Abstract
This article presents a network-controlled approach of user terminal mobility within anIP based WirelessLAN Access Network.
In a first part, this article makes a review of the mobility support, on the subject of emergingWLAN technologies asHIPERLAN/2 andIEEE 802.11, on the one hand, and, regardingIP networks as currently studied withinIETF, on the other hand. Both types ofIP mobility protocols are presented, either global mobility protocols such as MobileIP, or local mobility management protocols (micro mobility).
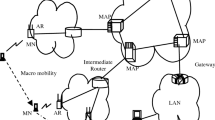
In the next part, the overall principles of our mobility management approach are explained; this approach is based on the implementation of a new network entity dedicated to the control of user terminal mobility.
The last part details a practical implementation of this approach. The implementation is carried out on the basis of Hierarchical MobileIPv6 (HMIPv6). The experimental results confirm the importance to carefully plan and control the user terminal mobility within largeIP based Access Networks, as this brings benefit to the user as well as to the operator.
Résumé
Cet article présente une approche de gestion, contrôlée par le réseau, de la mobilité des terminaux dans un réseau d’accèsIP construit à partir de réseaux locaux radio haut-débit (RLAN). Avant d’aborder les principes et les intérêts de cette approche, cet article dresse un rapide état de l’art du support de la mobilité, d’une part, dans lesRLAN émergents de typeIEEE 802.11 etHIPERLAN 2, et d’autre part, dans les réseauxIP en général, tel que cela est suggéré par les actuelles propositions à l’IETF de protocoles de mobilitéIP. Les protocolesIP gérant la mobilité globale, tel que MobileIP, aussi bien que la mobilité locale (micro-mobilité), sont alors étudiés. Ensuite, les grandes lignes de notre approche de gestion de mobilité, basée sur la mise en œuvre dans le réseau d’une entité capable de contrôler la mobilité des terminaux, sont expliquées. Le papier termine en détaillant une implémentation de cette approche, réalisée dans les laboratoires de France Télécom et basée sur le protocoleHMIPv6 (Hierarchical MobileIPv6). Les résultats expérimentaux obtenus confirment l’intérêt, aussi bien pour l’opérateur que pour l’utilisateur, de planifier et de contrôler par le réseau le déplacement des terminaux dans un réseau d’accèsIP de grande envergure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AP:
-
Access Point
- APC:
-
Access Point Controller
- APT:
-
Access Point Transmitter
- AR:
-
Access Router
- ARP:
-
Address Resolution Protocol
- CCOA:
-
Co-located Care-of Address
- COA:
-
Care-of Address
- DHCP:
-
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- EIRP:
-
Effective Isotropic Radiated Power
- FA:
-
Foreign Agent
- HA:
-
Home Agent
- LCOA:
-
Local Care of Address
- MAP:
-
Mobility Anchor Point
- MT:
-
Mobile Terminal
- NC-HMIPV6:
-
Network-Controlled Hierarchical MobileIPV6
- RA:
-
Router Advertisement
- SSID:
-
Service Set Identifier
- WAN:
-
Wide Area Network
- WLAN:
-
Wireless Local Access Network
References
Narten (T.),Nordmark (E.),Simpson (W.) “Neighbor Discovery forIP Version 6 (IPv6)”,RFC 2461IETF, December 1998.
IEEE 802.11, Standard for WirelessLAN, WirelessLAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) specifications, 1999
Draft Supplement toIEEE Std 802.11, “Recommended Practice for Multi-Vendor Access Point Interoperability via an Inter-Access Point Protocol across Distribution Systems SupportingIEEE 802.11 Operation”, January 2002
Technical Specification, “Broadband Radio Access Networks (BRAN);HIPERLAN Type 2; Data Link Control (DLC) layer; Part 2: Radio Link Control (RLC) sublayer
Perkins (C.) “Mobile IP”,IEEE Communications Magazine, May 1997.
Eardley (P.),Mihailovic (A.),Suihko (T.) “A Framework for The Evaluation ofIP Mobility Protocols”, InProceedings of PIMRC 2000, London,UK, September 2000.
Perkins (C.) “IP Mobility Support forIPV4, revised”,RFC 2002IETF, September 2001.
Droms (R.) “Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol”,RFC 2131IETF, March 1997.
Ferguson (P.),Senie (D.) “Network Ingress Filtering: Defeating Denial of Service Attacks which employIP Source Address Spoofing”,RFC 2267IETF, January 1998.
Montenegro (G) “Reverse Tunneling for Mobile IP, revised”,RFC 3024IETF, January 2001.
Perkins (C.),Johnson (D.) “Route Optimization in MobileIP”, DraftIETF, September 2001.
Johnson (D.),Perkins (C) “Mobility Support inIPv6”, DraftIETF, July 2001.
Gustafsson (E.),Johnsson (A.),Perkins (C.), “MobileIP Regional Registration”, DraftIETF, September 2001.
Soliman (H.),Castelluccia (C.),El-Malki (K.),Bellier (L.) “HierarchicalMIPV6 mobility management”, DraftIETF, July 2001.
Campbell (A.),Gomez (J.),Kim (S.),Turanyi (Z.),Wan (C.-Y.),Valko (A.), “Design, Implementation and Evaluation of Cellular IP”,Communication IEEE, July 2000.
Ramjee (R.),La Porta (T.),Thuel (S.),Varadhan (K.) “IP micro-mobility support usinghawaii”, DraftIETF, July 2000.
Dommety (G.),Yegin (A.E.),Perkins (C.),Tsirtsis (G.),El-Malki (K.),Khalil (M.), “Fast Handovers for MobileIPV6”, DraftIETF, March 2002.
Kempf (J.),Funato (D.),El-Malki (K.),Gwon (Y.),Pettersson (M.),Roberts (P.),Soliman (H.),Takeshita (A.),Yegin (A.E.) “Supporting Optimized Handover forIP Mobility — Requirements for Underlying Systems”, DraftIETF, June 2002.
Williams (C.E.),Yegin (A.E.),Kempf (J.), “Problem Statement for link-layer triggers work”, DraftIETF, June 2002.
Trossen (D.),Krishnamurthi (G.),Chaskar (H.),Kempf (J.) “Issues in candidate access router discovery for seamlessIP-level handoffs”, DraftIETF, June 2002.
Funato (D.),He (X.),Williams (C.),Takeshita (A.),Ali (M.D.),Nakfour (J.) “Geographically Adjacent Access Router Discovery Protocol”, DraftIETF, June 2002.
Jamadagni (S.),Pandey (S.R.) “A combined context transfer and candidate access router discovery protocol”, DraftIETF, March 2002.
Jayaraj (R.) “Cell-search list indications for seamless anticipative, resource-mindful handovers”, DraftIETF, May 2002.
Weyland (A.),Stattenberger (G.),Braun (T.) “User-controlled handover in wirelessLANS”,IEEE Workshop on Applications and Services in Wireless Networks 2002, Paris, France, July 3–5, 2002.
Khouaja (Y.),Bertin (P.),Guillouard (K.),Bonnin (J.-M.) “Hierarchical mobility controlled by the network”, Multiaccess, Mobility and Teletraffic for Wireless communications,6, edited by Xavier Lagrange,ENST Bretagne and Bijan Jabbari, George Mason University,Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, 2002.
Castellucia (C.) “A Hierarchical Mobile IPv6 proposal”,INRIA, November 1988
Bellier, http://www.inrialpes.fr/planete/people/bellier/hmip.html
Ist-2000-28584mind, MobileIP-based Network Developments, www.ist-mind.org
Ist-1999-10050Brain, Broadband Radio Access forIP based Networks, www.ist-brain.org
Perkins (C.), “IP Encapsulation withinIP”,RFC 2003IETF, Octobre 1996.
Plummer (D.), “An Ethernet Address Resolution Protocol: Or Converting Network Protocol Addresses to 48 bit Ethernet Addresses for Transmission on Ethernet Hardware”,STD 37,RFC 826, November 1992.
Stewart (R.),Xie (Q.),Morneault (K.),Sharp (C.),Schwarzbauer (H.),Taylor (T.),Rytina (I.),Kalla (M.),Zhang (L.),Paxson (V.), “Stream Control Transmission Protocol”,RFC 2960, October 2000.
Stewart (R.) “Stream Control Transmission Protocol (sctp Dynamic Address Reconfiguration”, draft-ietftsvwg-addip-sctp-05 (work in progress), May 2002.
Rosenberg (J.),Schulzrinne (H.),Camarillo (G.),Johnston (A.),Peterson (J.),Sparks (R.),Handley (M.),Schooler (E.) “SIP: Session Initiation Protocol”,RFC 3261, June 2002.
Wedlund (E.),Schulzrine (H.) “Mobility support usingSIP”,Second ACM/IEEE International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Multimedia (WoWMoM’99), Seattle —USA, August 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guillouard, K., Bertin, P., Khouaja, Y. et al. Network-controlled mobility within radio access networks based onWLAN technologies. Ann. Télécommun. 58, 369–396 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03001021
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03001021
Key words
- WirelessLAN
- High speed data network
- IP
- Mobile radiocommunication
- Radiocommunication handover
- Test facility
- Experimental result
- Numerical simulation