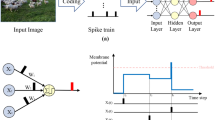
Abstract
Brain-inspired Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) have bio-plausibility and low-power advantages over Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs). Applications of SNNs are currently limited to simple classification tasks because of their poor performance. In this work, we focus on bridging the performance gap between ANNs and SNNs on object detection. Our design revolves around network architecture and spiking neuron. First, the overly complex module design causes spike degradation when the YOLO series is converted to the corresponding spiking version. We design a SpikeYOLO architecture to solve this problem by simplifying the vanilla YOLO and incorporating meta SNN blocks. Second, object detection is more sensitive to quantization errors in the conversion of membrane potentials into binary spikes by spiking neurons. To address this challenge, we design a new spiking neuron that activates Integer values during training while maintaining spike-driven by extending virtual timesteps during inference. The proposed method is validated on both static and neuromorphic object detection datasets. On the static COCO dataset, we obtain 66.2% mAP@50 and 48.9% mAP@50:95, which is +15.0% and +18.7% higher than the prior state-of-the-art SNN, respectively. On the neuromorphic Gen1 dataset, we achieve 67.2% mAP@50, which is +2.5% greater than the ANN with equivalent architecture, and the energy efficiency is improved by 5.7\(\times \). Code: https://github.com/BICLab/SpikeYOLO.
X. Luo, M. Yao—Equal contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bochkovskiy, A., Wang, C.Y., Liao, H.Y.M.: Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.10934 (2020)
Bu, T., Fang, W., Ding, J., DAI, P., Yu, Z., Huang, T.: Optimal ANN-SNN conversion for high-accuracy and ultra-low-latency spiking neural networks. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2022). https://openreview.net/forum?id=7B3IJMM1k_M
Cao, Y., Chen, Y., Khosla, D.: Spiking deep convolutional neural networks for energy-efficient object recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vision 113, 54–66 (2015)
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., Zagoruyko, S.: End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part I, pp. 213–229. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_13
Chollet, F.: Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1800–1807 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.195
Cordone, L., Miramond, B., Thierion, P.: Object detection with spiking neural networks on automotive event data. In: 2022 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2022)
Davies, M., et al.: Loihi: a neuromorphic manycore processor with on-chip learning. IEEE Micro 38(1), 82–99 (2018)
De Tournemire, P., Nitti, D., Perot, E., Migliore, D., Sironi, A.: A large scale event-based detection dataset for automotive. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.08499 (2020)
Deng, S., Li, Y., Zhang, S., Gu, S.: Temporal efficient training of spiking neural network via gradient re-weighting. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2022). https://openreview.net/forum?id=_XNtisL32jv
Diehl, P.U., Neil, D., Binas, J., Cook, M., Liu, S.C., Pfeiffer, M.: Fast-classifying, high-accuracy spiking deep networks through weight and threshold balancing. In: 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2015)
Ding, X., Zhang, X., Ma, N., Han, J., Ding, G., Sun, J.: Repvgg: making vgg-style convnets great again. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13733–13742 (2021)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2021). https://openreview.net/forum?id=YicbFdNTTy
Eshraghian, J.K., et al.: Training spiking neural networks using lessons from deep learning. Proc. IEEE 111(9), 1016–1054 (2023)
Fang, W., Yu, Z., Chen, Y., Huang, T., Masquelier, T., Tian, Y.: Deep residual learning in spiking neural networks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 21056–21069 (2021)
Gallego, G., et al.: Event-based vision: a survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(1), 154–180 (2020)
Girshick, R.: Fast r-cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1440–1448 (2015)
Girshick, R., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., Malik, J.: Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 580–587 (2014)
Guo, Y., et al.: Ternary spike: Learning ternary spikes for spiking neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.06372 (2023)
Guo, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, L., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Huang, X., Ma, Z.: Im-loss: information maximization loss for spiking neural networks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 156–166 (2022)
Guo, Y., et al.: Rmp-loss: regularizing membrane potential distribution for spiking neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 17391–17401 (2023)
Han, M., Wang, Q., Zhang, T., Wang, Y., Zhang, D., Xu, B.: Complex dynamic neurons improved spiking transformer network for efficient automatic speech recognition. In: Thirty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2023) (2023)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) Computer Vision - ECCV 2016, pp. 630–645. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2016)
Horowitz, M.: 1.1 computing’s energy problem (and what we can do about it). In: 2014 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference digest of technical papers, pp. 10–14. IEEE (2014)
Hu, J., et al.: High-performance temporal reversible spiking neural networks with \(\cal{O}(l)\) training memory and \(\cal{O}\)(1) inference cost. In: Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning (2024). https://openreview.net/forum?id=s4h6nyjM9H
Hu, Y., Zheng, Q., Jiang, X., Pan, G.: Fast-snn: fast spiking neural network by converting quantized ann. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(12), 14546–14562 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3275769
Hu, Y., Deng, L., Wu, Y., Yao, M., Li, G.: Advancing spiking neural networks toward deep residual learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, pp. 1–15 (2024)
Kim, S., Park, S., Na, B., Kim, J., Yoon, S.: Towards fast and accurate object detection in bio-inspired spiking neural networks through Bayesian optimization. IEEE Access 9, 2633–2643 (2020)
Kim, S., Park, S., Na, B., Yoon, S.: Spiking-yolo: spiking neural network for energy-efficient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 11270–11277 (2020)
Kim, Y., Park, H., Moitra, A., Bhattacharjee, A., Venkatesha, Y., Panda, P.: Rate coding or direct coding: Which one is better for accurate, robust, and energy-efficient spiking neural networks? In: ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 71–75. IEEE (2022)
Li, C., Jones, E.G., Furber, S.: Unleashing the potential of spiking neural networks with dynamic confidence. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 13304–13314 (2023)
Li, Y., He, X., Dong, Y., Kong, Q., Zeng, Y.: Spike calibration: Fast and accurate conversion of spiking neural network for object detection and segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.02702 (2022)
Li, Y., Geller, T., Kim, Y., Panda, P.: Seenn: towards temporal spiking early exit neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36 (2024)
Lin, T.Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2117–2125 (2017)
Lin, T.-Y., et al.: Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6-12, 2014, Proceedings, Part V, pp. 740–755. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
Maass, W.: Networks of spiking neurons: the third generation of neural network models. Neural Netw. 10(9), 1659–1671 (1997)
Merolla, P.A., et al.: A million spiking-neuron integrated circuit with a scalable communication network and interface. Science 345(6197), 668–673 (2014)
Mueller, E., Studenyak, V., Auge, D., Knoll, A.: Spiking transformer networks: a rate coded approach for processing sequential data. In: 2021 7th International Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2021)
Neftci, E.O., Mostafa, H., Zenke, F.: Surrogate gradient learning in spiking neural networks: bringing the power of gradient-based optimization to spiking neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 36(6), 51–63 (2019)
Panda, P., Aketi, S.A., Roy, K.: Toward scalable, efficient, and accurate deep spiking neural networks with backward residual connections, stochastic softmax, and hybridization. Front. Neurosci. 14, 653 (2020)
Pei, J., et al.: Towards artificial general intelligence with hybrid tianjic chip architecture. Nature 572(7767), 106–111 (2019)
Qiu, X., Zhu, R.J., Chou, Y., Wang, Z., Deng, L.j., Li, G.: Gated attention coding for training high-performance and efficient spiking neural networks. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 38, pp. 601–610 (2024)
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., Farhadi, A.: You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 779–788 (2016)
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02767 (2018)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster r-cnn: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 28 (2015)
Roy, K., Jaiswal, A., Panda, P.: Towards spike-based machine intelligence with neuromorphic computing. Nature 575(7784), 607–617 (2019)
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.C.: Mobilenetv2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
Schuman, C.D., Kulkarni, S.R., Parsa, M., Mitchell, J.P., Kay, B., et al.: Opportunities for neuromorphic computing algorithms and applications. Nature Comput. Sci. 2(1), 10–19 (2022)
Sengupta, A., Ye, Y., Wang, R., Liu, C., Roy, K.: Going deeper in spiking neural networks: Vgg and residual architectures. Front. Neurosci. 13, 95 (2019)
Su, Q., et al.: Deep directly-trained spiking neural networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6555–6565 (2023)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 5998–6008 (2017)
Wang, C.Y., Bochkovskiy, A., Liao, H.Y.M.: Yolov7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7464–7475 (2023)
Wang, W., et al.: Pyramid vision transformer: a versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 568–578 (2021)
Wang, Z., Fang, Y., Cao, J., Zhang, Q., Wang, Z., Xu, R.: Masked spiking transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1761–1771 (2023)
Wu, Y., Deng, L., Li, G., Zhu, J., Shi, L.: Spatio-temporal backpropagation for training high-performance spiking neural networks. Front. Neurosci. 12, 331 (2018)
Wu, Y., Deng, L., Li, G., Zhu, J., Xie, Y., Shi, L.: Direct training for spiking neural networks: faster, larger, better. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 1311–1318 (2019)
Yao, M., et al.: Temporal-wise attention spiking neural networks for event streams classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 10221–10230 (2021)
Yao, M., et al.: Spike-driven transformer v2: meta spiking neural network architecture inspiring the design of next-generation neuromorphic chips. In: The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations (2024). https://openreview.net/forum?id=1SIBN5Xyw7
Yao, M., et al.: Inherent redundancy in spiking neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 16924–16934 (2023)
Yao, M., et al.: Spike-driven transformer. In: Thirty-seventh Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (2023). https://openreview.net/forum?id=9FmolyOHi5
Yao, M., et al.: Spike-based dynamic computing with asynchronous sensing-computing neuromorphic chip. Nature Commun. 15(1), 4464 (May 2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-47811-6
Yao, M., et al.: Sparser spiking activity can be better: feature refine-and-mask spiking neural network for event-based visual recognition. Neural Netw. 166, 410–423 (2023)
Yao, M., et al.: Attention spiking neural networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(8), 9393–9410 (2023)
Yin, B., Corradi, F., Bohté, S.M.: Accurate and efficient time-domain classification with adaptive spiking recurrent neural networks. Nature Mach. Intell. 3(10), 905–913 (2021)
Yuan, M., Zhang, C., Wang, Z., Liu, H., Pan, G., Tang, H.: Trainable spiking-yolo for low-latency and high-performance object detection. Neural Netw. 172, 106092 (2024)
Zhang, J., et al.: Spiking transformers for event-based single object tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8801–8810 (2022)
Zhang, J., Tang, L., Yu, Z., Lu, J., Huang, T.: Spike transformer: monocular depth estimation for spiking camera. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part VII, pp. 34–52. Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20071-7_3
Zheng, H., Wu, Y., Deng, L., Hu, Y., Li, G.: Going deeper with directly-trained larger spiking neural networks. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 11062–11070 (2021)
Zhou, Z., et al.: Spikformer: when spiking neural network meets transformer. In: The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations (2023). https://openreview.net/forum?id=frE4fUwz_h
Zhu, X., Su, W., Lu, L., Li, B., Wang, X., Dai, J.: Deformable detr: deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2021). https://openreview.net/forum?id=gZ9hCDWe6ke
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by National Distinguished Young Scholars (62325603), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (62236009, U22A20103,62441606), Beijing Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (JQ21015), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (GZB20240824, 2024M753497), and CAAI-MindSpore Open Fund, developed on OpenI Community.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2025 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Luo, X., Yao, M., Chou, Y., Xu, B., Li, G. (2025). Integer-Valued Training and Spike-Driven Inference Spiking Neural Network for High-Performance and Energy-Efficient Object Detection. In: Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2024. ECCV 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 15090. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73411-3_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73411-3_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-73410-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-73411-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)