Abstract
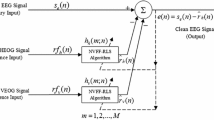
The paper presents an adaptive noise canceller (ANC) filter using an artificial neural network for real-time removal of electro-oculogram (EOG) interference from electro-encephalogram (EEG) signals. Conventional ANC filters are based on linear models of interference. Such linear models provide poorer prediction for biomedical signals. In this work, a recurrent neural network was employed for modelling the interference signals. The eye movement and eye blink artifacts were recorded by the placing of an electrode on the forehead above the left eye and an electrode on the left temple. The reference signal was then generated by the data collected from the forehead electrode being added to data recorded from the temple electrode. The reference signal was also contaminated by the EEG. To reduce the EEG interference, the reference signal was first low-pass filtered by a moving averaged filter and then applied to the ANC. Matlab Simulink was used for real-time data acquisition, filtering and ocular artifact suppression. Simulation results show the validity and effectiveness of the technique with different signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) of the primary signal. On average, a significant improvement in SNR up to 27 dB was achieved with the recurrent neural network. The results from real data demonstrate that the proposed scheme removes ocular artifacts from contaminated EEG signals and is suitable for real-time and short-time EEG recordings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arabi, A., andErfanian, A. (1999): ‘Neural adaptive filters for estimating brainstem auditory evoked potential’,Proc. Int. Conf. IEEE/EMBS, Atlanta, GA, USA,20, p. 431
Berg, P., andScherg, M. (1991): ‘Dipole models of eye activity and its application to the removal of eye artifacts from the EEG and MEG’,Clin. Physiol. Meas.,12, pp. 49–54
Berg, P., andScherg, M. (1994): ‘A multiple source approach to the correction of eye artifacts’,Electroenceph Clin. Neurophysiol.,90, pp. 229–241
Chan, F. H. Y., Lam, F. K., Poon, P. W. F., andQiu, W. (1995): ‘Detection of brainstem auditory evoked potential by adaptive filtering’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,33, pp. 69–75
Connor, J. T., Martin, R. D., andAtlas, L. E. (1994): ‘Recurrent neural networks and robust time series prediction’,IEEE Trans. Neural Netw.,5, pp. 240–254
Deng, Y., Wolf, W., Schnell, R., andAppel, U. (2000): ‘New aspects to event-synchronous cancellation of ECG interface: an application of the method in diaphragmatic EMG signals’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,47, pp. 1177–1184
Erfanian, A., andMahmoudi, B. (2002): ‘Real-time eye blink suppression using neural adaptive filters for EEG-based brain computer interface’,Proc. Int. Conf. IEEE/EMBS, Houston, USA,1, pp. 44–45
Giles, C. L., Kuhn, G. M., andWilliams, R. J. (1994): ‘Dynamic recurrent neural networks: theory and applications’,IEEE Trans. Neural Netw.,5, pp. 153–156
Gratton, G., Coles, M. G., andDonchin, E. (1983): ‘A new method for off-line removal of oucular artifact’,Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.,55, pp. 486–484
Grieve, R., Parker, P. A., Hudgins, B., andEnglehart, K. (2000): ‘Nonlinear adaptive filtering of stimulus artifact’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,47, pp. 389–395
Haykin, S. (1999): ‘Neural networks: A comprehensive foundation’ (Prentice-Hall, 1999)
He, P., Wilson, G., andRussell, C. (2004): ‘Removal of ocular artifacts from electro-encephalogram by adaptive filtering’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,42, pp. 407–412
James, C. J., Hagan, M. T., Jones, R. D., Bones, P. J., and Carroll, G. J. (1997): ‘Multireference adaptive noise cancelling applied to the EEG’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,44, pp. 775–779
Jung, T., Makeig, S., Humphries, C., Lee, T., Mckeown, M. J., Iragui, V., and Sejnowski, T. J. (2000): ‘Removing electroencephalographic artifacts by blind source separation’,Psychophysiology,37, pp. 163–178
Laguna, P., Jane, R., Meste, O., Poon, P. W., Caminal, P., Rix, H. and Thakor, N. V. (1992): ‘Adaptive filter for event-related bioelectric signals using an impulse correlated reference input: comparison with signal averaging techniques’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,39, pp. 1031–1044
Lins, O. G., Picton, T. W., Berg, P., and Scherg, M., (1993): ‘Ocular artifacts in recording EEG and event-related potentials potentials II: Source dipoles and source components’,Brain Topogr.,6, pp. 65–78
Makeig, S., Bell, A. J., Jung, T. P., andSejnowski, T. J. (1996): ‘Independent component analysis of electroencephalographic data’,Adv. Neural Info. Process. Syst.,8, pp. 145–151
Mathews, V. J. (1991): ‘Adaptive polynomial filters’,IEEE Signal Process. Mag.,5, pp. 10–26
Parsa, V., Parker, P. A., and Scott, R. (1998): ‘Adaptive stimulus artifact reduction in noncortical somatosensory evoked potential studies’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,45, pp. 165–179
Qui, W., Fung, K. S. M., Chan, F. H. Y., Lam, F. K., Poon, P. W. F., andHamernik, R. P. (2002): ‘Adaptive filtering of evoked potentials with radial-basis-function neural network prefilter’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,49, pp. 225–232
Rauf, F., andAhmed, H. M. (1997): ‘New nonlinear adaptive filters with applications to chaos’,Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos,7, pp. 1791–1809
Sadasivan, P. K., andDutt, D. N. (1997): ‘Development of Newton-type adaptive algorithm for minimization of EOG artifacts from noisy EEG signals’,Signal Process.,62, pp. 173–186
Strobach, P., Abraham-Fuchs, K., andHarer, W. (1994): ‘Event-synchronous cancellation of the heart interference in biomedical signals’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,41, pp. 343–350
Thakor, N. V., andYi-Sheng, Z. (1991): ‘Applications of adaptive filtering to ECG analysis: noise cancellation and arrhythmia detection’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,38, pp. 785–794
The Mathworks, Inc. (1990–2001): ‘Using Simulink’, (The Mathworks, Inc., 1994–2001)
The Mathworks, Inc., (1999–2000): ‘Real-Time Windows Target User's Guide’, (The Mathworks, Inc., 1999–2000)
Tsoi, A. C., andBack, A. D. (1994): ‘Locally recurrent globally feedforward networks: a critical review of architectures’,IEEE Trans. Neural Netw.,5, pp. 229–239
Vigario, R. N. (1997): ‘Extraction of ocular artifacts from EEG using independent component analysis’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,103, pp. 395–404
Widrow, B., andStreans, S. D. (1985): ‘Adaptive signal processing’, (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1985)
Woestenburg, J. C., Verbaten, M. N., andSlangen, J. L., (1983): ‘The remaoval of the eye-movement artifact from the EEG by regression analysis in the frequency domain’,Biol. Psych.,16, pp. 127–147
Yu, X., He, Z., andZhang, Y. (1994): ‘Time-varying adaptive filters for evoked potential estimation’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,41, pp. 1062–1071
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erfanian, A., Mahmoudi, B. Real-time ocular artifact suppression using recurrent neural network for electro-encephalogram based brain-computer interface. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 43, 296–305 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345969
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345969