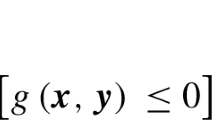Abstract
We present an algorithm for solving a large class of semi-infinite linear programming problems. This algorithm has several advantages: it handles feasibility and optimality together; it has very weak restrictions on the constraints; it allows cuts that are not near the most violated cut; and it solves the primal and the dual problems simultaneously. We prove the convergence of this algorithm in two steps. First, we show that the algorithm can find anε-optimal solution after finitely many iterations. Then, we use this result to show that it can find an optimal solution in the limit. We also estimate how good anε-optimal solution is compared to an optimal solution and give an upper bound on the total number of iterations needed for finding anε-optimal solution under some assumptions. This algorithm is generalized to solve a class of nonlinear semi-infinite programming problems. Applications to convex programming are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.J. Anderson, “A new primal algorithm for semi-infinite linear programming,” in: E.J. Anderson and A.B. Philpott, eds.,Infinite Programming (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1985) pp. 108–122.
A. Charnes, W.W. Cooper and K. Kortanek, “On representations of semi-infinite programs which have no duality gaps,”Management Science 12 (1965) 113–121.
A.R. Conn and N.I.M. Gould, “An exact penalty function for semi-infinite programming,”Mathematical Programming 37 (1987) 19–40.
I.D. Coope and G.A. Watson, “A projected Lagrangian algorithm for semi-infinite programming,”Mathematical Programming 32 (1985) 337–356.
G.B. Dantzig,Linear Programming and Extensions (Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey, 1963).
R.J. Duffin and L.A. Karlovitz, “An infinite linear program with a duality gap,”Management Science 12 (1965) 122–134.
R. Fletcher, “A nonlinear programming problem in statistics (educational testing),”SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing 2 (1981) 257–267.
S.-A. Gustafson and K.O. Kortanek, “Numerical treatment of a class of semi-infinite programming problems,”Naval Research Logistics Quarterly 20 (1973) 477–504.
R. Hettich, “An implementation of a discretization method for semi-infinite programming,”Mathematical Programming 34 (1986) 354–361.
R. Hettich, “A comparison of some numerical methods for semi-infinite programming,” in: R. Hettich ed.,Semi-infinite Programming (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1979) pp. 112–125.
A.J. Hoffman, “On approximate solutions of systems of linear inequalities,”Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards 49 (1952) 263–265.
D.E. Karney, “A duality theorem for semi-infinite convex programs and their finite subprograms,”Mathematical Programming 27 (1983) 75–82.
R.T. Rockafellar,Convex Analysis (Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey, 1972).
G.A. Watson, “Lagrangian methods for semi-infinite programming problems,” in: E.J. Anderson and A.B. Philpott, eds.,Infinite Programming (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1985) pp. 90–107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, H. A one-phase algorithm for semi-infinite linear programming. Mathematical Programming 46, 85–103 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01585730
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01585730