Abstract
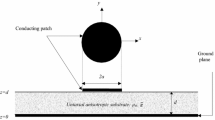
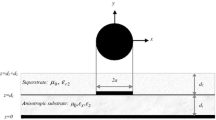
The analysis of conformal microstrip antennas printed on arbitrary curved surfaces is of importance as the shape of these surfaces directly influences the radioelectric performance of these antennas. This article proposes to simulate these structures using the finite difference time domain (fdtd) method developed in curvilinear coordinates. This method will be illustrated by several examples of conformal structures.
Résumé
L’étude d’antennes microrubans conformées imprimés sur des surfaces non planes quelconques s’avère d’autant plus indispensable que la forme de la surface influence directement les performances radioélectriques de l’antenne. Cet article propose de simuler ces structures par la méthode des différences finies dans le domaine temporel développée en coordonnées curvilignes. La méthode sera illustrée sur différents exemples de structures conformées.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luk (K.-M.), Lee (K.-F), Dahele (J.). Analysis of the cylindrical-rectangular patch antenna.IEEE Trans. AP,37, no 2, pp. 143–147, (Feb. 1989).
Chujo (W.), Konishi (Y.), Ohtaki (Y.), Yasukawa (K.). Performance of a spherical array antenna fabricated by vacuum forming technique.EMC,2, pp. 1511–1516, (Sept. 1990).
Kashiwa (T), Onishi (T.), Fukai (I.). Analysis of microstrip antennas on curved surface using the conformal gridsFd-Td method.IEEE Trans. AP,42, no 3, pp. 423–427, (March 1994).
Yee (K. S). Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving Maxwell’s equations in isotropic media.IEEE Trans. AP,14, pp. 302–307, (May 1966).
Reineix (A.), Jecko (B.). Analysis of microstrip patch antennas using finite difference time domain method.IEEE Trans. AP,37, no 11, pp. 1361–1369, (Nov. 1989).
Sheen (D.M.), Ali (S.M.), Abouzahra (M.D.), Kong (J.A.). Application of the three-dimensional finite-difference time-domain method to the analysis of planar microstrip circuits.IEEE trans. MTT,38, no 7, pp. 489–857, (July 1990).
Wu (C), Wu (K.L.), Bl (Z.Q.), Litva (J.). Accurate characterization of planar printed antennas using finite-difference time-domain.IEEE Trans. AP,40, no 5, pp. 526–534, (May 1992).
Slager (K. L.), Schneider (J. B.). A selective survey of the finite-difference time-domain literature.IEEE AP Magazine,37, no 4, pp. 39–56, (August 1995).
Jurgens (T.G.), Taflove (A.), Umashankar (K.), Moore (T.G.). Finite-difference time-domain modeling of curved surfaces.IEEE Trans. AP,40, no 4, pp. 357–366, (April 1992).
Dey (S.), Mittra (R.). A modified locally conformal finite-difference time-domain algorithm for modeling three-dimensional perfectly conducting objects.IEEE Microwave and Optical Technology Letters,17, no 6, pp. 349–352, (April 1998).
Holland (R.). Finite-difference solution of Maxwell’s equations in generalized nonorthogonal coordinates.IEEE Trans. Nuclear Science,30, no 6, pp. 4589–4591, (Dec 1983).
Fusco (M.A.), Smith (M.V.), Gordon (L.W.). A three-dimensionalFdtd algorithm in curvilinear coordinates.IEEE Trans. AP,39, no 10, pp. 1463–1471, (Oct. 1991).
Stratton (J.A.). Electromagnetic theory.Mcgraw Hill book company, INC, 702 p., (1941).
Fusco (M.).Fdtd algorithm in curvilinear coordinates.IEEE Trans. AP,38, no 1, pp. 76–89, (Jan. 1990).
Wu (C), Navarro (E.A.), Chung (P.Y), Litva (J.). Modeling of waveguide structures using the nonorthogonalFdtd method with aPml absorbing boundary.Microwave and Opt. Techn. Letters,8, no 4, pp. 226–228, (March 1995).
Roden (J. A.),Gedney (S. D.). Efficient implementation of the uniaxial-basedPml media in three-dimensional nonorthogonal coordinates with the use of theFdtd technique,14, no 2, pp. 71–75, (Feb. 1997).
Mur (G.). Absorbing boundary conditions for the finite-difference approximation of the time-domain electromagnetic field equations.IEEE Trans. EMC,23, no 4, pp. 377–382, (Nov. 1981).
Kitamurat (T.), Koshimae (T.), Hira (M.), Kurazono (S.). Analysis of cylindrical microstrip lines utilizing the finite difference time-domain method.IEEE Trans. MTT,42, no 7, pp. 1279–1282, (July 1994).
Cangellaris (A.C.). Time-domain finite methods for electromagnetic wave propagation and scattering.IEEE Trans. Magnetics 27, no 5, pp. 3780–3785, (Sept. 1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravard, K., Gillard, R. & Citerne, J. A rigolous analysis of conformal microstrip antennas using the fdtd method in curvilinear coordinates. Ann. Télécommun. 54, 19–29 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02998644
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02998644
Key words
- Patch antenna
- Printed antenna
- Conformal antenna
- Finite difference method
- Curvilinear coordonate
- Cylindrical configuration