Abstract
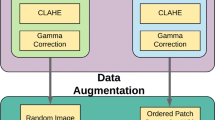
An essential step in diagnosing ocular illnesses is automatically segmenting retinal blood vessels. Although current deep-learning techniques have attained excellent accuracy in artery segmentation, maintaining vascular structural connections is still tricky. The most frequent consequence of diabetes, and the main factor in adult blindness, is diabetic retinopathy. Currently, diagnosing fundus pictures is the primary method clinicians use to pinpoint the origin of diabetic retinopathy. Conducting manual screening on a large scale for retinal health is challenging. Therefore, the objective of my article is to state the segmentation of retinal blood vessels for early retinal disease detection and diagnosis. The proposed research method includes a U-net network with VGG19 and ImageNet is the backbone for extracting retinal vessels, and the extraction performance is found to be better with respect to another existing approach in the literature. The proposed methodology includes pre-processing, augmentation, patching, and model setup and implementation. First, pre-processing the available data to enhance the vessels of retinal image. The skip connections, the semantic gap left by a direct simple connection is filled using the nested connection method to combine the feature maps obtained from the intermediate decoder with the original features from the encoder. Data augmentation is also done on the original image to increase resilience and avoid the overfitting issue brought on by insufficient data. A mixed loss function is suggested to address the class imbalance in vascular pictures. After exhaustive experimental analysis observed, the Accuracy, Area Under Curve (AUC), and Jaccard index values are 0.9728, 0.9961, and 0.9175 for the DRIVE Date-set and) 0.9668, 0.9851, and 0.8975 for STARE Date-set respectively. Compared to the DRIVE data set, the proposed strategy performed better at the beginning but worse towards the end for the STARE data set. For the DRIVE and STARE data sets, the final loss values were 0.1029 and 0.1154, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This article used DRIVE and STARE dataset which is taken from Kaggle. And link of the dataset given below: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/andrewmvd/drive-digital-retinal-imagesfor-vessel-extraction. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/vidheeshnacode/stare-dataset.
References
Sun W, Wang R. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation of very high resolution remotely sensed images combined with dsm. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett. 2018;15(3):474–8.
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun ACM. 2017;60(6):84–90.
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M, et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vision. 2015;115:211–52.
Maninis K-K, Pont-Tuset J, Arbelaez P, Van Gool L. Deep retinal image understanding. In: Medical Image Computing and ComputerAssisted Intervention–MICCAI 2016: 19th International Conference, Athens, Greece, October 17–21, 2016, Proceedings, Part II 19, pp. 140–148 (2016). Springer.
Zhang K, Zhang H, Zhou H, Crookes D, Li L, Shao Y, Liu D. Zebrafish embryo vessel segmentation using a novel dual resunet model. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2019;2019(1):8214975.
de Moor T, Rodriguez-Ruiz A, Merida AG, Mann R, Teuwen J. Automated soft tissue lesion detection and segmentation in digital mammography using a u-net deep learning network. 2018. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.06865
Gegundez-Arias ME, Marin-Santos D, Perez-Borrero I, VasalloVazquez MJ. A new deep learning method for blood vessel segmentation in retinal images based on convolutional kernels and modified u-net model. Comput Methods Prog Biomed. 2021;205:106081.
Kohler T, Budai A, Kraus MF, Odstrcilik J, Michelson G, Hornegger J. Automatic no-reference quality assessment for retinal fundus images using vessel segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 26th IEEE International Symposium on Computer-based Medical Systems, pp. 95–100 (2013). IEEE.
Kauppi T, Kamarainen J-K, Lensu L, Kalesnykiene V, Sorri I, Uusitalo H, Kalviainen H. Constructing benchmark databases and protocols for medical image analysis: diabetic retinopathy. Computat Math Methods Med. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/368514.
Decenciere E, Zhang X, Cazuguel G, Lay B, Cochener B, Trone C, Gain P, Ordonez R, Massin P, Erginay A, et al. Feedback on a publicly distributed image database: the messidor database. Image Anal Stereol. 2014;33(3):231–4.
Al-Diri B, Hunter A, Steel D, Habib M, Hudaib T, Berry S. A reference data set for retinal vessel profiles. In: 2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 2262–2265 (2008). IEEE.
Niemeijer M, Van Ginneken B, Cree MJ, Mizutani A, Quellec G, Sanchez CI, Zhang B, Hornero R, Lamard M, Muramatsu C, et al. Retinopathy online challenge: automatic detection of microaneurysms in digital color fundus photographs. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2009;29(1):185–95.
Abdulsahib AA, Mahmoud MA, Mohammed MA, Rasheed HH, Mostafa SA, Maashi MS. Comprehensive review of retinal blood vessel segmentation and classification techniques: intelligent solutions for green computing in medical images, current challenges, open issues, and knowledge gaps in fundus medical images. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinform. 2021;10:1–32.
Fraz MM, Remagnino P, Hoppe A, Uyyanonvara B, Rudnicka AR, Owen CG, Barman SA. Blood vessel segmentation methodologies in retinal images–a survey. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2012;108(1):407–33.
Zhou L, Li P, Yu Q, Qiao Y, Yang J. Automatic hemorrhage detection in color fundus images based on gradual removal of vascular branches. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 403 (2016). IEEE.
Usman I, Almejalli KA. Intelligent automated detection of microaneurysms in fundus images using feature-set tuning. IEEE Access. 2020;8:65187–96.
Long S, Huang X, Chen Z, Pardhan S, Zheng D. Automatic detection of hard exudates in color retinal images using dynamic threshold and svm classification: algorithm development and evaluation. BioMed Res Int. 2019;2019.
Qummar S, Khan FG, Shah S, Khan A, Shamshirband S, Rehman ZU, Khan IA, Jadoon W. A deep learning ensemble approach for diabetic retinopathy detection. IEEE Access. 2019;7:150530–9.
Ghazal M, Ali SS, Mahmoud AH, Shalaby AM, El-Baz A. Accurate detection of non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy in optical coherence tomography images using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access. 2020;8:34387–97.
Zhou W, Yi Y, Gao Y, Dai J, et al. Optic disc and cup segmentation in retinal images for glaucoma diagnosis by locally statistical active contour model with structure prior. Computat Math Methods Med. 2019;2019.
Qiao L, Zhu Y, Zhou H. Diabetic retinopathy detection using prognosis of microaneurysm and early diagnosis system for non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy based on deep learning algorithms. IEEE Access. 2020;8:104292–302.
Patel R, Chaware A. Transfer learning with fine-tuned mobilenetv2 for diabetic retinopathy. In: 2020 International Conference for Emerging Technology (INCET), pp. 1–4 (2020). IEEE.
Pour AM, Seyedarabi H, Jahromi SHA, Javadzadeh A. Automatic detection and monitoring of diabetic retinopathy using efficient convolutional neural networks and contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization. IEEE Access. 2020;8:136668–73.
Chen W, Yang B, Li J, Wang J. An approach to detecting diabetic retinopathy based on integrated shallow convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access. 2020;8:178552–62.
Qureshi I, Ma J, Abbas Q. Diabetic retinopathy detection and stage classification in eye fundus images using active deep learning. Multimed Tools Appl. 2021;80:11691–721.
Bilal A, Sun G, Mazhar S, Imran A, Latif J. A transfer learning and u-net-based automatic detection of diabetic retinopathy from fundus images. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng Imaging Visual. 2022;10(6):663–74.
Wang L, Guo S, Huang W, Qiao Y. Places205-vggnet models for scene recognition. 2015. arXiv preprint arXiv:1508.01667.
Kora P, Ooi CP, Faust O, Raghavendra U, Gudigar A, Chan WY, Meenakshi K, Swaraja K, Plawiak P, Acharya UR. Transfer learning techniques for medical image analysis: a review. Biocybern Biomed Eng. 2022;42(1):79–107.
Nahid A-A, Mehrabi MA, Kong Y. Histopathological breast cancer image classification by deep neural network techniques guided by local clustering. BioMed Res Int. 2018;2018:1–20.
Thanh NC, Long TQ, et al. Crf-efficientunet: an improved unet framework for polyp segmentation in colonoscopy images with combined asymmetric loss function and crf-rnn layer. IEEE Access. 2021;9:156987–7001.
Liskowski P, Krawiec K. Segmenting retinal blood vessels with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016;35(11):2369–80.
Martınez-Perez, ME, Hughes AD, Stanton AV, Thom SA, Bharath AA, Parker KH. Retinal blood vessel segmentation by means of scale-space analysis and region growing. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI’99: Second International Conference, Cambridge, UK, September 19–22, 1999. Proceedings 2, pp. 90–97 (1999). Springer.
Zana F, Klein J-C. Segmentation of vessel-like patterns using mathematical morphology and curvature evaluation. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2001;10(7):1010–9.
Jiang X, Mojon D. Adaptive local thresholding by verification-based multithreshold probing with application to vessel detection in retinal images. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2003;25(1):131–7.
Niemeijer M, Staal J, Van Ginneken B, Loog M, Abramoff MD. Comparative study of retinal vessel segmentation methods on a new publicly available database. In: Medical Imaging 2004: Image Processing, vol. 5370, pp. 648–656 (2004). SPIE.
Al-Diri B, Hunter A, Steel D. An active contour model for segmenting and measuring retinal vessels. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2009;28(9):1488–97.
Mendonca AM, Campilho A. Segmentation of retinal blood vessels by combining the detection of centerlines and morphological reconstruction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2006;25(9):1200–13.
Soares JV, Leandro JJ, Cesar RM, Jelinek HF, Cree MJ. Retinal vessel segmentation using the 2-d gabor wavelet and supervised classification. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2006;25(9):1214–22.
Singh NP, Srivastava R. Retinal blood vessels segmentation by using gumbel probability distribution function based matched filter. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2016;129:40–50.
Kumar R, Singh NP, et al. Retinal blood vessels segmentation using frechet pdf and msmo method. ELCVIA Electron Lett Comput Vis Image Anal. 2022;21(1):27–46.
Kumar KS, Singh NP. Segmentation of retinal blood vessel using generalized extreme value probability distribution function (pdf)-based matched filter approach. Pattern Anal Appl. 2023;26(1):307–32.
Saroj SK, Kumar R, Singh NP. Retinal blood vessels segmentation using wald pdf and msmo operator. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng Imaging Visual. 2023;11(2):215–32.
Hoover A, Kouznetsova V, Goldbaum M. Locating blood vessels in retinal images by piecewise threshold probing of a matched filter response. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2000;19(3):203–10.
Staal J, Abramoff MD, Niemeijer M, Viergever MA, Van Ginneken B. Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of the retina. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2004;23(4):501–9.
Ricci E, Perfetti R. Retinal blood vessel segmentation using line operators and support vector classification. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2007;26(10):1357–65.
Lam BS, Gao Y, Liew AW-C. General retinal vessel segmentation using regularization-based multiconcavity modeling. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010;29(7):1369–81.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All the authors they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
All the authors involved have agreed to participate in this submitted article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, P.K., Kaur, J. & Singh, N.P. An Intelligent Approach for Retinal Vessels Extraction Based on Transfer Learning. SN COMPUT. SCI. 5, 1072 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-03403-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-03403-1