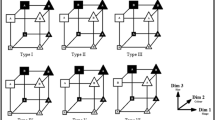
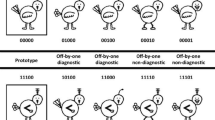
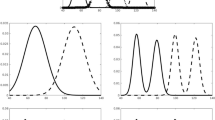
Abstract
The acquisition and the application of image categories are basic operations underlying the organization of human knowledge. Most traditional classification-learning paradigms reduce the learning process to a search for appropriate combinations of given, well-defined features. By contrast, the formation of image categories, for instance in medical diagnostics, is often characterised by a lack of knowledge concerning the relevant feature dimensions. Thus, the acquisition of unfamiliar complex images involves a specific perceptive component, i.e. feature analysis becomes part of the learning process. To describe human categorization performance we have developed a probabilistic Bayesian model where mental image categories are represented by virtual prototypes. We show that this approach not only allows for the description of visual field effects on the generation of image categories. It also permits to analyze the dynamics of the learning process. The resulting learning tomograms suggest that category learning of images is an integrative visual-cognitive task involving both processes of perceptual feature formation and hypothesis testing.
Zusammenfassung
Der Erwerb und das Anwenden bildkategorialer Konzepte gelten als kognitive Grundoperationen bei der Organisation menschlichen Wissens. Klassische Paradigmen zum Klassifikationslernen reduzieren den Lernvorgang zumeist auf die Entdeckung einer geeigneten Kombinatorik für bestimmte vorgegebene Merkmale. Demgegen- über sind Entscheidungsituationen des bildkategorialen Lernens, etwa im Bereich der medizinischen Diagnostik, häufig dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die relevanten Reizdimensionen a priori unbekannt sind. Klassifikationslernen von unvertrautem, komplexem Bildmaterial weist somit eine spezifisch perzeptive Komponente auf, d.h. die Merkmalsanalyse wird Teil des eigentlichen Lernvorgangs. Zur Beschreibung bildkategorialer Sehleistungen haben wir ein probabilistisches Bayes-Modell entwickelt, bei dem mentale Kategorien durch virtuelle Prototypen repräsentiert sind. Wir zeigen, daß dieser Ansatz nicht nur die Darstellung des Einflusses von Gesichtsfeldeffekten auf den Aufbau mentaler Bildkategorien ermöglicht, sondern auch die Analyse ihrer Dynamik während des Lernprozesses. Die hieraus resultierenden Lerntomogramme erweisen, daß bildkategoriales Lernen eine visuell-kognitive Leistung darstellt. Sie umfaßt gleichermaßen Prozesse der perzeptiven Merkmalskonstitution wie der induktiven Hypothesenbildung.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Ahmed, N. & Rao, K. R. (1975) Orthogonal transforms for digital signal processing. Berlin: Springer
Ashby, F. G. (1992) Multidimensional models of categorization. In: F. G. Ashby (Ed.), Multidimensional Models of Perception and Cognition (pp. 449–483). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum
Bourne, L. E., Jr. (1982) Typicality effects in logically defined categories. Memory & Cognition 10, 3–9
Brooks, L. (1978) Nonanalytic concept formation and memory for instances. In: E. Rosch & B. B. Lloyd (Hrsg.), Cognition and Categorization (pp. 169–211). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum
Bruner, J. S., Goodnow, J. & Austin, G. A. (1956) A study of thinking. New York: Wiley
Bruner, J. S. (1957) On perceptual readiness. Psychological Review 64, 123–152
Caelli, T., Rentschler, I. & Scheidler, W. (1987) Visual pattern recognition in humans. I. Evidence for adaptive filtering. Biological Cybernetics 57, 233–240
Christensen, E. E., Murry, R. C., Holland, K., Reynolds, J., Landay, M. J. & Moore, J. G. (1981) The effect of search time on perception. Radiology 138, 361–365
Duda, R. O. & Hart, P. E. (1973) Pattern classification and scene analysis. New York: Wiley
Estes, W. K. (1986a) Array models for category learning. Cognitive Psychology 18, 500–549
Estes, W. K. (1986b) Storage and retrieval processes in category learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 115, 155–174
Estes, W. K. (1989) Early and late memory processing in models for category learning. In: C. Izawa (Ed.), Current Issues in Cognitive Processes: The Tulane Flowerree Symposium on Cognition (pp. 11–24). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum
Estes, W. K. (1994) Classification and Cognition. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Flannagan, M. J., Fried, L. S. & Holyoak, K. J. (1986) Distributional expectations and the induction of category structure. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 12, 241–256
Fried, L. S. & Holyoak, K. J. (1984) Induction of category distributions: A framework for classification learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 10, 234–257
Gauß, C. F. (1809) Theoria motus. English Translation (1963): Theory of the Motion of the Heavenly Bodies about the Sun in the Conic Sections. New York: Dover
Gelb, A. (1974) Applied Optimal Estimation. Cambridge MA: MIT Press
Gluck, M. A., Bower, G. H. (1988) From conditioning to category learning: An adaptive network model. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 117, 225–244
Green, D. M. & Swets, J. A. (1974) Signal detection theory and psychophysics. New York: Krieger
Jüttner, M. (1998) Evidenzgestütztes Bilderkennen: Ein strukturorientiertes Modell für Klassifikations- und Generalisierungsleistungen beim visuellen Lernen. In: W. Krause & U. Kotkamp (Hrsg.) Intelligente Informationsverarbeitung (S. 139–146). Wiesbaden: Deutscher Universit ätsverlag
Jüttner, M. & Rentschler, I. (1996) Reduced perceptual dimensionality in extrafoveal vision. Vision Research 36, 1007–1021
Jüttner, M. & Rentschler, I. (2000) Scale invariant superiority of foveal vision in perceptual categorization. European Journal of Neuroscience 12, 353–359
Jüttner, M. & Strasburger, H. (1997) FORPXL - a Fortran interface to PXL, the Psychological Experiments Library. Spatial Vision 10, 491–493
Jüttner, M., Caelli, T. & Rentschler, I. (1997) Evidence-based pattern classification: A structural approach to human perceptual learning and generalization. Journal of Mathematical Psychology 41, 244–259
Koenderink, J. J., Bouman, M. A., Bueno de Mesquita, A. E. & Slappendel, S. (1978) Perimetry of contrast detection thresholds of moving spatial sine wave patterns. III. The target extent as a sensitivity controlling parameter. Journal of the Optical Society of America A 68, 854–860
Kruschke, J. K. (1992) ALCOVE: An exemplar-based connectionist model of category learning. Psychological Review 99, 22–44
Lakoff, G. (1987) Women, fire, and dangerous things. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press
Lesgold, A. M., Glaser, R., Rubinson, H. Klopfer, D., Feltovitch, P. & Wang, Y. (1988) Expertise in a complex skill: Diagnosing X-ray pictures. In: M. T. H. Chi, R. Glaser & M. J. Farr (Eds.), The nature of M. Jüttner, I. Rentschler: Bildkategoriales Lernen 113 expertise. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum
Levi, D. M., Klein, S. A. & Aitsebaomo, A. P. (1985) Vernier acuity, crowding and cortical magnification. Vision Research 25, 963–977
Luce, R. D. (1963) Detection and recognition. In: R. D. Luce, R. R. Bush & E. Galanter (Eds.), Handbook of mathematical psychology (pp. 103–189). New York: Wiley
Marr, D. & Hildreth, E. (1980) Theory of edge detection. Proceedings Royal Society of London Series 207B, 187–216
McClelland, J. L. & Rumelhart, D. E. (1985) Distributed memory and the representation of general and specific information. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 114, 159–188
Medin, D. L. & Schaffer, M. M. (1978) Context theory of classification learning. Psychological Review 85, 207–238
Norman, G. R., Brooks, L. R., Coblentz, C. L. & Babcock, C. J. (1992) The correlation of feature identification and category judgements in diagnostic radiology. Memory & Cognition 20, 344–355
Norman, M. F. (1972) Markov processes and learning models. New York: Academic Press
Nosofsky, R. M. (1986) Attention, similarity, and the identificationcategorization relationship. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 115, 39–57
Nosofsky, R. N., Kruschke, J. K. & S. McKinley, S. (1992) Combining exemplar-based category representations and connectionist learning rules. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition 18, 211–233
Posner, M. I. & Keele, S. W. (1968) On the genesis of abstract ideas. Journal of Experimental Psychology 77, 353–363
Posner, M. I. & Keele, S. W. (1970) Retention of abstract ideas. Journal of Experimental Psychology 83, 304–308
Reed, S. K. (1972) Pattern recognition and categorization. Cognitive Psychology, 3, 382–407
Rentschler, I., Jüttner, M. & Caelli, T. (1994) Probabilistic analysis of human supervised learning and classification. Vision Research 34, 669–687
Rentschler, I., J üttner, M. & Caelli, T. (1993) Ideal observers for supervised learning and classification. In: R. Steyer, K. F. Wender & K. F. Widamann (Eds.), Psychometric Methodology (pp. 440–445). Stuttgart: Fischer
Schyns, P. G. & Rodet, L. (1997) Categorization creates functional features. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 23, 681–696
Schyns, P. G., Goldstone, R. L. & Thibaut, J.-P. (1998) The development of features in object concepts. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 21, 1–54
Shanks D. R. & John, M. F. (1994) Characteristics of dissociable human learning systems. Behavioral Brain Sciences 17, 367–447
Shepard, R. N., Hovland, C. I. & Jenkins, H. M. (1961) Learning and memorization of classifications. Psychological Monographs, 75
Thompson, J. R. & Tapia, R. A. (1990) Nonparametric function estimation, modelling, and simulation. Philadelphia: Siam
Unzicker, A., Jüttner, M. & Rentschler, I. (1998) Similarity models of human visual recognition. Vision Research 38, 2289–2305
Virsu, V. & Rovamo, J. (1979) Visual resolution, contrast sensitivity and the cortical magnification factor. Experimental Brain Research 37, 475–494
Westheimer, G. (1982) The spatial grain of the perifoveal visual field. Vision Research 22, 157–162
Wickens, T. D. (1982) Models of behaviour. San Francisco: Freeman
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Diese Arbeit wurde von der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft (Ju 230/5-1, Re 337/10-2) gefördert
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jüttner, M., Rentschler, I. Bildkategoriales Lernen. Kognit. Wiss. 9, 103–113 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03354943
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03354943