Abstract
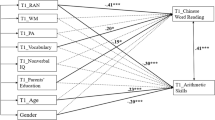
The present study investigated how phonological awareness and rapid automatized naming (hereafter, RAN), simultaneously contributed to Chinese reading and arithmetic fluency. Specifically, we proposed a new hypothesized mechanism that processing speed would mediate the relations of RAN with Chinese reading and arithmetic fluency. One hundred and forty-five Chinese children at the fifth grade were administered with a battery of measures, including three phonological processing measures, character reading, and whole number computation, as well as nonverbal IQ, and vocabulary knowledge. Path analyses revealed that phonological awareness and RAN were uniquely related to character reading and arithmetic fluency, while phonological memory was not significantly correlated to either character reading or arithmetic fluency, after controlling for age, nonverbal IQ, and vocabulary knowledge. Further analysis indicated that processing speed demonstrated a mediating effect on the importance of RAN in character reading, rather than in arithmetic fluency. Results underscore the potential importance of phonological awareness and RAN in character reading and arithmetic fluency, and the mediating role of processing speed in RAN to promote Chinese character reading fluency.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Amtmann D, Abbott RD, Berninger VW (2007) Mixture growth models of RAN and RAS row by row: Insight into the reading system at work over time. Read Writing: an Interdis J 20:785–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-006-9041-y
Baddeley A (2003) Working memory and language: an overview. J Commun Disord 36(3):189–208
Baddeley A (2010) Working Memory. Curr Biol 20(4):136–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.12.014
Baddeley A, Gathercole S, Papagno C (1998) The phonological loop as a language learning device. Psychol Rev 105(1):158–173
Berg DH (2008) Working memory and arithmetic calculation in children: the contributory roles of processing speed, short term memory, and reading. J Exp Child Psychol 99(4):288–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2007.12.002
Brydges CR, Reid CL, Campbell C, French N, Anderson M (2018) Executive functioning (fully) and processing speed (mostly) mediate intelligence deficits in children born very preterm. Intelligence 68:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2018.03.013
Bull R, Johnston RS (1997) Children’s arithmetical difficulties: contributions from processing speed, item identification, and short-term memory. J Exp Child Psychol 65:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1006/jecp.1996.2358
Chan BMY, Ho CSH (2010) The cognitive profile of Chinese children with mathematics difficulties. J Exp Child Psychol 107(3):260–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2010.04.016
Cheung H, Chen H-C, Lai CY, Wong OC, Hills M (2001) The development of phonological awareness: effects of spoken-language experience and orthography. Cognition 81:227–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-0277(01)00136-6
Cirino PT, Child AE, Macdonald KT (2018) Longitudinal predictors of the overlap between reading and math skills. Contemp Educ Psychol 54:99–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2018.06.002
Cui J, Georgiou GK, Zhang Y, Li Y, Shu H, Zhou X (2017) Examining the relationship between rapid automatized naming and arithmetic fluency in Chinese kindergarten children. J Exp Child Psychol 154:146–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2016.10.008
Cutting LE, Denckla MB (2001) The relationship of rapid serial naming and word reading in normally developing readers: an exploratory model. Read Writ 14(7–8):673–705. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012047622541
De Smedt B, Boets B (2010) Phonological processing and arithmetic fact retrieval: evidence from developmental dyslexia. Neuropsychologia 48(14):3973–3981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.10.018
De Smedt B, Taylor J, Archibald L, Ansari D (2010) How is phonological processing related to individual differences in children’s arithmetic skills? Dev Sci 13(3):508–520. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7687.2009.00897.x
Dehaene S, Spelke E, Pinel P, Stanescu R, Tsivkin S (1999) Sources of mathematical thinking: behavioral and brain-imaging evidence. Science 284(5416):970–974. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5416.970
Dehaene, S., & Cohen, L. (1998). Levels of representation in number processing. In Handbook of neurolinguistics (pp. 331–341). Academic Press.
Denckla MB, Rudel RG (1976) Rapid “automatized” naming (RAN): dyslexia differentiated from other learning disabilities. Neuropsychologia 14(4):471–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-3932(76)90075-0
Donders J, Janke K (2008) Criterion validity of the wechsler intelligence scale for children-fourth edition after pediatric traumatic brain injury. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 14(4):651–655. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355617708080752
Dunn LM, Dunn LM, Dunn DM (1997) The Peabody picture vocabulary Test, 3rd edn. American guidance services Inc., Circle Pines, MN
Durand M, Hulme C, Larkin R, Snowling M (2005) The cognitive foundations of reading and arithmetic skills in 7-to 10-year-olds. J Exp Child Psychol 91(2):113–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2005.01.003
Foster ME, Anthony JL, Clements DH, Sarama JH (2015) Processes in the development of mathematics in kindergarten children from title 1 schools. J Exp Child Psychol 140:56–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2015.07.004
Frischkorn GT, Schubert AL, Hagemann D (2019) Processing speed, working memory, and executive functions: independent or inter-related predictors of general intelligence. Intelligence 75:95–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2019.05.003
Fuchs LS, Compton DL, Fuchs D, Paulsen K, Bryant JD, Hamlett CL (2005) The prevention, identification, and cognitive determinants of math difficulty. J Educ Psychol 97(3):29–43. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.97.3.493
Fuchs LS, Fuchs D, Compton DL, Powell SR, Seethaler PM, Capizzi AM, Fletcher JM (2006) The cognitive correlates of third-grade skill in arithmetic, algorithmic computation, and arithmetic word problems. J Educ Psychol 98(1):29–43. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.98.1.29
Gathercole SE, Adams AM (1993) Phonological working memory in very young children. Dev Psychol 29(4):770–778. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.29.4.770
Geary DC (2011) Cognitive predictors of achievement growth in mathematics: a 5-year longitudinal study. Dev Psychol 47:1539–1552. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0025510
Geary DC, Hamson CO, Hoard MK (2000) Numerical and arithmetical cognition: a longitudinal study of process and concept deficits in children with learning disability. J Exp Child Psychol 77(3):236–263. https://doi.org/10.1006/jecp.2000.2561
Georgiou GK, Tziraki N, Manolitsis G, Fella A (2013) Is rapid automatized naming related to reading and mathematics for the same reason (s)? A follow-up study from kindergarten to Grade 1. J Exp Child Psychol 115(3):481–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2013.01.00
Grabner RH, Ansari D, Reishofer G, Stern E, Ebner F, Neuper C (2007) Individual differences in mathematical competence predict parietal brain activation during mental calculation. Neuroimage 38(2):346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.041
Grabner RH, Ansari D, Koschutnig K, Reishofer G, Ebner F, Neuper C (2009) To retrieve or to calculate? Left angular gyrus mediates the retrieval of arithmetic facts during problem solving. Neuropsychologia 47(2):604–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.10.013
Groeneveld RA, Meeden G (1984) Measuring skewness and kurtosis. J Royal Stat Soc: Ser D (The Stat) 33(4):391–399. https://doi.org/10.2307/2987742
Hecht SA, Torgesen JK, Wagner RK, Rashotte CA (2001) The relations between phonological processing abilities and emerging individual differences in mathematical computation skills: a longitudinal study from second to fifth grades. J Exp Child Psychol 79(2):192–227. https://doi.org/10.1006/jecp.2000.2586
Kail R, Hall LK (1994) Processing speed, naming speed, and reading. Dev Psychol 30(6):949–954. https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.12352
Kail RV, Lervåg A, Hulme C (2016) Longitudinal evidence linking processing speed to the development of reasoning. Dev Sci 19(6):1067–1074
Kirby JR, Parrila RK, Pfeiffer SL (2003) Naming speed and phonological awareness as predictors of reading development. J Educ Psychol 95(3):453–464. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.95.3.453
Koponen T, Georgiou G, Salmi P, Leskinen M, Aro M (2017) A meta-analysis of the relation between RAN and mathematics. J Educ Psychol 109(7):977–992. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000182
Koponen T, Eklund K, Heikkilä R, Salminen J, Fuchs L, Fuchs D, Aro M (2019) Cognitive correlates of the covariance in reading and arithmetic fluency: importance of serial retrieval fluency. Child Dev. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13287
Li H, Shu H, McBride CC, Liu H, Peng H (2012) Chinese children’s character recognition: visuo-orthographic, phonological processing and morphological skills. J Res Read 35(3):287–307. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9817.2010.01460.x
Liao CH, Georgiou GK, Parrila R (2008) Rapid naming speed and Chinese character recognition. Read Writ 21:231–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-007-9071-0
Lin D, McBride-Chang C, Shu H, Zhang Y, Li H, Zhang J, Levin I (2010) Small wins big: analytic pinyin skills promote Chinese word reading. Psychol Sci 21(8):1117–1122. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797610375447
Luo YC, Chen X, Deacon SH, Zhang J, Yin L (2013) The role of visual processing in learning to read Chinese characters. Sci Stud Read 17:22–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888438.2012.689790
Manis FR, Seidenberg MS, Doi LM (1999) See Dick RAN: rapid naming and the logitudinal prediction of reading subskills in first and second graders. Sci Stud Read 3:129–157. https://doi.org/10.1207/s1532799xssr0302_3
McBride-Chang C, Shu H, Zhou A, Wat CP, Wagner RK (2003) Morphological awareness uniquely predicts young children’s Chinese character recognition. J Educ Psychol 95(4):743. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.95.4.743
McBride-Chang C, Bialystok E, Chong KK, Li Y (2004) Levels of phonological awareness in three cultures. J Exp Child Psychol 89(2):93–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2004.05.001
McBride-Chang C, Lin D, Liu PD, Aram D, Levin I, Cho JR, Zhang Y (2012) The ABC’s of Chinese: Maternal mediating of Pinyin for Chinese children’s early literacy skills. Read Writing 25(1):283–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-010-9270-y
McBride–Chang, C., & Kail, R. V. (2002) Cross–cultural similarities in the predictors of reading acquisition. Child Dev 73(5):1392–1407. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00479
Näslund JC, Schneider W (1991) Longitudinal effects of verbal ability, memory capacity, and phonological awareness on reading performance. Eur J Psychol Educ 6(4):375. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03172772
Norton ES, Wolf M (2012) Rapid automatized naming (RAN) and reading fluency: implications for understanding and treatment of reading disabilities. Annu Rev Psychol 63:427–452. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100431
Pan J, McBride-Chang C, Shu H, Liu H, Zhang Y, Li H (2011) What is in the naming? A 5-year longitudinal study of early rapid naming and phonological sensitivity in relation to subsequent reading skills in both native Chinese and English as a second language. J Educ Psychol 103:897–908. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0024344
Peters L, De Smedt B (2018) Arithmetic in the developing brain: a review of brain imaging studies. Dev Cogn Neurosci 30:265–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2017.05.002
Pollack C, Ashby NC (2018) Where arithmetic and phonology meet: the meta-analytic convergence of arithmetic and phonological processing in the brain. Dev Cogn Neurosci 30:251–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2017.05.003
Powell D, Stainthorp R, Stuart M, Garwood H, Quinlan P (2007) An experimental comparison between rival theories of rapid automatized naming performance and its relationship to reading. J Exp Child Psychol 98(1):46–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2007.04.003
Primi R, Ferrão ME, Almeida LS (2010) Fluid intelligence as a predictor of learning: a longitudinal multilevel approach applied to math. Learn Individ Differ 20(5):446–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2010.05.001
Rivera SM, Reiss AL, Eckert MA, Menon V (2005) Developmental changes in mental arithmetic: evidence for increased functional specialization in the left inferior parietal cortex. Cereb Cortex 15(11):1779–1790. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhi055
Schlaggar BL, McCandliss BD (2007) Development of neural systems for reading. Annu Rev Neurosci 30:475–503. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.28.061604.135645
Shu H, Peng H, McBride-Chang C (2008) Phonological awareness in young Chinese children. Dev Sci 11(1):171–181. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7687.2007.00654.x
Simmons FR, Singleton C (2008) Do weak phonological representations impact on arithmetic development? A review of research into arithmetic and dyslexia. Dyslexia 14(2):77–94. https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.341
Siok WT, Fletcher P (2001) The role of phonological awareness and visual-orthographic skills in Chinese reading acquisition. Dev Psychol 37:886–899. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.37.6.886
Swanson HL (2006) Cognitive processes that underlie mathematical precociousness in young children. J Exp Child Psychol 93:239–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2005.09.006
Swanson HL (2011) Working memory, attention, and mathematical problem solving: a longitudinal study of elementary school children. J Educ Psychol 103:821–837. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0025114
Swanson HL, Beebe-Frankenberger M (2004) The relationship between working memory and mathematical problem solving in children at risk and not at risk for math disabilities. J Educ Psychol 96:471–491. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.96.3.471
Torgesen JK, Wagner RK, Rashotte CA, Burgess S, Hecht S (1997) Contributions of phonological awareness and rapid automatic naming ability to the growth of word-reading skills in second-to fifth-grade children. Sci Stud Read 1(2):161–185. https://doi.org/10.1207/s1532799xssr0102_4
Van Gelderen A, Schoonen R, De Glopper K, Hulstijn J, Simis A, Snellings P, Stevenson M (2004) Linguistic knowledge, processing speed, and metacognitive knowledge in first-and second-language reading comprehension: a componential analysis. J Educ Psychol 96(1):19–30. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.96.1.19
Wagner RK, Torgesen JK (1987) The nature of phonological processing and its causal role in the acquisition of reading skills. Psychol Bull 101(2):192–212
Wagner RK, Torgesen JK, Rashotte CA (1994) Development of reading-related phonological processing abilities: New evidence of bidirectional causality from a latent variable longitudinal study. Dev Psychol 30(1):73–87. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.30.1.73
Wang X, Tao B (1993) Chinese character recognition test battery and assessment scale for primary school children. Shanghai Education Press, Shanghai, China
Wechsler, D. (2012). Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence-Fourth Edition. San Antonio, TX: NCS Pearson
Wechsler, D. (2014). Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Fifth Edition technical and interpretive manual. San Antonio, TX: NCS Pearson.
Wei W, Georgiou GK, Deng C (2015) Examining the cross-lagged relationships between RAN and word reading in Chinese. Sci Stud Read 19(6):446–455. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888438.2015.1077447
Willcutt EG, Pennington BF, Olson RK, Chhabildas N, Hulslander J (2005) Neuropsychological analyses of comorbidity between reading disability and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: in search of the common deficit. Dev Neuropsychol 27(1):35–78. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326942dn2701_3
Willoughby M, Hong Y, Hudson K, Wylie A (2020) Between-and within-person contributions of simple reaction time to executive function skills in early childhood. J Exp Child Psychol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2019.104779
Wise JC, Pae HK, Wolfe CB, Sevcik RA, Morris RD, Lovett M et al (2008) Phonological awareness and rapid naming skills of children with reading disabilities and children with reading disabilities who are at risk for mathematics difficulties. Learn Disabil Res Pract 23:125–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jecp.2019.104779
Wolf M, Bowers PG (1999) The double-deficit hypothesis for the developmental dyslexias. J Educ Psychol 91(3):415–438. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.91.3.415
Woodcock, R., McGrew, K., & Mather, N. (2001). WoodcockJohnson III. Itasca, IL: Riverside.
Yang X, Meng X (2016) Dissociation between exact and approximate addition in developmental dyslexia. Res Dev Disabil 56:139–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2016.05.018
Yang X, Peng P, Meng X (2019a) Contributions of basic cognitive processing to Chinese reading: the mediation effect of basic language processing. Front Psychol 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02670
Yang X, Peng P, Meng X (2019b) How do metalinguistic awareness, working memory, reasoning, and inhibition contribute to Chinese character reading of kindergarten children? Infant Child Dev. https://doi.org/10.1002/icd.2122
Yang X, McBride C, Ho CSH, Chung CC (2019c) Longitudinal associations of phonological processing skills, Chinese word reading, and arithmetic. Read Writ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-019-09998-9
Yang X, Zhang X, Huo S, Zhang Y (2020) Differential contributions of cognitive precursors to symbolic versus non-symbolic numeracy in young Chinese children. Early Childhood Res Quarterly 53(2020):208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2020.04.003
Yang, X. & McBride, C. (2020). Phonological processing matters in early Chinese reading and mathematics. Educational Psychology.
Yeung P-S, Ho CS-H, Chik PP-M, Lo L-Y, Luan H, Chan DW-O, Chung KK-H (2011) Reading and spelling Chinese among beginning readers: What skills make a difference? Sci Stud Read 15:285–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888438.2010.482149
Zhang Y, Tardif T, Shu H, Li H, Liu H, McBride-Chang C, Zhang Z (2013) Phonological skills and vocabulary knowledge mediate socioeconomic status effects in predicting reading outcomes for Chinese children. Dev Psychol 49:665–671. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0028612
Zhang X, Räsänen P, Koponen T, Aunola K, Lerkkanen MK, Nurmi JE (2020) Early cognitive precursors of children’s mathematics learning disability and persistent low achievement: a 5-year longitudinal study. Child Dev 91(1):7–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13123
Funding
This study was funded by the STI 2030-Major Projects (2022ZD0211300 and 2021ZD0200500), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32000757), Beijing Education Science Planning of 14th Five-year (BEAA21030), Beijing Municipal Social Science Foundation (23JYC016), and by Major Research Projects in Philosophy and Social Sciences of the Ministry of Education (20JZD052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I do not have any interests that might be interpreted to influence the research, and APA ethical standards were followed in the conduct of the study. With the submission of this manuscript, I would like to undertake that this manuscript has not been published elsewhere, accepted for publication elsewhere or under editorial review for publication elsewhere.
Ethical approval
Ethics approval was granted by the University of the Corresponding Authors (No. 32000757). Written informed parental consent was obtained for all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Editor: Mikkel Wallentin (Aarhus University); Reviewers: Peter Thestrup Waade (Aarhus University) and Yu-Hsien [Natalie] Wang (Asia University, Taiwan).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Star, J.R., Zhu, X. et al. Phonological awareness and RAN contribute to Chinese reading and arithmetic for different reasons. Cogn Process 25, 443–455 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-024-01184-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-024-01184-2
Keywords
Profiles
- Jiajin Tong View author profile