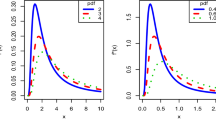
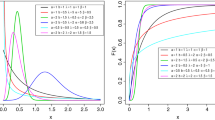
Summary
In this paper we investigate a Bayesian procedure for the estimation of a flexible generalised distribution, notably the MacGillivray adaptation of theg-and-k distribution. This distribution, described through its inverse cdf or quantile function, generalises the standard normal through extra parameters which together describe skewness and kurtosis. The standard quantile-based methods for estimating the parameters of generalised distributions are often arbitrary and do not rely on computation of the likelihood. MCMC, however, provides a simulation-based alternative for obtaining the maximum likelihood estimates of parameters of these distributions or for deriving posterior estimates of the parameters through a Bayesian framework. In this paper we adopt the latter approach. The proposed methodology is illustrated through an application in which the parameter of interest is slightly skewed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balanda, K. & MacGillivray, H. (1992), ‘Kurtosis and spread’,Can. J. Statist. 18, 17–30.
Bechhofer, R. (1954), ‘A single sample multiple-decision procedure for ranking means of normal populations with known variances’,Ann. Math. Statist. 25, 16–25.
Bechhofer, R., Santner, T. & Goldsman, D. (1995),Design and analysis of experiments for statistical selection, screening, and multiple comparisons, first edn, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, Chichester, Brisbane, Toronto, Singapore.
Besag, J. & Higdon, D. (1999), ‘Bayesian analysis of agricultural field experiments’,J. Royal Statist. Soc.-Series B,Methodological 61, 691–717.
Besag, J., Green, P., Higdon, D. & Mengersen, K. (1995), ‘Bayesian comptation and stochastic systems’,Statistical Science 10(1), 3–66.
Best, N., Cowles, M. & Vines, K. (1995), CODA Convergence diagnosis and output analysis software for Gibbs sampling output. Version 0.30, Technical report, MRC Biostatistics Unit, Institute of Public Health, Cambridge, UK.
Diebolt, J. & Robert, C. (1994), ‘Estimation of finite mixture distributions through Bayesian sampling’,J. Royal Statist. Soc.-Series B 56(2), 363–375.
Gelfand, A. & Smith, A. (1990), ‘Sampling based approaches to calculating marginal densities’,J. Amer. Statist. Assoc. 85, 398–409.
Geyer, C. (1996), Estimation and optimization of functions,in W. Gilks, S. Richardson & D. Spiegelhalter, eds, ‘Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice’, Chapman and Hall, London, pp. 241–258.
Gilks, W., Richardson, S. & Spiegelhalter, D. (1996),Markov Chain Monte Carlo in practice, Chapman and Hall, London.
Gupta, S. (1990), ‘Recent advances in statistical ranking and selection: theory and methods’,Taipei symposium in statistics pp. 133–166.
Hastings, H. (1970), ‘Monte Carlo sampling methods using Markov Chains and their applications’,Biometrika 57(1), 97–109.
Haynes, M., MacGillivray, H. & Mengersen, K. (1997), ‘Robustness of ranking and selection rules using generalisedg-and-k distributions’,J. Statist. Plan, and Inf. 65, 45–66.
Hoaglin, D. (1986), Summarizing shape numerically: The g-and-h distributions,in D. Hoaglin, F. Mosteller & J. Tukey, eds, ‘Exploring Data Tables, Trends and Shapes’, Wiley, New York.
MacGillivray, H. (1986), ‘Skewness and asymmetry: measures and orderings’,Ann. Statist. 14, 994–1011.
MacGillivray, H. & Balanda, K. (1988), ‘The relationships between skewness and kurtosis’,Aust. J. Statist. 30, 319–337.
Martinez, J. & Iglewicz, B. (1984), ‘Some properties of the Tukey g-and-h family of distributions’,Commun. Statist. A - Theor. Meth. 13, 353–369.
Mengersen, K. & Robert, C. (1996), Testing for mixture via entropy distance and Gibbs sampling,in J. Berger, J. Bernardo, A. Dawid, D. Lindley & A. Smith, eds, ‘Bayesian Statistics 5’, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 255–276.
Metropolis, N., Rosenbluth, A., Rosenbluth, M. & Teller, A. (1953), ‘Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines’,The Journal of Chemical Physics 21(6), 1087–1092.
Morris, C. & Christiansen, C. (1996), Hierarchical models for ranking and for identifying extremes, with applications,in J. Berger, J. Bernardo, A. Dawid, D. Lindley & A. Smith, eds, ‘Bayesian Statistics 5’, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 277–296.
Ramberg, J., Tadikamalla, P., Dudewicz, E. & Mykytka, E. (1979), ‘A probability distribution and its uses in fitting data’,Technometrics 21, 201–214.
Rayner, G. (2000), Statistical methodologies for quantile-based distributional families, PhD thesis, School of Mathematical Sciences, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia.
Rayner, G. & MacGillivray, H. (2002a), ‘Numerical maximum likelihood estimation for the g-and-k and generalized g-and-h distributions’,Statistics and Computing 12, 57–75.
Rayner, G. & MacGillivray, H. (2002b), ‘Weighted quantile-based estimation for a class of transformation distributions’,Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 39, 401–433.
Richardson, S. & Green, P. (1997), ‘On Bayesian analysis of mixtures with an unknown number of components’,J. Roy. Statist. Soc. (B).
Spiegelhalter, D., Thomas, A., Best, N. & Gilks, W. (1995),BUGS: Bayesian Inference using Gibbs Sampling, Version 0.5, MRC Biostatistics Unit, Cambridge.
Wood, J. & Bullimore, M. (1995), ‘Changes in the lower displacement limit for motion with age’,Opthal. Physiol. Opt. 15, 31–36.
Wood, J. & Bullimore, M. (1996), ‘Interocular differences in visual function in normal subjects’,Opthal. Physiol. Opt. 16, 507–512.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr J. Wood of the Centre for Eye Research, QUT, for the data on visual performance used in the example, and Associate Professor H. L. MacGillivray of the School of Mathematical Sciences, QUT, for useful discussions and suggestions. We also thank Dr G. Rayner, a Quantitative Analyst with the National Australia Bank, Melbourne, Australia, for assistance with generating the data samples and producing Figure 1. Comments and suggestions from anonymous referees, which contributed to a much stronger revised version of this paper, are gratefully acknowleged.
Most of the computations referred to in this Chapter were carried out on computing equipment supplied to the Centre in Statistical Science and Industrial Mathematics, Queensland University of Technology, under the Digital Equipment Agreement ERP No 2057.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haynes, M., Mengersen, K. Bayesian estimation ofg-and-k distributions using MCMC. Computational Statistics 20, 7–30 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02736120
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02736120