Abstract
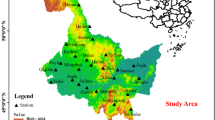
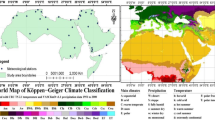
Potential Evapotranspiration (PET) estimation is essential for understanding water requirements in agricultural and hydrological studies, especially in water-scarce regions. This study introduces two novel machine learning (ML) models, Awhari1 and Awhari2, to improve aridity classification across Nigeria. Daily climate data between 1950 and 2022 from fifth European Reanalysis (ERA5) maximum temperature (Tmax), relative humidity (RH), wind speed (ws), actual (ea) and saturated vapour pressure (es) were used for this prupose. The Penman-Monteith (PM) method was utilised as a reference model to assess model accuracy, while Hargreaves and Thornthwaite models were evaluated for comparison. Results reveal that the Awhari2 model outperformed other models, excelling in sensitivity (3.535), specificity (3.916), and balanced accuracy (3.726) across all aridity classes, notably in Humid and Hyper Arid zones. Awhari1 model also showed high precision (3.611), in Semi-arid and arid regions Hargreaves and Thornthwaite underperformed, showing limited daptability to Nigeria’s diverse climatic zones. These findings support evaluating PET models’ performance before being applied in aridity studies. However, limitations in these models, such as their exclusion of solar radiation, suggest that future studies should expand climatic inputs to enhance predictive robustness. This study contributes valuable insights for improved PET modeling, critical for effective water resource management and agricultural planning in arid regions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Abdel-Fattah MK, Abd-Elmabod K, Zhang S, Z., Merwad A-RMA (2023) Exploring the Applicability of Regression models and Artificial neural networks for calculating reference evapotranspiration in arid regions. Sustainability 15(21):15494. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115494
Al-Dughairi ABA, Bourouba MF (2023a) Calibration of two models for estimating reference evapotranspiration by using FAO-56 penman-monteith model under arid conditions. Eng Herit J 7(2):113–121. https://doi.org/10.26480/gwk.02.2023.113.121
Al-Hasani AAJ, Shahid S (2023) Assessment of 40 Empirical Models for Estimating Reference Evapotranspiration under the three major climate zones of Iraq. J Irrig Drain Eng 149(11). https://doi.org/10.1061/JIDEDH.IRENG-10187
Allen RG (1993) Evaluation of a temperature difference method for computing grass reference evapotranspiration. Technical report, Water Resources Development and Management Service, and Water Development Division,
Allen RG (1998b) RAES, D., & SMITH, M. (1998). Crop evapotranspiration-Guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO Irrigation and drainage paper
Aschonitis V, Touloumidis D, ten Veldhuis M-C, Coenders-Gerrits M (2022) Correcting Thornthwaite potential evapotranspiration using a global grid of local coefficients to support temperature-based estimations of reference evapotranspiration and aridity indices. Earth Syst Sci Data 14(1):163–177. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-14-163-2022
Awhari PA, Luka BS, Yuguda TK (2022) Soil Quality Assessment of Savannah Sugar Company (Dangote Group) Farm, Numan, Adamawa State.(19752012). Am J Eng Res (AJER) 11(02):1–5
Awhari DP, Jamal MH, Muhammad MKI, Kamai MB, Yaseen ZM, Shahid S (2024) Development of temperature and mass transfer-based empirical models for estimating reference evapotranspiration in Nigeria. J Water Clim Change. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2024.260
Barontini S, Peli M, Rapuzzi C, Colosio P, Ranzi R (2022) A method to assess the uncertainty of Benfratello’s estimate of the irrigation deficit in a semiarid area and its GIS based application for anthropogenic and climate change scenarios. https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-egu22-8159
Bizimana H, Altunkaynak A, Kalin R, Rukundo E, Mugunga MM, Sönmez O, Tuncer G, Baycan A (2024) Assessment of rainfall and climate change patterns via machine learning tools and impact on forecasting in the City of Kigali. Earth Sci Inf 17(2):1229–1243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01231-8
Bodjrenou R, Cohard J-M, Hector B, Lawin EA, Chagnaud G, Danso DK, N’tcha M’po Y, Badou F, Ahamide B (2023) Evaluation of Reanalysis estimates of Precipitation, Radiation, and temperature over Benin (West Africa). J Appl Meteorol Climatology 62(8):1005–1022. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-21-0222.1
C3C, C (2023) ERA5 hourly data on single levels from 1940 to present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS).
Chinese Academy of Sciences (2023) January 19). Reassessment of mean and extreme climates over West Africa. Smart Water Magazine
Christensen J, Kjellström E, Giorgi F, Lenderink G, Rummukainen M (2010) Weight assignment in regional climate models. Climate Res 44(2–3):179–194. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr00916
Dauda AP, Jamal MH, Bin I, Muhammad MK, Hamed MM, Yaseen ZM, Salem A, G. S., Shahid S (2024) Simultaneous increase in temperature and dry days in west African transboundary Benue River Basin. Environ Earth Sci 83(12):369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-024-11687-y
Duniway MC, Benson C, Nauman TW, Knight A, Bradford JB, Munson SM, Witwicki D, Livensperger C, Van Scoyoc M, Fisk TT, Thoma D, Miller ME (2022) Geologic, geomorphic, and edaphic underpinnings of dryland ecosystems: Colorado Plateau landscapes in a changing world. Ecosphere 13(11). https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.4273
El Kenawy AM (2024) Hydroclimatic extremes in arid and semi-arid regions: status, challenges, and future outlook. In Hydroclimatic Extremes in the Middle East and North Africa (pp. 1–22). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-824130-1.00012-6
Elbeltagi A, El-Ssawy W, Mohamed A, Mahmoud SM, Mokhtar A, Pande CB (2024) Irrigation Water requirement and estimation of ETo based on the remote sensing, GIS, and Other Technologies. Sustainability of Natural resources. CRC, pp 250–265. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003303237-14
Gbode IE, Babalola TE, Diro GT, Intsiful JD (2023) Assessment of ERA5 and ERA-Interim in reproducing Mean and Extreme climates over West Africa. Adv Atmos Sci 40(4):570–586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-022-2161-8
Hamed MM, Khan N, Muhammad MKI, Shahid S (2022) Ranking of empirical evapotranspiration models in different climate zones of Pakistan. Land 11(12):2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11122168
Hargreaves GH, Samani ZA (1985) Reference crop evapotranspiration from temperature. Appl Eng Agric 1:96–99
Kadison RV (2002) The Pythagorean Theorem: I. The finite case. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(7), 4178–4184. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.032677199
Khan N, Shahid S, Ismail T, Ahmed K, Nawaz N (2019) Trends in heat wave related indices in Pakistan. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 33(1):287–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-018-1605-2
Kyaw AK, Hamed MM, Kamruzzaman M, Shahid S (2023) Spatiotemporal changes in population exposure to heat stress in South Asia. Sustainable Cities Soc 93:104544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2023.104544
Li H, Jiang C, Choy S, Wang X, Zhang K, Zhu D (2022) A comprehensive study on factors affecting the calibration of potential evapotranspiration derived from the Thornthwaite Model. Remote Sens 14(18):4644. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184644
Li S, Zhang D, Xing Y, Zhang C, Wang Z, Ma R, He K, Wang P (2024) Interannual dynamics and controlling factors of the ratio of actual to potential evapotranspiration across typical ecosystems within the Heihe River Basin. Hydrol Process 38(1). https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.15073
Moazami S, Golian S, Kavianpour MR, Hong Y (2014) Uncertainty analysis of bias from satellite rainfall estimates using copula method. Atmos Res 137:145–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.08.016
Moratiel R, Bravo R, Saa A, Tarquis AM, Almorox J (2020) Estimation of evapotranspiration by the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO) Penman–Monteith temperature (PMT) and Hargreaves–Samani (HS) models under temporal and spatial criteria – a case study in Duero basin (Spain). Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 20(3):859–875. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-20-859-2020
Muhammad M, Nashwan M, Shahid S, Ismail T, Song Y, Chung E-S (2019) Evaluation of empirical reference Evapotranspiration models using compromise programming: a case study of Peninsular Malaysia. Sustainability 11(16):4267. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164267
Muhammad MKI, Hamed MM, Harun S, Sa’adi Z, Sammen S, Sh., Al-Ansari N, Shahid S, Scholz M (2024) Heatwaves in Peninsular Malaysia: a spatiotemporal analysis. Sci Rep 14(1):4255. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-53960-x
Mukpuou SM, Pandey A, Chowdary VM (2021) Reference crop evapotranspiration estimation using remote sensing technique. 91–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58051-3_7
Petrakis RE, Norman LM, Villarreal ML, Senay GB, Friedrichs MO, Cassassuce F, Gomis F, Nagler PL (2024) An Ensemble Mean Method for Remote sensing of actual evapotranspiration to Estimate Water Budget Response across a Restoration Landscape. Remote Sens 16(12):2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122122
Quagraine KA, Nkrumah F, Klein C, Klutse NAB, Quagraine KT (2020) West African summer Monsoon Precipitation variability as represented by Reanalysis Datasets. Climate 8(10):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8100111
Ruiz-Ortega FJ, Clemente E, Martínez-Rebollar A, Flores-Prieto JJ (2024) An evolutionary parsimonious approach to estimate daily reference evapotranspiration. Sci Rep 14(1):6736. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-56770-3
Safdar M, Shahid MA, Zaman M, Rasul F, Muzammal H, Raza A, Sabir RM, Zafar U (2023) Drought Monitoring with multiple indices and management through various techniques: a review. 4th Int Electron Conf Appl Sci 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-16602
Scherbaum F, Kuehn NM (2011) Logic Tree Branch weights and probabilities: summing up to one is not enough. Earthq Spectra 27(4):1237–1251. https://doi.org/10.1193/1.3652744
Sezen C (2023) Pan evaporation forecasting using empirical and ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) based data-driven models in the Euphrates sub-basin, Turkey. Earth Sci Inf 16(4):3077–3095. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01078-5
Shadkani S, Hashemi S, Pak A, Lahijan AB (2024) Random Forest and Multilayer Perceptron hybrid models integrated with the genetic algorithm for predicting pan evaporation of target site using a limited set of neighboring reference station data. Earth Sci Inf 17(2):1261–1280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01237-2
Shaloo, Kumar B, Bisht H, Rajput J, Mishra AK, TM, K. K., Brahmanand PS (2024) Reference evapotranspiration prediction using machine learning models: an empirical study from minimal climate data. Agron J 116(3):956–972. https://doi.org/10.1002/agj2.21504
Shan Y, Wei J, Zan B (2024) Improving estimates of land–atmosphere Coupling through a Novel Framework of Land Aridity classification. Geophys Res Lett 51(2). https://doi.org/10.1029/2023GL106598
Shiru MS, Chung E-S (2021) Performance evaluation of CMIP6 global climate models for selecting models for climate projection over Nigeria. Theoret Appl Climatol 146(1–2):599–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03746-2
Shrikant, Reddy GVS, Manjunath MK, Patil R, Kulkarni PS (2023) Predicting potential evapotranspiration for Kalaburagi District using a Seasonal Arima Model. Int J Environ Clim Change 13(11):2073–2082. https://doi.org/10.9734/ijecc/2023/v13i113367
Siddiqi N (2006) Credit risk scorecards: developing and implementing intelligent credit scoring. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey
Silva JLB, da, Bezerra AC, de Almeida CDGC, Lima DF, de Andrade FHN, Jiménez KJ (2021) Comparison of the reference evapotranspiration among empirical methods and Penman-Monteith in Semiarid Region of Northeastern Brazil. Revista Brasileira De Geografia Física 14(1):001–015. https://doi.org/10.26848/rbgf.v14.1.p001-015
Soni AK, Tripathi JN, Ghosh K, Singh P, Sateesh M, Singh KK (2024) Estimation of regional-scale near real time reference evapotranspiration using remote sensing and weather data to improve agriculture advisory. Earth Sci Inf 17(1):679–697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01197-z
Steinkopf J, Engelbrecht F (2022) Verification of ERA5 and ERA-Interim precipitation over Africa at intra-annual and interannual timescales. Atmos Res 280:106427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106427
Tarek M, Brissette FP, Arsenault R (2020) Evaluation of the ERA5 reanalysis as a potential reference dataset for hydrological modelling over North America. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 24(5):2527–2544. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-24-2527-2020
Thornthwaite CW (1948) An approach toward a rational classification of climate. Geographical Reviews 38:55–94
Tripathi IM, Mahto SS, Kushwaha AP, Kumar R, Tiwari AD, Sahu BK, Jain V, Mohapatra PK (2024) Dominance of soil moisture over aridity in explaining vegetation greenness across global drylands. Sci Total Environ 917:170482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170482
UNEP (1992) World Atlas of Desertification. Https://Wedocs.Unep.Org/20.500.11822/42137
Wang H, Liu Y, Wang Y, Yao Y, Wang C (2023) Land cover change in global drylands: a review. Sci Total Environ 863:160943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160943
Xing L, Feng Y, Cui N, Guo L, Du T, Wu Z, Zhang Y, Wen S, Gong D, Zhao L (2023) Estimating reference evapotranspiration using Penman-Monteith equation integrated with optimized solar radiation models. J Hydrol 620:129407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129407
Yan S, Wu L, Fan J, Zhang F, Zou Y, Wu Y (2021) A novel hybrid WOA-XGB model for estimating daily reference evapotranspiration using local and external meteorological data: applications in arid and humid regions of China. Agric Water Manage 244:106594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106594
Zhao X, Li Y, Zhao Z, Xing X, Feng G, Bai J, Wang Y, Qiu Z, Zhang J (2022) Prediction model for Daily Reference Crop Evapotranspiration based on hybrid algorithm in semi-arid regions of China. Atmosphere 13(6):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060922
Zomer RJ, Xu J, Trabucco A (2022) Version 3 of the global Aridity Index and potential evapotranspiration database. Sci Data 9(1):409. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-022-01493-1
Funding
This research work did not receive any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
APD: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing - Review & Editing, Visualization; MHJ: Formal analysis, Investigation, Data Curation, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review & Editing, Visualization, Supervision; MKM: Formal analysis, Investigation, Data Curation, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review & Editing, Visualization, Supervision; IAB: Formal analysis, Investigation, Supervision. SS: methodology, software, validation, Formal analysis, investigation, Data curation, writing—review & editing, visualization, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Ethics approval
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All the authors consented to publish the paper.
Additional information
Communicated by: Hassan Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Awhari, D.P., Jamal, M.H.B., Muhammad, M.K.I. et al. Evaluating evapotranspiration models for precise aridity mapping based on UNEP- aridity classification. Earth Sci Inform 18, 194 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-025-01706-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-025-01706-2