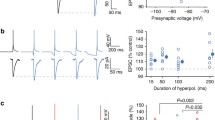
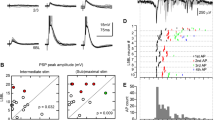
Abstract
In the guinea-pig hippocampal CA3 region, the synaptic connection from pyramidal neurons tostratum pyramidale inhibitory neurons is remarkable. Anatomically, the connection usually consists of a single release site on an interneuronal dendrite, sometimes 200 μm or more from the soma. Nevertheless, the connection is physiologically powerful, in that a single presynaptic action potential can evoke, with probability 0.1 to 0.6, a postsynaptic action potential with latency 2 to 6 ms. We construct a model interneuron and show that the anatomical and physiological observations can be reconciled if the interneuron dendrites are electrically excitable. Excitable dendrites could also account for depolarization-induced amplification of the pyramidal cell-interneuron EPSP in the voltage range subthreshold for spike generation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arancio O, Korn H, Gulyas A, Freund T, Miles R (1994) Excitatory synaptic connections onto rat hippocampal inhibitory cells may involve a single transmitter release site.J. Physiol. 481:395–405.
Benardo LS, Masukawa LM, Prince DA (1982) Electrophysiology of isolated hippocampal pyramidal dendrites.J. Neurosci. 2:1614–1622.
Buhl EH, Han Z-S, Lörinczi Z, Stezhka VV, Karnup SV, Somogyi P (1994) Physiological properties of anatomically identified axo-axonic cells in the rat hippocampus.J. Neurophysiol. 71:1289–1307.
Buzsáki G, Eidelberg E (1983) Phase relations of hippocampal projection cells and interneurons to theta activity in the anesthetized rat.Brain Res. 266:334–339.
Contreras D, Curró Dossi R, Steriade M (1993) Electrophysiological properties of cat reticular thalamic neurones in vivo.J. Physiol. 470:273–294.
Gulyás AI, Miles R, Hájos N, Freund T (1993) Precision and variability in postsynaptic target selection of inhibitory cells in the hippocampal CA3 region.Eur. J. Neurosci. 5:1729–1751.
Gulyás AI, Miles R, Sik A, Tóth K, Tamamaki N, Freund TF (1993) Hippocampal pyramidal cells excite inhibitory neurons through a single release site.Nature 366:683–687.
Hestrin S (1993) Different glutamate receptor channels mediate fast excitatory synaptic currents in inhibitory and excitatory cortical neurons.Neuron 11:1083–1091.
Hillman D, Chen S, Aung TT, Cherksey B, Sugimori M, Llinás RR (1991) Localization ofP-type calcium channels in the central nervous system.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:7076–7080.
Huguenard JR, Hamill OP, Prince DA (1988) Developmental changes in Na+ conductances in rat neocortical neurons: Appearance of a slowly inactivating component.J. Neurophysiol. 59:778–795.
Jahr CE, Stevens CF (1990) Voltage dependence of NMDA-activated macroscopic conductances predicted by single-channel kinetics.J Neurosci. 10:3178–3182.
Kim HG, Connors BW (1993) Apical dendrites of the neocortex: Correlation between sodium- and calcium-dependent spiking and pyramidal cell morphology.J. Neurosci. 13:5301–5311.
Knöpfel T, Gähwiler BH (1992) Activity-induced elevations of intracellular calcium concentration in pyramidal and nonpyramidal cells of the CA3 region of rat hippocampal slice cultures.J. Neurophysiol. 68:961–963.
Knowles WD, Schwartzkroin PA (1981) Local circuit synaptic interactions in hippocampal brain slices.J. Neurosci. 1:318–322.
Kuno M, Llinás R (1970a) Enhancement of synaptic transmission by dendritic potentials in chromatolyzed motoneurones of the cat.J. Physiol. 210:807–821.
Kuno M, Llinás R (1970b) Alterations of synaptic action in chromatolyzed motoneurones of the cat.J. Physiol. 210:823–838.
Lacaille J-C (1991) Postsynaptic potentials mediated by excitatory and inhibitory amino acids in interneurons ofstratum pyramidale of the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slicesin vitro.J. Neurophysiol. 66:1441–1454.
Llinás R, Nicholson C (1971) Electrophysiological properties of dendrites and somata in alligator Purkinje cells.J. Neurophysiol. 34:532–551.
Llinás R, Sugimori M (1980) Electrophysiological properties ofin vitro Purkinje cell dendrites in mammalian cerebellar slices.J. Physiol. 305:197–213.
Maekawa K, Purpura DP (1967) Properties of spontaneous and evoked synaptic activities of thalamic ventrobasal neurons.J. Neurophysiol. 30:360–381.
Major G (1992) The physiology, morphology and modelling of cortical pyramidal neurones. D.Phil. Thesis, Merton College, Oxford University.
McBain C, Dingledine R (1993) Heterogeneity of synaptic glutamate receptors on CA3 stratum radiatum interneurones of rat hippocampus.J. Physiol. 462:373–392.
Michelson HB, Wong RKS (1991) Excitatory synaptic responses mediated by GABAA receptors in the hippocampus.Science 253:1420–1423.
Miles R (1990) Synaptic excitation of inhibitory cells by single CA3 hippocampal pyramidal cells of the guinea-pigin vitro. J. Physiol. 428:61–77.
Miles R (1991) Tetanic stimuli induce a short-term enhancement of recurrent inhibition in the CA3 region of guinea-pig hippocampusin vitro.J. Physiol. 443:669–682.
Miles R, Wong RKS (1984) Unitary inhibitory synaptic potentials in the guinea-pig hippocampusin vitro.J. Physiol. 356:97–113.
Miles R, Wong RKS (1987) Inhibitory control of local excitatory circuits in the guinea-pig hippocampus.J. Physiol. 388:611–629.
Misgeld U, Frotscher M (1986) Postsynaptic-GABAergic inhibition of non-pyramidal neurons in the guinea-pig hippocampus.Neuroscience 19:193–206.
Perouansky M, Yaari Y (1993) Kinetic properties of NMDA receptormediated synaptic currents in rat hippocampal pyramidal cellsversus interneurones.J. Physiol. 465:223–244.
Sah P, Hestrin S, Nicoll RA (1990) Properties of excitatory postsynaptic currents recordedin vitro from rat hippocampal interneurones.J. Physiol. 430:605–616.
Sik A, Tamamaki N, Freund TF (1993) Complete axon arborization of a single CA3 pyramidal cell in the rat hippocampus, and its relationship with postsynaptic parvalbumin-containing interneurons.Eur. J. Neurosci. 5:1719–1728.
Spencer WA, Kandel ER (1961) Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons IV. Fast prepotentials.J. Neurophysiol. 24:272–285.
Stafstrom CE, Schwindt PC, Chubb MC, Crill WE (1985) Properties of persistent sodium conductance and calcium conductance of layer V neurons from cat sensorimotor cortex in vitro.J. Neurophysiol. 53:153–170.
Stuart GJ, Sakmann B (1994) Active propagation of somatic action potentials into neocortical pyramidal cell dendrites.Nature 367:69–72.
Thurbon D, Field A, Redman S (1994) Electrotonic profiles of interneurons in stratum pyramidale of the CA1 region of rat hippocampus.J. Neurophysiol. 71:1948–1958.
Traub RD, Jefferys JGR, Miles R, Whittington MA, Tóth K (1994) A branching dendritic model of a rodent CA3 pyramidal neurone.J. Physiol. 481:79–95.
Traub RD, Jefferys JGR, Whittington MA (1994) Enhanced NMDA conductances can account for epileptiform activities induced by low Mg2+ in the rat hippocampal slice.J. Physiol. 478:379–393.
Traub RD, Llinás R (1977) The spatial distribution of ionic conductances in normal and axotomized motorneurons.Neuroscience 2:829–849.
Traub RD, Miles R (1991)Neuronal Networks of the Hippocampus, New York: Cambridge University Press.
Traub RD, Miles R, Jefferys JGR (1993) Synaptic and intrinsic conductances shape picrotoxin-induced synchronized after-discharges in the guinea-pig hippocampal slice.J. Physiol. 461:525–547.
Traub RD, Wong RKS, Miles R, Michelson H (1991) A model of a CA3 hippocampal pyramidal neuron incorporating voltage-clamp data on intrinsic conductances.J. Neurophysiol. 66:635–650.
Westenbroek RE, Merrick DK, Catterall WA (1989) Differential subcellular localization of theR I andR II Na+ channel subtypes in central neurons.Neuron 3:695–704.
Whittington MA, Traub RD, Jefferys JGR (1995) Synchronized oscillations in interneuron networks driven by metabotropic glutamate receptor activation.Nature 373:612–615.
Williams S, Samulack DD, Beaulieu C, Lacaille J-C (1994) Membrane properties and synaptic responses of interneurons located near the stratum lacunosum-moleculare/radiatum border of area CA1 in whole-cell recordings from rat hippocampal slices.J. Neurophysiol. 71:2217–2235.
Wong RKS, Prince DA, Basbaum AI (1979) Intradendritic recordings from hippocampal neurons.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 76:986–990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Traub, R.D., Miles, R. Pyramidal cell-to-inhibitory cell spike transduction explicable by active dendritic conductances in inhibitory cell. J Comput Neurosci 2, 291–298 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00961441
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00961441