Abstract
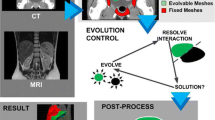
Active models are widely used for segmentation of medical images. One of the key issues of active models is the initialization phase which affects significantly the segmentation performance. This paper presents a novel method for an automatic initialization of different types of active models by exploiting an adaptive mesh generation technique which is suitable for automatic detection of multiple organs. This method has been applied on MR images and results show the ability of the proposed method in simultaneously extracting initial approximate boundaries that are close to the exact boundaries of multiple organs. The effect of the proposed initialization algorithm on the segmentation has been tested on a series of arm and thoracic MR images and the results show an improvement in the convergence and speed of active model segmentation of multiple organs with respect to those obtained using manual initialization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kass, M., Witkin, A., Terzopoulos, D.: Snakes: active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1(4), 321–331 (1988)
Liu, T., et al.: Improving image segmentation by gradient vector flow and mean shift. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 29(1), 90–95 (2008)
He, L., et al.: A comparative study of deformable contour methods on medical image segmentation. Image Vis. Comput. 26(2), 141–163 (2008)
Li, C., Huang, R., Ding, Z., Gatenby, C., Metaxas, D., Gore, J.: A variational level set approach to segmentation and bias correction of images with intensity inhomogeneity. In: Metaxas, D., Axel, L., Fichtinger, G., Székely, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2008. LNCS, vol. 5242, pp. 1083–1091. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-85990-1_130
Gao, Y., Tannenbaum, A., Kikinis, R.: Simultaneous multi-object segmentation using local robust statistics and contour interaction. In: Menze, B., Langs, G., Tu, Z., Criminisi, A. (eds.) MCV 2010. LNCS, vol. 6533, pp. 195–203. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-18421-5_19
Lee, M., et al.: Segmentation of interest region in medical volume images using geometric deformable model. Comput. Biol. Med. 42(5), 523–537 (2012)
Ardon, R., Cohen, L.: Fast constrained surface extraction by minimal paths. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 69(1), 127–136 (2006)
Neuenschwander, W., et al.: Initializing snakes [object delineation]. In: 1994 Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 1994 (1994)
Ge, X., Tian, J.: An automatic active contour model for multiple objects. In: 2002 Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (2002)
Tauber, C., Batatia, H., Ayache, A.: A general quasi-automatic initialization for snakes: application to ultrasound images. In: 2005 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, ICIP 2005 (2005)
Tauber, C., Batatia, H., Ayache, A.: A robust active contour initialization and gradient vector flow for ultrasound image segmentation. In: MVA (2005)
Bing, L., Acton, S.T.: Automatic active model initialization via poisson inverse gradient. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 17(8), 1406–1420 (2008)
Saha, B.N., Ray, N., Zhang, H.: Automating snakes for multiple objects detection. In: Kimmel, R., Klette, R., Sugimoto, A. (eds.) ACCV 2010. LNCS, vol. 6494, pp. 39–51. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-19318-7_4
Courchesne, O., Guibault, F., Dompierre, J., Cheriet, F.: Adaptive mesh generation of MRI images for 3D reconstruction of human trunk. In: Kamel, M., Campilho, A. (eds.) ICIAR 2007. LNCS, vol. 4633, pp. 1040–1051. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-74260-9_92
Chenyang, X., Prince, J.L.: Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 7(3), 359–369 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mohebpour, M.R., Guibault, F., Cheriet, F. (2017). Mesh-Based Active Model Initialization for Multiple Organ Segmentation in MR Images. In: Karray, F., Campilho, A., Cheriet, F. (eds) Image Analysis and Recognition. ICIAR 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10317. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59876-5_47
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59876-5_47
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-59875-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-59876-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)