Abstract
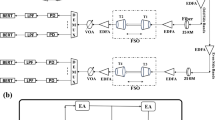
We review the principle and characteristics of cascaded Raman fiber lasers in their telecommunication applications. The fundamentals of Raman fiber lasers are described, such as pumping scheme, fiber type and reflectors. We explain simple equations forcw laser operation as well as a possible way to calculate spectral width. We investigate the common issues in the use of Raman fiber lasers: theoretical optimization, control of the linewidth, suppression level of the other Stokes orders and relative intensity noise. Finally the more complex multiple-wavelength Raman fiber lasers are reviewed.
Résumé
Le principe et les caractéristiques des lasers à effet Raman sont revus dans le contexte de leur application dans les télécommunications. Tout d’abord les éléments constituants les lasers de Raman sont décrits, c’est-à-dire le pompage, le type de fibre et les réflecteurs. Les équations permettant une modélisation simple du laser sont expliquées, ainsi qu’une façon possible de calculer la largeur spectrale. Ensuite les problèmes se posant fréquemment lors de la conception et l’utilisation de lasers de Raman sont abordés: optimisation théorique, contrôle de la largeur spectrale, niveau de suppression des ordres de Stokes intermédiaires et fluctuations d’intensité. Enfin, les lasers émettant plusieurs longueurs d’ondes simultanément sont étudiés.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grubb (S.G.),Strasser (T.),Cheung (Wy.),Reed (W.A.),Mizrachi (V.),Erdogan (T.),Lemaire (P.J.),Vengsarkar (A.M.),Digiovanni (D.J.), High power, 1.48 µm cascaded Raman laser in germanosilicate fibers, Proc.Optical Amp. and their Applications Conf., SaA4 pp. 197–199 (1995).
Mermelstein (M.D.),Headley (C.),Bouteiller (J.-C.),Steinvurzel (P.),Horn (C.),Feder (K.),Eggleton (B.J.), A high-efficiency power-stable three-wavelength configurable Raman fiber laser, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., PD3 (2001).
Hansen (P.B.), Eskildsen (L.), Grubb (S.G.), Stentz (A.J.), Strasser (T.A.), Judkins (J.), Demarco (J.J.), Pedrazzani (R.), Digiovanni (D. J.), Capacity upgrades of transmission systems by Raman amplification,IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett.,9 (2), pp. 262–264 (1997).
Bromage (J.),Bouteiller (J.-C.),Thiele (H.J.),Brar (K.),Park (J.H.),Headley (C.),Nelson (L.E.),Qian (Y.),Demarco (J.),Stulz (S.),Leng (L.),Zhu (B.),Eggleton (B.J.), S-band all-Raman amplifiers for 40×10 Gb/s transmission over 6×100 km of non-zero dispersion fiber,Proc. Optical Fiber Communication Conf., PD4 (2001).
Rottwitt (K.),Stentz (A.),Nielsen (T.),Hansen (P.),Feder (K.),Walker (K.), Transparent 80 km hi-directionally pumped distributed Raman amplifier with second order pumping,Proc. European Conf. on Optical Communications, II-144 (1999).
Paperny (Sb.), Karpov (V.I.),Clements (W.R.L.), Third-order cascaded Raman amplification,Proc. Optical Fiber Communication Conf., FB4 (2002).
Roy (F.), Leplingard (F.), Lorcy (L.), Le Sauze (A.), Baniel (P.), Bayart (D.), 48% power conversion efficiency in single pump gain-shifted thulium-doped fibre amplifier,Electron. Lett.,37(15), pp 943–945 (2001).
Pask (H.M.), Archambault (J.L.), Hanna (D.C.), Reekie (L.), Russell (P.St.J.), Townsend (J.E.), Tropper (A.C.) (A.C.), Operation of cladding-pumped Yb3+ -doped silica fibre lasers in 1-mm region,Electron. Lett.,30 (11), pp. 863–865 (1994).
Karpov (V.I.),Dianov (E.M.),Kurkov (A.S.),Paramonov (V.M.),Protopopov (V.N.),Bachynski (M.P.),Clements (W.R.L.), LD-pumped 1.48 mm laser based on Yb-doped double-clad fiber and phosphorosilicate-fiber Raman converter, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., WM3 pp. 202–204 (1999).
Minelly (J.D.),Taylor (E.R.),Jedrzejewski (K.P.),Wang (J.),Payne (D.N.), laser-diode pumped neodymium-doped fibre laser with output power >1W, Proc.Conf. on Lasers and Electro-Optics, CWE-6 (1992).
Headley (C.),Mermelstein (M.D.),Bouteiller (J.-C.), Raman fiber lasers, in Raman amplifiers for telecommunications, edited by ISLAM (M.N.), Ch. 11,Springer Verlag, New York (2003).
Goldberg (L.), Cole (B.), Snitzer (E.), V-groove side-pumped 1.5 mm fibre ampliferElectron. Lett.,33, pp. 2127–2129 (1997).
Grudin (A.B.),Nilsson (J.),Turner (P.W.),Renaud (C.C.),Clarkson (W.A.),Payne (D.N.), Single clad coiled optical fibre for high power lasers, amplifiers, Proc.Conf. on Lasers and Electro-Optics, CPD26 (1999).
Qian (Y.),Povlsen (J.H.),Knudsen (S.N.),Gruner-Nielsen (L.), On Rayleigh backscattering and nonlinear effects evaluations and Raman amplification characterizations od single-mode fibers,Proc. Optical Amp. and their Applications Conf., OMD18 (2000).
Normandin (X.),Leplingard (F.),Bourova (E.),Leclère (C.),Lopez (T.),Gurin (J.-J.),Bayart (D.), Experimental assessment of phospho-silicate fibers for three wavelength (1427 nm, 1455 nm, 1480 nm) reconfigurable Raman lasers, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., TuB2-1 (2002).
Prabhu (M.), Kim (N.S.), Jianren (L.), Ueda (K.), Output characteristics of high-power continuous wave Raman fiber laser at 1484 nm using phosphosilicate fiber,Optical Review,7 (5), pp. 455–461 (2000).
Shibata (N.), Horigudhi (M.), Edahiro (T.), Raman spectra of binary high-silica glasses and fibers containing GeO2, P2O5 and B2O3, J. Non-Crystalline Solids,45, pp. 115–126 (1981).
Bromage (J.), Rottwitt (K.), Lines (M.E.), A method to predict the Raman gain spectra of germanosilicate fibers with arbitrary index profiles,IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett.,14, pp. 24–26 (2002).
Hill (K.O.), Fujii (Y.), Johnson (D.C.), Kawasaki (B.S.), Photosensitivity in optical waveguides: Application to reflection filter fabrication,Appl. Phys. Lett. 32 (10), p. 647 (1978).
Kashyap (R.), Fiber Bragg Gratings, Academic Press, San Diego (1999).
Jackson (S.D.), Muir (P.H.), Theory and numerical simulation of nth-order cascaded Raman fiber lasers, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B,18 (9) pp. 1297–1306 (2001).
Reed (W.A.),Coughran (W.C.),Grubb (S.G.), Numerical modeling of cascadedcw Raman fiber amplifiers and lasers, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., WD1 pp. 107–109 (1995).
Rini (M.),Cristiani (I.),Degiorgio (V.), Numerical Modeling and Optimization of cascadedcw Raman fiber lasers,IEEE J. Quantum Electronics,36(10), (2000).
Bouteiller (J.-C.), Spectral modeling of Raman fiber lasers, to appear inIEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., Dec. 2003.
Rottwitt (K.),Bromage (J.),Stentz (A.J.),Leng (L.),Lines (M.E.),Smith (H.), Scalling of the Raman gain coefficient: applications to germanosilicate fibers, to appear inIEEE J. Lightwave Technol. in July 2003.
Hill (K.O.),Johnson (D.C.),Kawasaki (B.S.),Macdonald (R.I.),cw three-wave mixing in single-mode optical fibers,J. Appl. Phys.,49 (10), (1978).
Agrawal (G.P.), Nonlinear fiber optics. London,Academic Press (1995).
Foley (B.), Dakss (M.L.), Davies (R.W.), Melman (P.), Gain saturation in fiber Raman amplifiers due to stimulated Brillouin scattering,IEEE J. Lightwave Technol.,7 (12), pp 2024–2032 (1989).
Bouteiller (J.-C.), Linewidth predictions for Raman fibre lasers, submitted toElec. Lett.
Fludger (C.R.S.), Handerek (B.), Mears (R.J.), Pump to signal RIN transfer in Raman fibre Amplifiers,Electron. Lett.,37 (1), pp. 15–17 (2001).
Fludger (C.R.S.), Handerek (B.), Mears (R.J.), Pump to signal RIN transfer in Raman fiber amplifiers,IEEE J. Lightwave Technol.,19, pp. 1140–1148 (2001).
Headley (C.), Mermelstein (M.D.), Bouteiller (J.-C.), RIN transfer analysis in the pump depletion regime for Raman fibre amplifiers,Electron. Lett.,38, pp. 403–405 (2002).
Mermelstein (M. D.),Brar (K.),Headley (C.), RIN transfer suppression technique for 2nd order Raman pumping, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., ThB5 (2003).
Rottwitt (K.),Kidorf (H.D.), A 92 nm bandwidth Raman amplifier, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., PD6 (1998).
Chang (D.I.), Lim (D.S.), Jeon (M.Y.), Lee (H.K.), Kim (K.H.), Park (T.), Dual wavelength cascaded Raman fiber laser,Electron. Lett.,36, pp. 1365–1368 (2001).
Paperny (S.B.),Karpov (V.I.),Clements (W.R.L.), Efficient dual-wavelength Raman fiber laser, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., paper WDD15-1 (2001).
Mermelstein (M.D.),Headley (C.),Bouteiller (J.-C.),Steinvurzel (P.),Horn (C.),Feder (K.),Eggleton (B. J.), A High-Efficiency Power-Stable three-Wavelength Configurable Raman Fiber Laser, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., Paper PD3-1 (2001).
Mermelstein (M.D.), Headley (C.), Bouteiller (J.-C.), Steinvurzel (P.), Feder (K.), Eggleton (B.J.), Configurable three-wavelength Raman fiber laser for Raman amplification and dynamic gain flattening, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett.,13(12), pp 1286–1288 (2001).
Eggleton (B.J.), Rogers (J.A.), Westbrook (P.S.) ET AL., Electrically tunable power efficient dispersion compensating fiber Bragg grating, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett.,11 (7), pp. 854–856 (1999).
Mermelstein (M.D.),Horn (C.),Bouteiller (J.-C.),Steinvurzel (P.),Feder (K.),Headley (C.),Eggleton (B.J.), Six wavelength Raman fiber laser for C+L-band Raman amplification, Proc.Conf. on Lasers and Electro-Optics CThJ1 (2002).
Leplingard (F.), Borne (S.), Lorcy (L.), Lopez (T.), Gurin (J.-J.), Moreau (C.), Martinelli (C.), Bayart (D.), Six output wavelength Raman fibre laser for Raman armplification,Electron. Lett.,38, pp. 886–887 (2002).
Mermelstein (M.D.),Horn (C.),Huang (Z.),Steinvurzel (P.),Feder (K.),Luvalle (M.),Bouteiller (J.-C.),Headley (C.),Eggleton (B.J.), Configurability of a three-wavelength Raman fiber laser for gain ripple minimization and power partitioning, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., TuJ2 (2002).
Feder (K.),Westbrook (P.S.),Ging (J.),Reyes (P.),Carver (G.), A compact low resolution wavelength monitor applied to Raman pump power monitoring, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., MF37 (2003).
Labrunie (L.),Boubal (F.),Brandon (E.),Buet (L.),Darbois (N.),Dufournet (D.),Havard (V.),Le Roux (P.),Mesic (M.),Piriou (L.),Tran (A.),Blondel (J.-P.), 1.6 Terabit/s (160 × 10.66 Gbit/s) unrepeatered transmission over 321 km using second order pumping distributed Raman amplification, Proc.Optical Amp. and their Applications Conf., PD3 (2001).
Bouteiller (J.-C.),Brar (K.),Radic (S.),Bromage (J.),Wang (Z.),Headley (C.), Dual-order Raman pump providing improved noise figure and large gain bandwidth, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., FB3 (2002).
Bouteiller (J.-C.), Brar (K.), Bromage (J.), Radic (S.), Wang (Z.), Headley (C.), Dual-order Raman pump, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett.,15 (2), pp. 212–214 (2003).
Leplingard (F.),Borne (S.),Martinelli (C.),Leclère (C.),Lopez (T.),Guérin (J.),Bayart (D.),fwm-assisted Raman laser for second-order Raman pumping, Proc.Optical Fiber Communication Conf., ThB4 pp. 431–432 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouteiller, J.C. Raman fiber lasers for optical communication application. Ann. Télécommun. 58, 1342–1363 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03001734
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03001734
Key words
- Optical telecommunication
- Laser
- Optical fiber
- Raman process
- Stimulated Raman Scattering
- Bragg reflection
- Non linear optics
- Multifrequency operation