Abstract
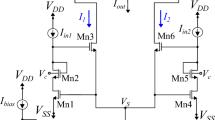
As an approach to constructing highly organized and intelligent image recognition systems mimicking the visual architecture in the human brain, we have designed an image processing circuit that performs a directional pixel-state propagation algorithm based on a pixel-parallel architecture using pulse-width modulation (PWM) signals. Directional pixel-state propagation can be used for subjective contour generation, which is a typical function of the visual system in the human brain to fill gaps in natural-image information. A PWM-mode circuit can provide more compact circuit configuration than digital circuits, and can achieve focal-plane analog processing by combining with image sensors without A/D converters. Such circuits are suitable for repetitive algorithms, which require offset-free arithmetic. The proof-of-concept LSI chip has been designed and fabricated using a 0.25 \(\upmu \)m mixed-signal CMOS process. There are 35 \(\times \) 35 processing units included in the chip, the operation cycle time for propagation step is 2.2 \(\upmu \)s, and the power consumption is 363 mW at a supply voltage of 3.3 V. In experiments using this LSI chip, we have successfully generated subjective contours of Kanizsa figures.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Carmona-Galán, F. Jiménez-Garrido, C.M. Domínguez-Mata, R. Domínguez-Castro, S.E. Meana, I. Petras, A. Rodríguez-Vázquez, Second-order neural core for bioinspired focal-plane dynamic image processing in CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 51(5), 913–925 (2004)
G. Cauwenberghs, J. Waskiewicz, Focal-plane analog VLSI cellular implementation of the boundary contour system. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 46(2), 327–334 (1999)
R. Dominguez-Castro, S. Espejo, A. Rodríguez-Vázquez, R.A. Carmona, P. Foldesy, A. Zarándy, P. Szolgay, T. Szirányi, T. Roska, A 0.8-\(\mu \)m CMOS two-dimensional programmable mixed-signal focal-plane array processor with on-chip binary imaging and instructions storage. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 32(7), 1013–1026 (1997)
P. Dudek, Adaptive sensing and image processing with a general-purpose pixel-parallel sensor/processor array integrated circuit, in International Workshop on Computer Architecture for Machine Perception and Sensing (2006), pp. 1–6
P. Dudek, P.J. Hicks, A general-purpose processor-per-pixel analog SIMD vision chip. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 52(1), 13–20 (2005)
B. Erkmen, R.A. Vural, N. Kahraman, T. Yildirim, A mixed mode neural network circuitry for object recognition application. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(1), 29–46 (2013)
R. Etienne-Cummings, Z.K. Kalayjian, D. Cai, A programmable focal-plane MIMD image processor chip. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 36(1), 64–73 (2001)
J. Fernández-Berni, L. Acasandrei, R. Carmona-Galán, A. Barriga-Barros, A. Rodríguez-Vázquez, Power-efficient focal-plane image representation for extraction of enriched Viola-Jones features, in IEEE Proceedings of International Symposium Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) (2012), pp. 3122–3125
J. Fernández-Berni, R. Carmona-Galán, L. Carranza-González, FLIP-Q: A QCIF resolution focal-plane array for low-power image processing. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 46(3), 669–680 (2011)
R.C. Galán, F. Jiménez-Garrido, R. Domínguez-Castro, S. Espejo, T. Roska, C. Rekeczky, I. Petrás, A. Rodríguez-Vázquez, A bio-inspired two-layer mixed-signal flexible programmable chip for early vision. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 14(5), 1313–1336 (2003)
B.S. Hadad, D. Maurer, T.L. Lewis, The development of contour interpolation: evidence from subjective contours. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 106, 163–176 (2010)
A. Iwata, T. Morie, M. Nagata, Merged analog-digital circuits using pulse modulation for intelligent SoC applications. IEICE Trans. Fund. E84–A(2), 486–496 (2001)
Y. Joo, J. Park, M. Thomas, K.S. Chung, M.A. Brooke, N.M. Jokerst, D.S. Wills, Smart CMOS focal plane arrays: a Si CMOS detector array and sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter imaging system. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 5(2), 296–305 (1999)
G. Kanizsa, Subjective contours. Sci. Am. 234(4), 48–52 (1976)
Y. Kim, T. Morie, A pixel-parallel anisotropic diffusion algorithm for subjective contour generation, in IEEE Proceedings of International Symposium Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) (2005), pp. 4237–4240
Y. Kim, T. Morie, A pixel circuit implementing an anisotropic diffusion algorithm for subjective contour generation using merged analog-digital circuit approach. J. Signal Process. 10(4), 259–262 (2006)
M. Koyanagi, T. Fukushima, T. Tanaka, High-density through silicon vias for 3-D LSIs. Proc. IEEE 97(1), 49–59 (2009)
G. Linán, R. Domínguez-Castro, S. Espejo, A. Rodríguez-Vázquez, ACE16K: a programmable focal plane vision processor with 128x128 resolution, in European Conference on Circuit Theory and Design (ECCTD) (2001), pp. I345–I348
T. Morie, Y. Kim, A subjective-contour generation LSI system with expandable pixel-parallel architecture for vision systems, in IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) (2009), pp. 478–479
T. Morie, K. Murakoshi, M. Nagata, A. Iwata, Pulse modulation techniques for nonlinear dynamical systems and a CMOS chaos circuit with arbitrary 1-D maps. IEICE Trans. Electron. E87–C(11), 1856–1862 (2004)
T. Morie, J. Umezawa, A. Iwata, A pixel-parallel image processor for Gabor filtering based on merged analog-digital architecture, in 2004 Symposium on VLSI Circuits (2004), pp. 212–213
M. Motoyoshi, Through-silicon via. Proc. IEEE 97(1), 43–48 (2009)
F.D.V.R. Oliveira, H.L. Haas, J.G.R.C. Gomes, A. Petraglia, CMOS imager with focal-plane analog image compression combining DPCM and VQ. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 60(5), 1331–1344 (2013)
J. Poikonen, M. Laiho, A. Paasio, MIPA4k: a 64x64 cell mixed-mode image processor array, in IEEE Proceedings of International Symposium Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) (2009), pp. 1927–1930
J. Poikonen, A. Paasio, An 8\(\times \)8 cell analog order-statistic-filter array with asynchronous grayscale morphology in 0.13-\(\mu \)m CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 56(8), 1541–1553 (2009)
C. Posch, D. Matolin, R. Wohlgenannt, A QVGA 143 dB dynamic range frame-free PWM image sensor with lossless pixel-level video compression and time-domain CDS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 46, 259–275 (2011)
N. Takahashi, K. Fujita, T. Shibata, A pixel-parallel self-similitude processing for multiple-resolution edge-filtering analog image sensors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 56(11), 2384–2392 (2009)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Haichao Liang and Yuichiro Yamaguchi for their assistance in simulation and chip measurement. This work was partly supported by funding from MEXT, Japan, via a 21st Century COE program (center #J19). The LSI chip design was supported by VLSI Design and Education Center (VDEC), the University of Tokyo in collaboration with Cadence Design Systems, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y., Morie, T. A PWM-Mode Pixel-Parallel Image-Processing Circuit Performing Directional State-Propagation and Its Application to Subjective Contour Generation. Circuits Syst Signal Process 34, 605–623 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-014-9871-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-014-9871-9