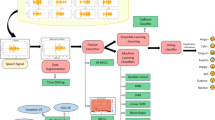
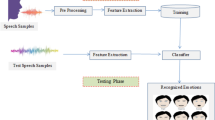
Abstract
Some of the most exciting applications of Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) focus on gathering emotions in daily life contexts, such as social robotics, voice assistants, entertainment industries, and health support systems. Among the most popular social humanoids launched in the last years, Softbank Pepper® can be remarked. This humanoid sports an exciting multi-modal emotional module, including face gesture recognition and Speech Emotion Recognition. On the other hand, a competitive SER algorithm for embedded systems [2] based on a bag of models (BoM) method was presented in previous works. As Pepper is an exciting and extensible platform, current work represents the first step to a series of future social robotics projects. Specifically, this paper systematically compared Pepper’s SER module (SER-Pepper) against a new release of our SER algorithm based on a BoM of XTraTress and CatBoost (SER-BoM). A complete workbench to achieve a fair comparison has been deployed, including other issues: selecting two well-known SER datasets, SAVEE and RAVNESS, and a standardised playing and recording environment for the files of the former datasets. The SER-BoM algorithm has shown better results in all the validation contexts.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Pepper NAO operating system doesn’t allow launching the SER-Pepper module fed with files stored inside Pepper.
- 2.
The hyperparameters for CatBoost and ExtraTree were {iterations = 10000, learning_rate = 0.04} and {n_estimators = 20000} respectively.
References
Ahsan, M., Kumari, M.: Physical features based speech emotion recognition using predictive classification. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 8(2), 63–74 (2016)
de la Cal, E., Gallucci, A., Villar, J.R., Yoshida, K., Koeppen, M.: A first prototype of an emotional smart speaker. In: Sanjurjo González, H., Pastor López, I., García Bringas, P., Quintián, H., Corchado, E. (eds.) SOCO 2021. AISC, vol. 1401, pp. 304–313. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87869-6_29
Documentation, S.R.: Pepper SER algorithm - ALVoiceEmotionAnalysis (2012). http://doc.aldebaran.com/2-5/naoqi/audio/alvoiceemotionanalysis.html#alvoiceemotionanalysis
Dorogush, A.V., Ershov, V., Gulin, A.: CatBoost: gradient boosting with categorical features support, pp. 1–7 (2018)
Geurts, P., Ernst, D., Wehenkel, L.: Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 63(1), 3–42 (2006)
Haq, S., Jackson, P., Edge, J.: Audio-visual feature selection and reduction for emotion classification. In: Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 39, pp. 7420–7431 (2008)
Haq, S., Jackson, P.J.B.: Speaker-dependent audio-visual emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Auditory-Visual Speech Processing (AVSP 2008), Norwich, UK (2009)
Haq, S., Jackson, P.J.B.: Machine Audition: Principles, Algorithms and Systems. Chap. Multimodal, pp. 398–423. IGI Global, Hershey (2010)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. CoRR abs/1512.0 (2015)
Livingstone, S.R., Russo, F.A.: The Ryerson audio-visual database of emotional speech and song (RAVDESS): a dynamic, multimodal set of facial and vocal expressions in north American english. PLoS ONE 13(5), e0196391 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196391
Mitsuyoshi, S., Ren, F., Tanaka, Y., Kuroiwa, S.: Non-verbal voice emotion analysis system 2(4), 4198 (2006)
Pandey, A.K., Gelin, R.: A mass-produced sociable humanoid robot: pepper: the first machine of its kind. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 25(3), 40–48 (2018)
Van Erp, M., Vuurpijl, L., Schomaker, L.: An overview and comparison of voting methods for pattern recognition. In: Proceedings - International Workshop on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition, IWFHR, pp. 195–200 (2002)
Acknowledgement
This research has been funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economics and Industry, grant PID2020-112726RB-I00, by the Spanish Research Agency (AEI, Spain) under grant agreement RED2018-102312-T (IA-Biomed), and by the Ministry of Science and Innovation under CERVERA Excellence Network project CER-20211003 (IBERUS) and Missions Science and Innovation project MIG-20211008 (INMERBOT). Also, by Principado de Asturias, grant SV-PA-21-AYUD/2021/50994, and by European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (project DIH4CPS) under the Grant Agreement no 872548. And by CDTI (Centro para el Desarrollo Tecnológico Industrial) under projects CER-20211003 and CER-20211022 and by ICE (Junta de Castilla y León) under project CCTT3/20/BU/0002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
de la Cal, E., Sedano, J., Gallucci, A., Valderde, P. (2023). A Comparison of Two Speech Emotion Recognition Algorithms: Pepper Humanoid Versus Bag of Models. In: García Bringas, P., et al. 17th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2022). SOCO 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 531. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18050-7_62
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18050-7_62
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-18049-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-18050-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)