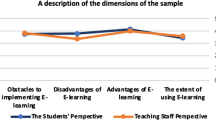
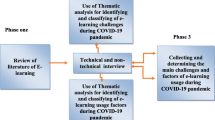
Abstract
The acceptance of e-learning depends substantially on three factors: effective learning for the learners, effective providing of authors in producing learning contents and their economical application in enterprises and organizations. Optimal learning requires a representation and a dressing of teaching subjects, which consider the possibilities and boundary conditions of e-learning. In order to reduce arduous reading on the screen, e-learning-contents have to be available as scripts or books for the learners. The e-learning-platform W3L (Web Life Long Learning) realizes these requirements and makes “Blended Learning plus printr” possible. The W3L-Plattform can be acquired under license or used as ASP users.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Balzert, Helmut: Lehrbuch der SoftwareTechnik. Band 1. 2. Auflage, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2001.
Hettrich, A.; Koroleva, N.: Marktstudie Learning Management Systeme (LMS) und Learning Content Management Systeme (LCMS) — Fokus deutscher Markt. Fraunhofer Institut fü r Arbeitswirtschaft und Organisation, Juni 2003, ISBN 3-8167-6237-9.
Highsmith, J.: Agile Software Development Ecosystems. Addison-Wesley, Boston 2002.
Erke, H.: Psychologische Grundlagen der visuellen Kommunikation. Institut für Psychologie, Abteilung Angewandte Psychologie, Braunschweig 1975.
Kohl, K.: Entwicklung einer Single Source Publishing Fachkonzeptkomponente — Automatisierte Erzeugung von XML-Dokumenten und deren Transformation. Diplomarbeit im Studiengang Wirtschaftsinformatik an der Fachhochschule Dortmund, 09/2002.
L3-Autorentraining: JANUS Software Projekte GmbH. http://www.janus-projekte.de, Bielefeld 2001.
Niegemann, H.: Neue Lernmedien konzipieren, entwickeln, einsetzen. Hans Huber Verlag, Bern 2001.
Wandmacher, J.: Software-Ergonomie. de Gruyter-Verlag, Berlin 1993.
Zwintzscher, O.: Komponentenbasierte & generative Software-Entwicklung, Generierung komponentenbasierter Software aus erweiterten UML-Modellen. W3L GmbH, Herdecke 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balzert, H., Balzert, H. & Zwintzscher, O. Die E-Learning-Plattform W3L. Wirtschaftsinf 46, 129–138 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03250932
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03250932