Abstract
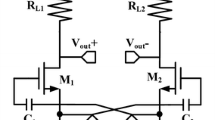
The special LNA topologies resulting from loading a simple LNA with a set of Q-enhanced inductors are analyzed and compared. The Q of the on-chip spiral inductors that form the LNA load is enhanced by using a negative resistance realized with a cross-coupled differential pair degenerated and biased in various ways. The performance of the LNA is presented for the following types of Q-enhancement circuit: ideal negative resistor (ideal cell), tail-biased non-degenerated cross-coupled differential pair (classic cell), tail-biased resistively degenerated cross-coupled differential pair (resistive cell), tail-biased LC degenerated cross-coupled differential pair (B-cell), self-biased LC degenerated cross-coupled differential pair (BB-cell). The analysis focuses on the benefits of each cell related to s-parameter response, noise and linearity and the interdependency of Q vs. center frequency during tuning. Low voltage design challenges are addressed by presenting the advantages of the novel self-biased LC degenerated cross-coupled differential pair (BB-cell).



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Aparin, P. Katzin, Active GaAs MMIC band-pass filters with automatic frequency tuning and insertion loss control. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 10, 1068–1073 (1995)
C. Barth, I.R. Linscott, U.S. Inan, A double notch RF filter architecture for saw-less GPS receivers, in Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), IEEE International Symposium on (2011), pp. 1804–1807. doi:10.1109/ISCAS.2011.5937935
D. Bormann, T. Werth, S. Kaehlert, C. Schmits, S. Heinen, A fully integrated q-enhanced notch filter LNA for TX blocker suppression in FDD systems, in Radio-Frequency Integration Technology, 2009. RFIT 2009. IEEE International Symposium on (2009), pp. 154–157. doi:10.1109/RFIT.2009.5383699
D. Bormann, T. Werth, N. Zimmermann, R. Wunderlich, S. Heinen, A comparison of bandwidth setting concepts for q-enhanced lc-tanks in deep-sub micron CMOS processes, in Electronics, Circuits and Systems, 2008. ICECS 2008. 15th IEEE International Conference on (2008), pp. 726–729. doi:10.1109/ICECS.2008.4674956
K. Christensen, T. Lee, E. Bruun, A high dynamic range programmable CMOS front-end filter with a tuning range from 1850–2400 MHz, in Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing (Kluwer Academic, Norwell, 2005)
Freescale Semiconductors, MBC13916 general purpose SiGe: C RF cascode low noise amplifier (2006). http://www.freescale.com/
B. Georgescu, I. Finvers, F. Ghannouchi, 2 GHz Q-enhanced active filter with low passband distortion and high dynamic range. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 9, 2029–2039 (2006)
X. He, W.B. Kuhn, A 2.5-GHz low-power, high dynamic range self-tuned Q-enhanced LC filter in SOI. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 8, 1618–1628 (2005)
W.B. Kuhn, Design of integrated, low power, radio receivers in BiCMOS technologies. PhD dissertation, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University (1995). http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/theses/available/etd-81197-164118/unrestricted/KUHN.PDF
W.B. Kuhn, A. Elshabini-Riad, F.W. Stephenson, Centre-tapped spiral inductors for monolithic bandpass filter. Electron. Lett. 1, 625–626 (1995)
W.B. Kuhn, D. Nobbe, D. Kelly, A.W. Osborn, Dynamic range performance of on-chip RF bandpass filters. IEEE Trans. Circuits. Syst. II, pp. 685–694 (2003)
T.H. Lee, The Design of CMOS Radio-frequency Integrated Circuits (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1998)
D. Li, Y. Tsividis, A 1.9 GHz Si active LC filter with on-chip automatic tuning, in IEEE Int. Solid State Circuits Conf. Dig. Tech. Papers (2001), pp. 368–369
D. Li, Y. Tsividis, Design techniques for automatically tuned integrated gigahertz-range active LC filters. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, pp. 967–977 (2002)
J. Nakaska, J. Haslett, 2 GHz automatically tuned Q-enhanced CMOS bandpass filter, in Microwave Symposium, 2007. IEEE/MTT-S International (2007), pp. 1599–1602. doi:10.1109/MWSYM.2007.379991
H. Pekau, J. Kulyk, J.W. Haslett, L. Belostotski, Linearization techniques for cross-coupled transconductor circuits used in integrated q-enhanced lc filters, in Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2006. CCECE ’06. Canadian Conference on (2006), pp. 541–546. doi:10.1109/CCECE.2006.277739
W.M. Sansen, Analog Design Essentials (Springer, Berlin, 2006)
C. Schmits, T. Werth, J. Hausner, A new q-enhancement architecture for saw-less communication receiver in 65-nm CMOS, in Radio-Frequency Integration Technology, 2009. RFIT 2009. IEEE International Symposium on (2009), pp. 158–161. doi:10.1109/RFIT.2009.5383743
C. Schultz, H. Doppke, M. Hammes, R. Kreienkamp, L. Lemke, S. van Waasen, An l-band receiver-front-end-architecture using adaptive q-enhancement techniques in 65nm CMOS as enabler for single-saw GPS receivers, in Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC) (IEEE, New York, 2011), pp. 1–4. doi:10.1109/RFIC.2011.5940615
P. Wambacq, W.M. Sansen, Distortion Analysis of Analog Integrated Circuits (Kluwer Academic, Norwell, 1998)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Alberta Informatics Circle of Research Excellence, the University of Calgary, and the Canadian Microelectronics Corporation. Thanks are due to the reviewers for useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Georgescu, B., Nakaska, J., Finvers, I. et al. Comparative Analysis of Tunable Q-Enhancement Filter Cell Topologies in a 2.4 GHz LNA. Circuits Syst Signal Process 31, 1577–1597 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9398-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9398-x