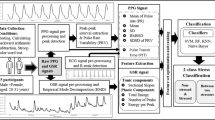
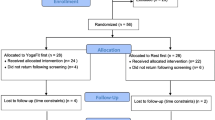
Abstract
Yoga has become crucial mode of intervention in enhancing mental health through empirical and data-supported methodologies. This study investigates the effects of yoga interventions after cognitive task on physiological and psychological parameters, specifically blood pressure (BP) and State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) scores, using optimized machine learning techniques. The primary objective was to analyze and predict how different yoga practices impact individual health outcomes through stress reduction. The initial phase involved collecting baseline data on BP and STAI parameters from participants before and after interventions. The various machine learning algorithms were employed to model the data, with a focus on their performance in predicting changes in BP and anxiety levels as measured by the STAI. In like manner, subsequent analysis using DT and RF models demonstrated promising results in terms of accuracy, with RF and DT particularly effective in handling the complex patterns in the combined BP and STAI data. Further, the Artificial Bee Colony algorithm was applied to optimize the hyper-parameters of the DT and RF models. The optimized models, termed BP-STAI Combined-Optimized DT and BP-STAI Combined-Optimized RF, achieved accuracies of 69.90% and 75.43%, respectively. These results highlight a significant improvement over the non-optimized models and underscore the effectiveness of combining physiological and psychological data in predictive analytics. The findings provide valuable insights into cognitive-driven stress reduction and the broader implications of employing advanced data-driven approaches in health and wellness research.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bienertova-Vasku J, Lenart P, Scheringer M. Eustress and distress: neither good nor bad, but rather the same? BioEssays. 2020;42(7):1900238.
Melchior M, Figueiredo N, Roversi A, Dubanchet A, Bui E, Vadell-Martínez J, Barbui C, Purgato M, Ayuso-Mateos JL, Mediavilla R, et al. Addressing mental health problems among persons without stable housing in the context of the covid-19 pandemic: study protocol for a randomised trial. respond–france. BMC Public Health. 2023;23(1):2275.
Organization WH, et al. Guidelines for the management of conditions that are specifically related to stress (2013)
Anderzén-Carlsson A, Persson Lundholm U, Köhn M, Westerdahl E. Medical yoga: Another way of being in the world-a phenomenological study from the perspective of persons suffering from stress-related symptoms. Int J Qual Stud Health Well Being. 2014;9(1):23033.
Bhide SR, Bhargav H, Gangadhar BN, Desai G. Exploring the therapeutic potential of yoga philosophy: a perspective on the need for yoga-based counselling program (ybcp) in common mental disorders. Indian J Psychol Med. 2023;45(4):420–9.
Zok A, Matecka M, Bienkowski A, Ciesla M. Reduce stress and the risk of burnout by using yoga techniques. pilot study. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1370399.
Westerink, H.J., Garvelink, M.M., Uden-Kraan, C.F., Zouitni, O., Bart, H.A., Wees, P.J., Nat, P.B., Group, S.P.P.S. Evaluating patient participation in value-based healthcare: current state and lessons learned. Health Expect. 2024;27(1):13945.
Sadruddin S, Khairnar VD, Vora DR. Issues and challenges in detecting mental stress from multimodal data using machine intelligence. SN Comput Sci. 2024;5(4):1–22.
Albaladejo-González M, Ruipérez-Valiente JA, Gómez Mármol F. Evaluating different configurations of machine learning models and their transfer learning capabilities for stress detection using heart rate. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2023;14(8):11011–21.
Kadyan V, Bawa P, Akhtar MM, Singh M. Speech-based alzheimer’s disease classification system with noise-resilient features optimization. In: 2023 31st irish conference on artificial intelligence and cognitive science (AICS), IEEE 2023;pp. 1–4.
Sau A, Bhakta I. Screening of anxiety and depression among seafarers using machine learning technology. Inf Med Unlocked. 2019;16: 100228.
Shobhika PK, Chandra S. Prediction and comparison of psychological health during covid-19 among Indian population and Rajyoga meditators using machine learning algorithms. Procedia Comput Sci. 2023;218:697–705.
Michalak J, Crane C, Germer CK, Gold E, Heidenreich T, Mander J, Meibert P, Segal ZV. Principles for a responsible integration of mindfulness in individual therapy. Mindfulness. 2019;10:799–811.
Awada M, Becerik Gerber B, Lucas GM, Roll SC. Stress appraisal in the workplace and its associations with productivity and mood: Insights from a multimodal machine learning analysis. PLoS ONE. 2024;19(1):0296468.
Song Y, Lindquist R. Effects of mindfulness-based stress reduction on depression, anxiety, stress and mindfulness in korean nursing students. Nurse Educ Today. 2015;35(1):86–90.
Parvizi J, Kastner S. Human intracranial eeg: promises and limitations. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21(4):474.
Seo S-H, Lee J-T, Crisan M. Stress and eeg. Convergence and hybrid information technologies 2010, Vol. 27
Mennin DS, Fresco DM, Ritter M, Heimberg RG. An open trial of emotion regulation therapy for generalized anxiety disorder and cooccurring depression. Depress Anxiety. 2015;32(8):614–23.
Svetlov AS, Nelson MM, Antonenko PD, McNamara JP, Bussing R. Commercial mindfulness aid does not aid short-term stress reduction compared to unassisted relaxation. Heliyon 2019;5(3)
Nanthakumar C. Yoga for anxiety and depression-a literature review. J Ment Health Train Educ Pract. 2020;15(3):157–69.
Gonzalez M, Pascoe MC, Yang G, Manincor M, Grant S, Lacey J, Firth J, Sarris J. Yoga for depression and anxiety symptoms in people with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychooncology. 2021;30(8):1196–208.
Gallagher A, Kring D, Whitley T. Effects of yoga on anxiety and depression for high risk mothers on hospital bedrest. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020;38: 101079.
Sharma N, Sahni PS, Sharma US, Kumar J, Garg R. Effect of yoga on the stress, anxiety, and depression of covid-19-positive patients: a quasi-randomized controlled study. Int J Yoga Ther. 2022;32(2022):8.
James-Palmer A, Anderson EZ, Zucker L, Kofman Y, Daneault J-F. Yoga as an intervention for the reduction of symptoms of anxiety and depression in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Front Pediatr. 2020;8:78.
Capon H, O’Shea M, Evans S, McIver S. Yoga complements cognitive behaviour therapy as an adjunct treatment for anxiety and depression: Qualitative findings from a mixed-methods study. Psychol Psychother Theory Res Pract. 2021;94(4):1015–35.
Kavzoglu T, Colkesen I. Entropic distance based k-star algorithm for remote sensing image classification. Fresenius Environ Bull. 2011;20(5):1200–7.
Srivastava T, Srivastava T. Introduction to knn, k-nearest neighbors: Simplified. Vidhya: Anal; 2014.
Ortiz-Bejar J, Graff M, Tellez ES, Ortiz-Bejar J, Jacobo JC. K-nearest neighbor regressors optimized by using random search. In: 2018 IEEE international autumn meeting on power, electronics and computing (ROPEC), IEEE 2018;pp. 1–5.
Cavazos J, O’boyle MF. Method-specific dynamic compilation using logistic regression. ACM SIGPLAN Notices. 2006;41(10):229–40.
Sanchez RN, Amaral JN, Szafron D, Pirvu M, Stoodley M. Using support vector machines to learn how to compile a method. In: 2010 22nd international symposium on computer architecture and high performance computing, IEEE 2010;pp. 223–230
Park E, Kulkarni S, Cavazos J. An evaluation of different modeling techniques for iterative compilation. In: Proceedings of the 14th international conference on compilers, architectures and synthesis for embedded systems, 2011;pp. 65–74
Johnson S, Shanmugam V. Effective feature set construction for svm-based hot method prediction and optimisation. Int J Comput Sci Eng. 2011;6(3):192–205.
Turmel D, Carlier S, Bruyneel AV, Bruyneel M. Tailored individual yoga practice improves sleep quality, fatigue, anxiety, and depression in chronic insomnia disorder. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):267.
Medina J, Hopkins L, Powers M, Baird SO, Smits J. The effects of a hatha yoga intervention on facets of distress tolerance. Cogn Behav Ther. 2015;44(4):288–300.
Deepeshwar S, Kumar D. Beneficial effect of yoga-based lifestyle intervention on anxiety and depression in young adults: non-randomized controlled study. (2022)
Broughton MK. Yoga for depression and anxiety: a review of published research and implications for healthcare providers. R I Med J. 2016;99(3):20.
Shannahoff-Khalsa D, Fernandes RY, Pereira CAdB, March JS, Leckman JF, Golshan S, Vieira MS, Polanczyk GV, Miguel EC, Shavitt RG. Kundalini yoga meditation versus the relaxation response meditation for treating adults with obsessive-compulsive disorder: A randomized clinical trial. Front Psychiatry. 2019;10: 468272.
Rahmadani A, Setianingsih C, Dirgantara FM, Ambarita AR, Arifin HI, Manalu IP, Pratama ML. Depression, anxiety, and stress disorders detection in students during the covid-19 pandemic using naïve bayes algorithm. In: BIO web of conferences, EDP sciences. 2023;vol. 75:p. 01003.
Harsha M, Kaur A. A review of" machine learning approaches to assess psychological health: a comparative analysis of non-meditators and meditators". In: 2023 14th international conference on computing communication and networking technologies (ICCCNT), IEEE. 2023;pp. 1–7.
Bansal JC, Sharma H, Jadon SS, Clerc M. Spider monkey optimization algorithm for numerical optimization. Memetic Comput. 2014;6:31–47.
Al-Azza AA, Al-Jodah AA, Harackiewicz FJ. Spider monkey optimization: a novel technique for antenna optimization. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett. 2015;15:1016–9.
Gupta K, Deep K, Bansal JC. Spider monkey optimization algorithm for constrained optimization problems. Soft Comput. 2017;21:6933–62.
Faris H, Aljarah I, Al-Betar MA, Mirjalili S. Grey wolf optimizer: a review of recent variants and applications. Neural Comput Appl. 2018;30:413–35.
Nadimi-Shahraki MH, Taghian S, Mirjalili S. An improved grey wolf optimizer for solving engineering problems. Expert Syst Appl. 2021;166: 113917.
Mirjalili S, Saremi S, Mirjalili SM, Coelho LdS. Multi-objective grey wolf optimizer: a novel algorithm for multi-criterion optimization. Expert Syst Appl. 2016;47:106–19.
TSai P-W, Pan J-S, Liao B-Y, Chu S-C, et al. Enhanced artificial bee colony optimization. Int J Innov Comput Inf Control. 2009;5(12):5081–92.
Diwold K, Aderhold A, Scheidler A, Middendorf M. Performance evaluation of artificial bee colony optimization and new selection schemes. Memetic Comput. 2011;3:149–62.
Oliva D, Cuevas E, Pajares G. Parameter identification of solar cells using artificial bee colony optimization. Energy. 2014;72:93–102.
Li G, Niu P, Xiao X. Development and investigation of efficient artificial bee colony algorithm for numerical function optimization. Appl Soft Comput. 2012;12(1):320–32.
Gao W, Liu S. Improved artificial bee colony algorithm for global optimization. Inf Process Lett. 2011;111(17):871–82.
Van Buuren S, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K. mice: multivariate imputation by chained equations in r. J Stat Softw. 2011;45:1–67.
Niranjan P, Balaram P. Immediate effect of ujjayi pranayama on attention and anxiety among university students: a randomised self-control study. J Clin Diagn Res 2022;16(2).
Kumar P, Garg S, Garg A. Assessment of anxiety, depression and stress using machine learning models. Procedia Comput Sci. 2020;171:1989–98.
Mittal S, Mahendra S, Sanap V, Churi P. How can machine learning be used in stress management: a systematic literature review of applications in workplaces and education. Int J Inf Manag Data Insights. 2022;2(2): 100110.
Rosales MA, Bandala AA, Vicerra RR, Dadios EP. Physiological-based smart stress detector using machine learning algorithms. In: 2019 IEEE 11th international conference on humanoid, nanotechnology, information technology, communication and control, environment, and management (HNICEM), IEEE 2019;pp. 1–6.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AG conceptualized and designed the study, performed the analysis, and wrote the original draft. VK contributed to data collection and interpretation and critically reviewed the manuscript. ST supervised the project and was involved in the final editing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Consideration
The study adheres to the ethical guidelines in data colleciton established by Patanjali Research Centre, Haridwar, India.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A., Kadyan, V. & Telles, S. Investigating the Psychological Outcomes Through Yoga for Stress Reduction Using Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques. SN COMPUT. SCI. 5, 1173 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-03489-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-03489-7