Abstract
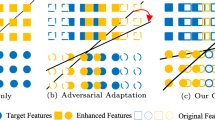
In this paper, we propose a novel unsupervised domain adaptation re-ID framework by fusing feature adversarial learning and self-similarity clustering. Different from most of the existing works which only regard the source domain data as network pretraining data, we use the source domain data both in network pretraining and finetuing stage. Concretely, we construct an feature adversarial learning module to learn domain invariant feature representations. The feature extractor network is optimized in an adversarial training manner through minimizing the discrepancy of feature representations between source and target domains. To further enhance the discriminability of the feature extractor network, we design the self-similarity clustering module to mine the implicit similarity relationships among the unlabeled samples of the target domain. By unsupervised clustering, we can generate pseudo-identity labels for the target domain data, which are then combined with the labeled source data together to train the feature extractor network. Additionally, we present a relabeling algorithm to construct correspondence between two groups of pseudo-identity labels generated by two iterative clusterings. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen, J., Qu, Y., Zhang, W., et al.: Wasserstein distance guided representation learning for domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, pp. 4058–4065 (2018)
Sun, B., Feng, J., Saenko, K.: Return of frustratingly easy domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, pp. 2058–2065 (2016)
Fu, Y., Wei, Y., Wang, G., et al.: Self-similarity grouping: a simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seoul, pp. 6111–6120 (2019)
Goodfellow, I.J., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, p. 27 (2014)
Deng, W., Zheng, L., Kang, G., et al.: Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, pp. 994–1003 (2018)
Wei, L., Zhang, S., Gao, W., et al.: Person transfer GAN to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, pp. 79–88 (2018)
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Generalizing a person retrieval model hetero- and homogeneously. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018, Part XIII. LNCS, vol. 11217, pp. 176–192. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8_11
Peng, J., Wang, H., Fu, X.: Cross Domain Knowledge Learning with Dual-branch Adversarial Network for Vehicle Re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.00006 (2019)
Yu, H., Zheng, W., Wu, A., et al.: Unsupervised person re-identification by soft multilabel learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, pp. 2143–2152 (2019)
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Luo, Z., et al.: Invariance matters: exemplar memory for domain adaptive person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, pp. 598–607 (2019)
Fan, H., Zheng, L., Yan, C., et al.: Unsupervised person re-identification: clustering and fine-tuning. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 14, 83 (2018)
Ge, Y., Chen, D., Li, H.: Mutual mean-teaching: pseudo label refinery for unsupervised domain adaptation on person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (2020, in press)
Song, L., Wang, C., Zhang, L., et al.: Unsupervised domain adaptive re-identification: Theory and practice. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.11334 (2018)
Wen, Y., Zhang, K., Li, Z., Qiao, Yu.: A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016, Part VII. LNCS, vol. 9911, pp. 499–515. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46478-7_31
Arthur, D., Sergei, V.: k-means++: the advantages of careful seeding. In: Proceedings of the Eighteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (2007)
Luo, H., Gu, Y., Liao, X., et al.: Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In: Proceedings of The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (2019)
Luo, H., Jiang, W., Gu, Y., et al.: A strong baseline and batch normalization neck for deep person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 22(10), 2597–2609 (2019)
Schroff, F., Kalenichenko, D., Philbin, J.: FaceNet: a unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In: Proceedings of The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2015)
Liu, X., Liu, W., Ma, H., et al.: Large-scale vehicle re-identification in urban surveillance videos. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Mulimedia & Expo, pp. 1–6 (2016)
Liu, H., Tian, Y., Wang, Y., et al.: Deep relative distance learning: tell the difference between similar vehicles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2167–2175 (2016)
Zheng, L., Shen, L., Tian, L., et al.: Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Vision (2015)
Zheng, Z., Zheng, L., Yang, Y.: Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In: Proceedings of The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (2017)
Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Tian, Q., Wang, S.: Beyond part models: person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018, Part IV. LNCS, vol. 11208, pp. 501–518. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01225-0_30
Wang, G., Yuan, Y., Chen, X., et al.: Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of ACM Multimedia Conference on Multimedia Conference, pp. 274–282 (2018)
Zheng, L., Huang, Y., Lu, H., et al.: Pose invariant embedding for deep person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(9), 4500–4509 (2019)
Zhu, K., Guo, H., Liu, Z., Tang, M., Wang, J.: Identity-guided human semantic parsing for person re-identification. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020, Part III. LNCS, vol. 12348, pp. 346–363. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58580-8_21
Qian, X., Qian, X., et al.: Pose-normalized image generation for person re-identification. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018, Part IX. LNCS, vol. 11213, pp. 661–678. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01240-3_40
Zheng, Z., Yang, X., Yu, Z., et al.: Joint discriminative and generative learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2019)
Guo, H., Zhao, C., Liu, Z., et al.: Learning coarse-to-fine structured feature embedding for vehicle re-identification. In: Proceedings of AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 6853–6860 (2018)
Guo, H., Zhu, K., Tang, M., et al.: Two-level attention network with multi-grain ranking loss for vehicle re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28, 4328–4338 (2019)
Yao, Y., Zheng, L., Yang, X., Naphade, M., Gedeon, T.: Simulating content consistent vehicle datasets with attribute descent. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020, Part VI. LNCS, vol. 12351, pp. 775–791. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58539-6_46
Sun, B., Saenko, K.: Deep CORAL: correlation alignment for deep domain adaptation. In: Hua, G., Jégou, H. (eds.) ECCV 2016, Part III. LNCS, vol. 9915, pp. 443–450. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49409-8_35
Ganin, Y., Lempitsky, V.: Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (2017)
Isola, P., Zhu, J., Zhou, T., et al.: Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2017)
Zhu, J., Park, T., Isola, P., et al.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Vision (2017)
Choi, Y., Choi, M., Kim, M., et al.: StarGAN: unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain image-to-image translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2018)
Karl, P.: LIII. on lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. London, Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 2, 559–572 (1901)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., et al.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (2016)
Kingma, D., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: Proceedings of International Conference for Learning Representations (2015)
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., et al.: PyTorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2019)
Yan, X., Misra, I., Gupta, A., et al.: ClusterFit: Improving Generalization of Visual Representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.03330 (2019)
Huang, C., Li, Y., Change Loy, C., et al.: Learning deep representation for imbalanced classification. In Proceedings of The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Liao, S., Hu, Y., Zhu, X., et al.: Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2015)
Peng, P., Xiang, T., Wang, Y., et al.: Unsupervised cross-dataset transfer learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Yu, H., Wu, A., Zheng, W.: Crossview asymmetric metric learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Vision (2017)
Wang, J., Zhu, X., Gong, S., et al.: Transferable joint attribute-identity deep learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2018)
Li, Y., Yang, F., Liu, Y., et al.: Adaptation and re-identification network: an unsupervised deep transfer learning approach to person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2018)
Qi, L., Wang, L., Huo, J., et al.: A novel unsupervised camera-aware domain adaptation framework for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (2019)
Zhang, X., Cao, J., Shen, C., et al.: Self-training with progressive augmentation for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. In: Proceedings of The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (2019)
Wang D., Zhang S.: Unsupervised person re-identification via multi-label classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yan, T., Guo, H., Liu, S., Zhao, C., Tang, M., Wang, J. (2021). Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Re-Identification with Feature Adversarial Learning and Self-similarity Clustering. In: Del Bimbo, A., et al. Pattern Recognition. ICPR International Workshops and Challenges. ICPR 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12664. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68799-1_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68799-1_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-68798-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-68799-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)