Abstract
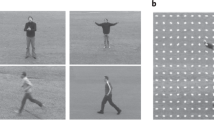
VLSI design of a competitive neural network for video motion detection is presented. Massively parallel neurocomputing is performed by compact and efficient neuroprocessors. Local data transfer between the neuroprocessors is carried out by using an analog point-to-point interconnection scheme, while global data communication between the host computer and neuroprocessors is achieved through a digital common bus. Experimental results of the analog circuit blocks and system-level analysis on a sequence of real-world images are also presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Pazdny, “On the information in optical flows,”Computer Vision, Graphics and Image Processing, vol. 22, 1983, pp. 239–259.
J. Hutchinson, C. Koch, J. Luo, and C. Mead, “Computing motion using analog and binary resistive networks,”IEEE Computer Magazine, 1988, pp. 52–63.
B. Horn and B. Schunck, “Determining optical flow,”Artificial Intelligence, vol. 17, 1981, pp. 185–203.
Y. Zhou and R. Chellappa, “Computation of optical flow using a neural network,”Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Neural Networks, vol. 2, 1988, pp. 71–78.
Y.-T. Zhou, R. Chellappa, “A network for motion perception,”Proc. of IEEE/INNS International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, vol. II, 1990, pp. 875–884.
S. Ullman,The Interpretation of Visual Motion, Cambridge, MA: M.I.T. Prss, 1979.
T. Morishita, Y. Tamura, and T. Otsuki, “A BiCMOS analog neural network with dynamically updated weights, ”Technical Digest of IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 1990, pp. 142–143.
B.W. Lee and B.J. Sheu, “A compact and general-purpose neural chip with electrically programmable synapses,”IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference Proceedings, 1990, pp. 26.6.1–26.6.4.
C. Toumazou, F.J. Lidgey, and D.G. Haigh, (Eds),Analog IC Design: The Current-Mode Approach, England, IEE/Peter Peregrinus, 1990.
R. Gregorian and G.C. Temes,Analog MOS Integrated Circuits for Signal Processing, New York: John Wiley, 1986.
P.W. Hollis and J.J. Paulos, “Artificial neural networks using MOS analog multipliers,”IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, vol. 25, 1990, p. 849–855.
S. Satyanarayana, Y.P. Tsividis, and H.P. Graf, “A reconfigurable VLSI neural network,”IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, vol. 27, 1992, pp. 67–81.
B.J. Sheu, J. Choi, W.-C. Fang, and C.-F Chang, “An analog neural network processor for self-organizing mapping,”Technical Digest of IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 1992, pp. 136–137, 266.
J. van der Spiegel, P. Muller, D. Blackman, P. Chance, C. Donham, R. Etienne, and P. Kinget, “An analog neural computer with modular architecture for real-time dynamic computations, ”IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, vol. 27, 1992, pp. 82–92.
B.E. Boser and E. Sackinger, “An analog neural network processor with programmable network topology,”Technical Digest of IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 1991, pp. 184–185.
N.I. Khachab and M. Ismail, “A nonlinear CMOS analog cell for VLSI signal and information processing,”IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, vol. 26, 1991, pp. 1689–1699.
J. Lazzaro, S. Ryckebush, M.A. Mahowald, and C.A. Mead, “Winner-take-all network of O(N) complexity,”Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems—I, pp. 703–711, San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kauffman, 1989.
A.G. Andreou et al., “Current-mode subthreshold MOS circuits for analog VLSI neural systems,”IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, vol. 2, 1991, pp. 205–213.
B.W. Lee and B.J. Sheu,Hardware Annealing in Analog VLSI Neurocomputing, Boston: Kluwer Academic, 1991.
R. Hecht-Nielsen,Neurocomputing, Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1990, pp. 64–70.
J. Choi and B.J. Sheu, “Analog VLSI neural network imnplementations of hardware annealing and winner-take-all functions,”Proc. of 34th Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 1991.
P. Allen and D. Holberg,CMOS Analog Circuit Design, New York: Holt, Rinehart, and Winston, 1987.
C. Tomovich, “MOSIS—A gateway to silicon,”IEEE Circuits and Devices Magazine, vol. 4, 1988, pp. 22–23.
G. Lewicki, “Foresight: A fast turn-around and low cost ASIC prototyping alternative,”Proc. of IEEE ASIC Seminar and Exhibit, p. 6–8.1/8.2, 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was partially supported by National Science foundation under Grant MIP-8904172 and by TRW Inc.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Jc., Sheu, B.J. & Chellappa, R. A mixed-signal VLSI competitive neuroprocessor for video motion detection. J VLSI Sign Process Syst Sign Image Video Technol 6, 57–66 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01581959
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01581959