Abstract
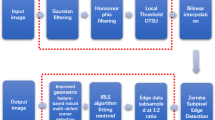
In this paper, we present a technique for measuring the amount of blur of an edge and using this information to determine the distance of a micromanipulator probe from a wafer surface in very large scale integration (VLSI) wafer probing. In this application, a soft and reliable touch of the probe with a metal pad in the wafer is a sensitive operation. The wafer is focused and several images of the probe while approaching the wafer are analyzed. In our theory, the amount of blur is calculated from the height of the step edge and the slope of the intensity profile at the zero crossing. Hence, our formula is simple and easy to use. We estimate the distance of the probe from the surface of the wafer and obtain a robust measure, i.e., one which is valid even in the presence of significant noise in the images. In order to validate our methods, we have experimented with various VLSI patterns as backgrounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beddoe-Stephens C (1982) Semiconductor wafer probing, Test and Measurement World, pp. 33–35
Dantu R, (1990) A Computer Vision System for VLSI Wafer Probing. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Concordia University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Dantu RV, Dimopoulos NJ, Patel RV, Al-Khalili AJ (1989) Micromanipulator vision for wafer probing, IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, vol. 2, pp. 114–117
Engl WL (1986) Process and Device Modelling. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Company
Grossmann P (1987) Depth from focus, Pattern Recognition Letters, vol. 5, pp. 63–69
Hausler G, Korner E (1984) Simple focusing criterion, Applied Optics, vol. 23
Hwang T, Clark JJ, Yuille AL (1989) A depth recovery algorithm using defocus information, IEEE Computer Society International Conference on Pattern Recognition, San Diego, California
Marapane SB, Trivedi MM (1989) Region-based stereo analysis for robotic applications, IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, vol. 19, pp. 1447–1464
Pentland AP (1987) A new sense for depth of field, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 9, pp. 523–531
Pentland AP, Darrel T, Turk M, Huang W (1989) A simple real-time range camera, in IEEE Computer Society International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, California
Subbarao M, Natarajan G (1988) Depth recovery from blurred edges, IEEE Computer Society International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Ann Arbor, Michigan, pp. 498–503
Subbarao M (1989) Machine Vision for Inspection and Measurement, New York, Academic Press, pp. 101–126
Subbarao M (1988) Parallel depth recovery by changing camera parameters, IEEE Computer Society International Conference on Computer Vision, Florida, pp. 149–155
Williams TW (1986) VLSI Testing. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Company
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dantu, R.V., Dimopoulos, N.J., Patel, R.V. et al. Depth perception using blurring and its application in VLSI wafer probing. Machine Vis. Apps. 5, 35–45 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01213528
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01213528