Abstract
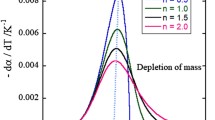
Different temperature, power, flow rate and other factors have different effects on the removal of soot particles in the tail gas of simulated diesel vehicles, and the removal effect of each kind of soot particle catalytic removal method is also different. In order to further improve the effect of soot particle catalytic removal, a statistical analysis method of soot particle catalytic removal method based on big data is designed. Using large data technology to extract catalytic removal methods of soot particles, detailed analysis of each method was carried out, and the soot combustion performance of soot particles catalytic removal method was compared. The results showed that the removal of soot particles based on perovskite catalyst was more effective than that of soot particle removal method based on sol-gel preparation method, and that soot particles were catalyzed by low temperature plasma. The combustion performance of the removal method is better, and the catalytic removal performance is more superior.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Z., Qiu, L., Cheng, X., et al.: The evolution of soot morphology and nanostructure in laminar diffusion flame of surrogate fuels for diesel. Fuel 211(1), 517–528 (2018)
Zhao, F., Yang, W., Yu, W., et al.: Numerical study of soot particles from low temperature combustion of engine fueled with diesel fuel and unsaturation biodiesel fuels. Appl. Energy 211(1), 187–193 (2018)
Liu, S., Bai, W., Liu, G., et al.: Parallel fractal compression method for big video data. Complexity 2018, 2016976 (2018)
Joo, P.H., Gigone, B., Griffin, E.A., et al.: Soot primary particle size dependence on combustion pressure in laminar ethylene diffusion flames. Fuel 220(15), 464–470 (2018)
Abian, M., Martin, C., Nogueras, P., et al.: Interaction of diesel engine soot with NO2 and O-2 at diesel exhaust conditions. Effect of fuel and engine operation model. Fuel 212(15), 455–461 (2018)
Shen, J., Feng, X., Liu, R., et al.: Tuning SnO 2 surface with CuO for soot particulate combustion: The effect of monolayer dispersion capacity on reaction performance[J]. Chinese J. Catalysis 40(6), 905–916 (2019)
Alcan, G., Yilmaz, E., Unel, M., et al.: Estimating soot emission in diesel engines using gated recurrent unit networks. IFAC Proc. Vol. 52(3), 544–549 (2019)
Liu, S., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., et al.: Introduction of key problems in long-distance learning and training. Mobile Netwk. Appl. 24(1), 1–4 (2019)
Jerez, A., Cruz Villanueva, J.J., Figueira, D.S.L.F., et al.: Measurements and modeling of PAH soot precursors in coflow ethylene/air laminar diffusion flames. Fuel 236(15), 452–460 (2019)
Duvvuri, P.P., Sukumaran, S., Shrivastava, R.K., et al.: Modeling soot particle size distribution in diesel engines. Fuel 243(1), 70–78 (2019)
Shuai, L., Weiling, B., Nianyin, Z., et al.: A fast fractal based compression for MRI images. IEEE Access 7, 62412–62420 (2019)
Zhang, R., Pham, P.X., Kook, S., et al.: Influence of biodiesel carbon chain length on in-cylinder soot processes in a small bore optical diesel engine. Fuel 235(1), 1184–1194 (2019)
Liu, S., Glowatz, M., Zappatore, M., et al.: e-Learning, e-Education, and Online Training. Springer International Publishing, Berlin (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Meng, Xh., Yang, P., Qin, Hb., Duan, Lh. (2021). Statistical Analysis of Catalytic Removal of Soot Particles Based on Big Data. In: Liu, S., Xia, L. (eds) Advanced Hybrid Information Processing. ADHIP 2020. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 348. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67874-6_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67874-6_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-67873-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-67874-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)