Abstract.
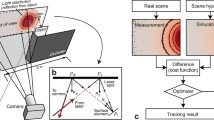
We present a new active vision technique called zoom tracking. Zoom tracking is the continuous adjustment of a camera's focal length in order to keep a constant-sized image of an object moving along the camera's optical axis. Two methods for performing zoom tracking are presented: a closed-loop visual feedback algorithm based on optical flow, and use of depth information obtained from an autofocus camera's range sensor. We explore two uses of zoom tracking: recovery of depth information and improving the performance of scale-variant algorithms. We show that the image stability provided by zoom tracking improves the performance of algorithms that are scale variant, such as correlation-based trackers. While zoom tracking cannot totally compensate for an object's motion, due to the effect of perspective distortion, an analysis of this distortion provides a quantitative estimate of the performance of zoom tracking. Zoom tracking can be used to reconstruct a depth map of the tracked object. We show that under normal circumstances this reconstruction is much more accurate than depth from zooming, and works over a greater range than depth from axial motion while providing, in the worst case, only slightly less accurate results. Finally, we show how zoom tracking can also be used in time-to-contact calculations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 February 2000 / Accepted: 19 June 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fayman, J., Sudarsky, O., Rivlin, E. et al. Zoom tracking and its applications. Machine Vision and Applications 13, 25–37 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00013268
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00013268