paper reviews and studies the passive interaction, proactive interaction and active interaction. It also conducts information classification and preliminary analysis on the main products of 50 home service robots, and the main functions, interaction forms and forms of 30 major competing products. Scientific analysis and user feedback were collected for market sales, market pricing, user feedback, etc.; data from 12 research reports were comprehensively compared; 142 valid questionnaires were collected for intelligent product demand surveys which are covering 18-71 years old, 20 The provinces and cities, the consumption level of 4 stalls, the occupation of 19 fields; the behavior observation and in-depth user interviews of three family types (three families, single-sex youth, empty nesters) are in progress.
2 Related Work
2.1 Agent in Home Service Robot
Agent refer to smart agents, artificial intelligence products, and so on. Bjorn Hermans pointed out that the basic attributes of the agent have self-control ability, social ability, reaction ability, active, temporary continuity, and goal-oriented ability [3]; Michael Wooldridge and Nicholas R. Jennings pointed out that the agent has “strong” and “weak” [4]; Daze discriminates the concept of agent and agency, and expounds the current research scope and research trends of HAI [5]; Zhao Longwen and Hou Yibin pointed out that agent is a three-tier structure consisting of mentality, internal behavior, and external behavior, it is an entity with high self-control ability that operates in a dynamic environment, and its fundamental goal is to accept and provide assistance to another entity [6]. Chen Gang et al. [7] studied the social organization method of agent and the performance of the cooperative behavior of agent in home service robot, and discussed the trustworthy relationship between agents and users.
2.2 The Needs of Users in Family Environment
With the development of Home automation, smart home systems, and pervasive computing, interaction design evolves from desktop systems to mobile devices of smart environments. In recent years, the research on agent has been more biased towards family scenarios. There have been a number of smart products with family-centric scenes such as Pepper, Luna, iRobot, Ecovacs Sweeping robot, Google Home and more. Compared with agent of typical environment such as office environment, outdoor public places and educational institutions, family agents need to consider the members privacy, individualized needs, emotional needs, appropriate interaction modes, trigger thresholds and speech design. We obtained the user’s demand about family agent based on the above user interviews and questionnaires (see Fig. 1).
3 Three Kinds of Interaction
3.1 Passive Interaction
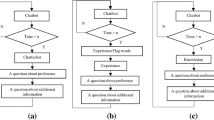
At present, The Human-Agent Interaction is divided into four stages: wake-up, input, calculation, and output. The user wakes up the agent through behavioral information such as languages, actions, and inputs instructions. The agent use machine vision and speech recognition to process digital and non-digitized instructions and output language, text and other feedbacks to the user. This form of interaction is passive for the user, and the author draws the passive interaction model (see Fig. 2). In family environment, users wake up the agent through the names of “XiaoDu XiaoDu” and “TmallGenie” and trigger one-way interaction with the agent. The whole process strengthens the user’s initiative, and the agent lack information fusion in offline environment and online environment, lack of integration of digital and non-digital information, lack of strong correlation of knowledge graph, and lack of data migrants. Passive interaction make the whole process boring and short-lived.
Through the above questionnaires, household interviews, market research, etc., the following problems exist in the passive interaction of family agents:
-
Training sample limitations, limited satisfaction with user needs
-
The level of semantic understanding is not high, and the ability of continuous dialogue is poor.
-
Awakening form is single, one way trigger form
-
Diversity of family characteristics, lack of satisfaction with the individual needs of family members
-
Low intelligence and low family integration
-
The result of the answer is mechanized and predictable
-
No feedback incentive
-
Lack of environmental perception, emotional perception and mind awareness
3.2 Proactive Interaction
Due to the limitations of the development of artificial intelligence technology, the development of the interaction of the agent does not immediately change from passive interaction to active interaction. It needs to experience proactive interaction. At present, the distinction between proactive interaction and active interaction is not obvious at Domestic and foreign. A proactive HMI can be run on top of a context- aware system and it tries to predict next feasible action based on the context [8]. Proactive HMIs can suggest the next step from context or from the history of the user [9]. For getting the proper context proactive HMI need to monitor the world around it which requires sensors and actuators [10]. The current academic research on proactive interaction is usually to connect it to context-aware technology, emphasizing the system’s calculation of the scene, ignoring knowledge graph based on entities and relationships.
The author believes that proactive interaction is an intermediate state from passive interaction to active interaction. Proactive interaction can “force” the agent to make user preference analysis results when the development of the intelligent feedforward system is not perfect. It can guide and intervene in the choice of agent solutions. The proactive interaction “forces” the agent to use the input or feedback information of the user as the data foundation for the feed-forward in the next related task. In this interaction process, the agent needs to passively collect the personalized information and preferences of the user. After passive interactive learning, the agent will actively interact according to the user’s situation next time. Proactive interaction is a better way to ease technical problems. Its continuous development can make the machine reach the constant perception of the environment, consciousness and emotion, and it can form the active interaction of the agent. At present, it mainly focuses on: schedule reminder, search related information push, the active endurance charging of the sweeping robot, etc., obviously the user needs to be satisfied by the active interaction.
3.3 Active Interaction
Active interaction essentially generate intelligent information data to activate interactive scenarios through multi-modal perception, context awareness, intelligent environment technology, multi-dimensional inductive interface, cognitive science and other technologies, and the data collected can verify and correct the correlation of machine technology such as knowledge graph. Because of that, the machine continuously improves the initiative accuracy. For example, Lomo Shopping, the latest product launched by Segway Robotics, attracts many sales in the form of active communication through the technology of position sensing, NOMI with NIO ES8, Baidu Car OS, and others.
In the questionnaire survey of the agent, the choice of the agent “can’t do big things” and “nothing to use eggs” accounted for 28.87% and 21.83% respectively, more than half of the doubts about the intelligence of the family agent, the user’s choice and user experience have a close relationship, and the introduction of active interaction can effectively improve intelligence.
Active interaction uses Silent Interface to substitute emotional listening and Embodied cognition feedback, allowing users to self-direct into the introspective state, and actively choose to judge, the agent expresses listening and feedback after active interaction, the user choose Feedback form and recognize the results, this form can achieve the goal of human-machine to a certain extent.
Through contrast analysis with passive interaction, proactive interaction, the author divides the active interaction into five parts: knowledge graph input with entity and relationship as information source, agent feedforward, agent output, user judgment and user feedback (see Fig. 3). By continuously inputting environmental information, emotional information, and consciousness information, the agent continuously completes the accuracy of the user image under the knowledge graph, and appropriately feeds forward the opportunity when it is associated with the user, and outputs it in the form of language, text, etc., user judgment and decision intelligence. The body actively interacts with the results, and feedbacks and responses. The accumulated feedback results can form the feedforward of the active interaction, and can also improve the accuracy of the active interaction of the agent.
3.4 Comparison Study Between Active Interaction and Passive Interaction
-
Different starting points
The passive interaction process starts from the user’s voice, action, text input, expression, lip movement and other user behavior such as wake-up response commands. These call points have been preset and if the user’s instruction behavior is fuzzy or inaccurate, it will affect accuracy. Active interaction is not complete triggered by a specific user behavior but based on big data operations of intelligent analysis of images, scenes, behaviors, and it based on the analysis results to form a feedforward, which is speculating the user’s needs and intentions. And then active provide relevant solutions to achieve the active of the interaction process.
-
Different information input stages
The information input of passive interaction occurs in the process of the task, and the user behavior as the starting point is input to the agent, but the information input of active interaction is to actively acquire the intent information, user characteristic information and space of the mobile phone before the interaction task is initiated. Environmental information serves as the basis for the formation of feedforward. The subject in passive interaction process is always the user, and the agent is the object that accepts the information and performs the task. The subject in the process of active interaction is the alternation of the user and the agent. The agent is no longer just the performer of the task, but can learn and accumulate the direction of the task, and truly realize the positive communication with the return rather than mechanical response and execution.
-
Passive interaction lacks user feedback mechanism and feedforward data content
In passive interaction, the agent’s behavior for the user is a fixed input and output, which is modeled. In the active interaction, the agent continuously optimizes the feedforward mechanism of the active interaction according to the user’s judgment and feedback, making it more user-friendly. Behavior and intention to form a personalized, customized service. For example, in a passive interaction, when the agent asks about the weather, the agent’s answer is only to answer the local situation. In the active interaction, the agent not only answers the local weather conditions, but also may take the initiative according to the user’s schedule. Prompt for weather conditions at the destination of the trip, or proactively alert the user to the weather changes in the location of the relatives.
The author compares passive interaction, proactive interaction and active interaction (see Table 1).
Table 1. Passive interaction vs. Proactive interaction vs Active interaction
4 Active Interaction in Smart Speakers Agent of Home Service Robot
4.1 Strong Active Interaction and Weak Active Interaction
Active interaction based on the weight of the user’s dominant role in the interaction process can be divided into strong active interaction and weak active interaction (see Table 2). Strong active interaction includes: notification, reminder, push and function inquiry. In this process, the user’s dominance is small, the speech uses more declarative sentences, and the function inquiry is mostly judged and selected, and the options provided to the user are less, for example, “When do you need to turn on the air conditioner for you?”, “Do you need to remind you tomorrow?” Weak active interaction mainly includes suggestions, content inquiries, and some careless words or actions that are not meaningful. Words use questions that have no clear options. For example, “Do you think the room temperature is right?”, “Welcome home!”
Strong active interaction and weak active interaction have no advantages and disadvantages, and fusion each other. In the design process, attention should be paid to the cooperation between strong active interaction and weak active interaction to form a coordinated and unified relationship, so as to adapt to home scenarios. Strong active interaction can effectively enhance the intelligent experience of the agent to the user, but too much makes the user feel invaded.
Weak active interaction can strengthen the user’s sense of ownership, but too much will reduce the intelligence of the agent to the user. Therefore, it is especially important to find a balance between them. This requires not only the planning of functions and speech in the early design of the agent. Due to the differences between individuals and groups, the agents in the family space are more important to form a family in the process of continuous learning and accumulation. The big data of the environment provides users with personalized and active interaction solutions.
4.2 Suggestions for the Family Smart Speakers in Active Interaction Design
-
Guarantee user privacy.
Active interaction associates user information through knowledge maps, but avoids multi-member intercommunication of controversial private information, ensuring users’ trust in the agent and selective sharing.
-
Ensure the perceptibility of active interaction.
Active interaction in the application process, it is necessary to let the user perceive the occurrence of active interaction through the intelligent body language and give the user the right to choose, so that the user feels the initiative of the agent, instead of feeling controlled by the agent.
-
The active interaction trigger mechanism changes with the user’s adaptability.
The staged active interaction trigger mechanism is to ensure that the user does not have an “over-smart” experience for the home agent, such as the reminder of the anniversary, the push of the news.
-
Provide options to give users decision-making power and initiative.
Providing alternative results to the user, allowing the user to enhance the sense of control of the agent by selecting, can also effectively reduce concerns about over smart.
-
Humanoid communication logic.
The active interaction of the human-like communication logic needs to be output through the semantic understanding of the association, such as: Need to wear more clothes tomorrow? The agent needs to locate the weather function, answer the user’s answer about the dressing, and then push the relevant weather information.
4.3 Design Case
-
Design background and the target user selection
The intervention of the active interaction of the agent can be applied in a variety of home environments to serve different groups of people. The author takes the interaction between the elderly group and the agent as a case. Through the observation of the interaction behavior of the elderly community, it is found that the elderly are full of expectations for the agent, but there are problems such as a single communication problem in the communication interaction. If you do not know the content of the conversation, you can forget the wake-up words directly. Issue instructions, talk to the agent at the same time, etc.
The elderly do not save the artificial form. Compared with the traditional passive interface, the young people become the ashes users through learning. In the process of using the agent, the elderly group is more inclined to the rookie player forever. The operations you master will always be patient with the agent.
-
User research
The author recorded the use of smart speakers by the elderly Ren for 24 h, and excerpted the original sentence as follows (see Table 3):
Table 3. User’s original words and scenes The author finds that the function and content of the elderly are not particularly clear to the elderly. Every time they say nothing, they don’t know what questions to ask. They often forget the name of the agent, which prevents the agent from starting.
-
Introducing an active interaction model
The author made an improved design of the intelligent speaker service process based on active interaction model and active interaction form above (see Fig. 4):
5 Conclusion
The interaction from passive interaction to proactive interaction to active interaction need to accurately identify task feature information, object relationship information, spatial scene information, relationship knowledge graph, etc. in a complex environment. With the active interaction, the individual needs of the members are satisfied, and the user’s trust in the intelligence of the agent is enhanced. To a certain extent, the agent do active recommendation and service through the contact of the knowledge graph which can compensate for the disadvantages of the machine semantic understanding. Active interaction also make the intelligent agent in home service robot become active which consequently enhance the user’s good willing and experience to communicate with the agent.
References
Begole, B.: Responsive media: media experiences in the age of thinking machines. APSIPA Trans. on Signal Inf. Process., 6 (2017)
Dasgupta, I., Wang, J., Chiappa S., et al.: Causal Reasoning from Meta-reinforcement Learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.08162 (2019)
Hermans B.: Intelligent Software Agents on the Internet: Chapters 6–7. First Monday, vol. 2(3) (1997)
Wooldridge, M., Jennings, N.: Intelligent agents: theory and practice. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 10(2), 115–152 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1017/s0269888900008122
Da, Z., Lu, C.: Interaction between human and agent: artificial intelligence system design related to people. Decoration 11, 14–21 (2016)
Zhao, L., Hou, Y.: Intelligent software: from object-oriented to agent-oriented. Comput. Eng. Appl., (05), 41–43+125 (2001)
Chen, G., Lu, R.Q.: The relation Web model: an organizational approach to agent cooperation based on social mechanism. J. Comput. Res. Dev. 40(1), 107–114 (2003)
Hämäläinen, V.P.: Usability testing methodology of proactive HMIs for virtual control room, pp. 13–14 (2014)
De Boeck, J., Verpoorten, K., Luyten, K., Coninx, K.: A Comparison between Decision Trees and Markov Models to Support Proactive Interfaces. In: 18th International Conference on Database and Expert Systems Applications (DEXA 2007), pp. 94–98 (2007)
Tennenhouse, D.: Proactive computing. Commun. ACM 43(5), 43–50 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Qin, J., Chen, Z., Zhang, W., Guan, D., Wu, Z., Zhao, M. (2019). Research on Active Interaction Design for Smart Speakers Agent of Home Service Robot. In: Marcus, A., Wang, W. (eds) Design, User Experience, and Usability. User Experience in Advanced Technological Environments. HCII 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11584. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23541-3_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23541-3_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-23540-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-23541-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)