Abstract
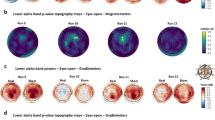
The study compared traditional spectral analysis and a new scale-invariant method, the analysis of the length distribution of low-variability periods (LDLVPs), to distinguish between electro-encephalogram (EEG) signals with and without a weak stressor, a low-level modulated microwave field. During the experiment, 23 healthy volunteers were exposed to a microwave (450 MHz) of 7 Hz frequency on-off modulation. The field power density at the scalp was 0.16 mW cm−2. The experimental protocol consisted of ten cycles of repetitive microwave exposure. Signals from frontal EEG channels FP1 and FP2 were analysed. Smooth power spectrum and length distribution curves of low-variability periods, as well as probability distribution close to normal, confirmed that stationarity of the EEG signal during recordings was achieved. The quantitative measure of LDLVPs provided a significant detection of the effect of the stressor for the six subjects exposed to the microwave field but for none of the sham recordings. The spectral analysis revealed a significant result for one subject only. A significant effect of the exposure to the EEG signal was detected in 25% of subjects, with microwave exposure increasing EEG variability. The effect was not detectable by power spectral measures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babloyantz, A., andDestexhe, A. (1988): ‘Is the normal heart a periodic oscillator?’,Biol. Cybern.,58, pp. 203–211.
Costa, M., Goldberger, A. L., andPeng, C.-K. (2002): ‘Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series’,Phys. Rev. Lett.,89, 068102 (http://link.aps.org/abstract/PRL/v89/e068102, accessed August 2004)
D'Andrea, J. A., Chou, C. K., Johnston, S. A., andAdair, E. R. (2003): ‘Microwave effects on nervous system’,Bioelectromagnetics,S6, pp. 107–147
Elger, C. E. andLenherz, K. (1997): ‘Seizure prediction by nonlinear time series analysis of brain electrical activity’.Eur. J. Neurosci.,10, pp. 786–789
Hinrikus, H., Parts, M., Lass, J., andTuulik, V. (2004): ‘Changes in human EEG caused by low-level modulated microwave exposure’,Bioelectromagnetics,25, pp 431–440
Huupponen, E., Himanen, S. L., Hasan, J., andVarri, A. (2003): ‘Automatic analysis of electro-encephalogram sleep spindle frequency throughout the night’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,41, pp. 727–732
Ivanov, P. Ch., Rosenblum, M. G., Amaral, L. A. N., Struzik, Z., Havlin, S., Goldberger, A. L., andStanley, H. E. (1999): ‘Multifractality in human heartbeat dynamics’,Nature,399, pp. 461–465
Kalda, J., Säkki, M., Vainu, M., andLaan, M. (2001): ‘Zipf's law in human heartbeat dynamics’, http://arxiv.org/abs/physics/0110075
Kalda, J., Säkki, M., Vainu, M., andLaan, M. (2004): ‘Nonlinear and scale-invariant analysis of heart rate variability’,Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. Phys.-Math,53, pp. 26–44
Kantz, H., andSchreiber, T. (1997): ‘Nonlinear time series analysis’ (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1997)
Krause, C. M., Sillanmäki, L., Koivisto, M., Häggqvist, A., Saarela, C., Revonsuo, A., Laine, M., andHämäläinen, H. (2000): ‘Effects of electromagnetic fields emitted by cellular phones on the electroencephalogram during a visual working memory task’Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 76, pp. 1659–1667
Lass, J., Tuulik, V., Ferenets, R., Rusalo, R., andHinrikus, H. (2002): ‘Effects of 7 Hz-modulated 450 MHz electromagnetic radiation on human performance in visual memory tasks’,Int. J. Radiat. Biol.,78, pp. 937–944
Lipping, T., Olejarczyk, E., andParts, M. (2003): ‘Fractal dimension analysis of the effects of photic and microwave stimulation on the brain function’,Proc. World Cong. Med. Phys. & Biomed. Eng., Sydney, Australia, (CD-ROM) ISBN 1877040142, paper 3695
Lopes da Silva, F. H., Hoeks, A., Smith, H., andZettenberg, L. H. (1974): ‘Model of brain rhythmic activity: the alpha-rhythm of the thalamus’,Kybernetik 15, pp. 27–37
Lopes da Silva, F. H., Pijn, J. P., Velis, D., andNijssen, P. C. G. (1997): ‘Alpha rhythms: noise, dynamics and models’,Int. J. Neurophys.,26, pp. 237–249
Lopes da Silva, F., Blanes, W., Kalitzin, S. N., Parra, J., Suffczynski, P., andVelis, D.N. (2003): ‘Epilepsies as dynamical diseases of brain systems: basic models of the transition between normal and epileptic activity’,Epilepsia,44, pp. 72–83
McSharry, P. E., Smith, L. A., andTarassenko, L. (2003): ‘Comparison of predictability of epileptic seizures by linear and nonlinear methods’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,50, pp. 628–633
Niedermeyer, E., andLopes da Silva, F. (1993): ‘Electroencephalography, basic principles, clinical applications and related fields’, (William & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1993)
Parts, M., Lipping, T., Lass, J., andHinrikus, H. (2003): ‘Bispectrum for the detection of the effect of photic and microwave exposure on human EEG’,Proc. 25th IEEE EMBS Ann. Int. Conf., Cancun, Mexico, CD-ROM, pp. 2327–2330
Peng, C. K., Mietus, J., Hausdorff, J. M., Havlin, S., Stanley, H. E., andGoldberger, A. L. (1993): ‘Long-range anticorrelations and non-Gaussian behavior of the heartbeat’,Phys. Rev. Lett.,70, pp. 1343–1347
Pereda, E., Gamundi, A., Rial, R., andGonzalez, J., (1998): ‘Nonlinear behaviour of human EEG: fractal exponent versus correlation dimension in awake and sleep stages’,Neurosci. Lett.,250, pp. 91–94
Röschke, J., Fell, J., andMann, K. (1997): ‘Non-linear dynamics of alpha and theta rhythm: correlation dimensions and Lyapunov exponents from healthy subject's spontaneous EEG’,Int. J. Psychophysiol.,26, pp. 251–261
Rosso, O. A., Figliola, A., Creso, J., andSerrano, E. (2004): ‘Analysis of wavelet-filtered tonic-clonic electroencephalogram recordings’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,42, pp. 516–523
Säkki, M., Kalda, J., Vainu, M., andLaan, M. (2004a): ‘The distribution of low-variability periods in human heartbeat dynamics’,Physica A.,338, pp. 255–260
Säkki, M., Kalda, J., Vainu, M., andLann, M. (2004b): ‘What does measure the scaling exponent of the correlation sum in the case of human heart rate?’,Chaos,14, pp. 138–144
Shen, Y., Olbrich, E., Achermann, P., andMeier, P. F. (2003): ‘Dimensional complexity and spectral properties of the human sleep EEG’,Clin. Neurophysiol.,114, pp. 199–209
Sinha, R. K. (2004): ‘Electro-encephalogram disturbances in different sleep-wake states following exposure to high environmental heat’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,42, pp. 282–287
Theiler, J., andRapp, P. E. (1996): ‘Re-examination of the evidence for low-dimensional, non-linear structure in the human electroencephalogram’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,98, pp. 213–222
van Drongelen, W., Nayak, S., Frim, D. M., Kohrman, M. H., Towle, V. L., Lee, H. C., McGee, A. B., Chico, M. S., andHecox, K. E. (2003): ‘Seizure anticipation in pediatric epilepsy: use of Kolmogorov entropy’,Pediatr. Neurol.,29, pp. 207–213
Wang, X.-J. (1994): ‘Multiple dynamic modes of thalamic relay neurons: rhythmic bursting and intermittent phase-locking’,Neuroscience,59, pp. 21–31
Widman, G., Schreiber, T., Rehberg, B., Hoeft, A., andElger, C. E. (2000): ‘Quantification of depth of anesthesia by nonlinear time, series analysis of brain electrical activity’,Phys. Rev. E.,62, pp. 8380–8386
Wood, A. W., Hamblin, D. L., andCroft, R. J. (2003): ‘The use of a ‘phantom scalp’ to assess the possible direct pickup of mobile phone handset emissions by electroencephalogram electrode leads’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,41, pp. 470–472
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bachmann, M., Kalda, J., Lass, J. et al. Non-linear analysis of the electroencephalogram for detecting effects of low-level electromagnetic fields. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 43, 142–149 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345136
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345136