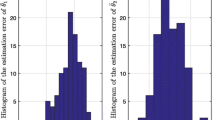
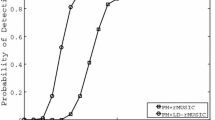
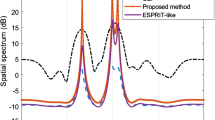
Abstract
This paper presents an adaptive tracking algorithm for the subspace-based direction of arrival estimation of multiple sources in a nonstationary, environment. The nonstationarities are due to moving sources or to timevarying distortions of the sensor array shape. The proposed algorithm relies on the properties of a linear operator, referred to as the Propagator, which only exploits the linear independency of the source steering vectors. The Propagator allows not only the calibration of the array shape, but also the determination of the source and the noise subspaces without any eigendecomposition of the cross-spectral matrix of the received signals. A gradientbased adaptive algorithm is here proposed for the on-line estimation of the Propagator. A theoretical analysis of the behaviour of this algorithm in a nonstationary environment is given. Simulations are carried out in the case of moving sources and in the case of a time-varying array shape. They exhibit the good performances of the proposed algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Bienvenu and L. Kopp, “Optimality of high resolution array processing using the eigensystem approach,”IEEE Trans. Acoust., Speech, Signal Processing Vol. ASSP-31, pp. 1235–1247, Oct. 1983.
R.O. Schmidt, “Multiple emitter location and signal parameters estimation,”Proceedings of the RADC Spectrum Estimation Workshop, Oct. 1979.
J.P. Le Cadre et al., “La calibration d'antenne,”IEEE Traitement du Signal, Special Issue, J.P. Le Cadre (Ed.), Vol. 10, Nos. 5–6, dy1993.
J. Munier and G.Y. Delisle, “Spatial analysis using new properties of the cross-spectral matrix,”IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, Vol. SP-39, pp. 746–749, March 1991.
S. Marcos and M. Benidir, “On a high resolution array processing method non-based on the eigenanalysis approach,”Proceedings of ICASSP-90, Albuquerque, New Mexico, 1990, pp. 2955–2958.
S. Marcos, “Calibration of a distorted towed array using a propagation operator,”Journal of Acoust. Society of America, Vol. 93, No. 4, pp. 1987–1994, March 1993.
R.D. DeGroat, “Non-iterative subspace tracking,”IEEE Trans. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vol. 40, No. 3, pp. 571–577, March 1992.
R.D. DeGroat and A. Roberts, “Highly parallel eigenvector update algorithms with application to signal processing,”Proceedings of SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng., Vol. 696, pp. 62–70, Aug. 1986.
R. Schreiber, “Implementation of adaptive array algorithms,”IEEE Trans. on ASSP, Vol. ASSP-34, pp. 1038–1045, Oct. 1986.
C.H. Bischof and G.M. Schroff, “On updating signal subspaces,”IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, Vol. SP-40, No. 1, pp. 96–105, Jan. 1992, Oct. 1983.
K.C. Sharman, “Adaptive algorithms for estimating the complete covariance eigenstructure,”Proceedings of IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. SpeechICASSP, pp. 1401–1403, 1986.
G.W. Stewart, “An updating algorithm for subspace tracking,”IEEE Trans. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 1535–1541, June 1992.
J.F. Yang and M. Kaveh, “Adaptive eigensubspace algorithms for direction or frequency estimation and tracking,”IEEE Trans. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vol. ASSP-36, pp. 241–251, Feb. 1988.
P. Comon and G.H. Golub, “Tracking a few extreme singular values and vectors in signal processing,”Proceedings of the IEEE, Vo. 78, No. 8, pp. 1327–1343, Aug. 1990.
S. Marcos, A. Marsal, and M. Benidir, “The propagator method for source bearing estimation,”Signal Processing, Vol. 42, No. 2, pp. 121–138, March 1995.
S. Marcos and J. Munier, “Le Propagateur et son estimation adaptative,” Actes du Colloque GRETSI, Juan les Pins, France, Sept. 1989, pp. 489–492.
S. Marcos and O. Macchi, “Tracking capability of the LMS algorithm: Application to an asynchronous echo canceller,”IEEE Trans. on ASSP, Vol. ASSP-35, pp. 1570–1578, Nov. 1987.
B. Yang, “Projection approximation subspace tracking,”IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, Vol. SP-43, No. 1, pp. 95–107, Jan. 1995.
A. Eriksson, P. Stoca, and T. Soderstrom, “On-line subspace algorithms for tracking moving sources,”IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, Vol. SP-42, pp. 2319–2330, Sept. 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marcos, S., Benidir, M. & Sanchez-Araujo, J. An adaptive tracking algorithm for direction finding and array shape estimation in a nonstationary environment. J VLSI Sign Process Syst Sign Image Video Technol 14, 107–118 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925272
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925272