Abstract
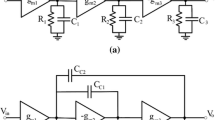
A novel frequency compensation technique, named Regular Miller plus Reversed Indirect Compensation (RMRIC), is presented in this paper for fast-settling three-stage amplifiers. The RMRIC topology includes, on the one hand, a Miller capacitor combined with one nulling resistor connected between the first stage and the third stage, and on the other hand, an indirect compensation capacitor in series with a resistor added between the first and the second stage, which improves remarkably the performance such as gain–bandwidth product (GBW) and sensitivity of the proposed amplifier. Detailed design considerations are carried out to demonstrate the stability of the compensation technique. Circuit simulation results show the amplifier driving a 2-pF load capacitance achieves a 9.25-GHz GBW dissipating only 16.5 mW with a 1.2 V supply voltage using a TSMC 65 nm CMOS technology, which shows a significant improvement in figure of merits. The implemented amplifier reaches a settling time of 3.35 ns with 0.006 % accuracy.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.A. Aamir, P. Harikumar, J.J. Wikner, Frequency compensation of high-speed, low-voltage CMOS multistage amplifiers, in International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2013, pp. 381–384
K. Bult, Analog design in deep sub-micron CMOS, in European Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2000, pp. 126–132
K. Bult, G.J.G.M. Geelen, A fast-settling CMOS op amp for SC circuits with 90-dB gain. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 25(6), 1379–1384 (1991)
R.G.H. Eschauzier, L.P.T. Kerklaan, J.H. Huijsing, A 100-MHz 100-dB operational amplifier with multipath nested Miller compensation structure. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 27(12), 1709–1717 (1992)
R.G.H. Eschauzier, R. Hogervorst, J.H. Huijsing, A programmable 1.5 V CMOS class-AB operational amplifier with hybrid nested Miller compensation for 120 dB gain and 6 MHz UGF. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 29(12), 1497–1504 (1994)
S. Golabi, M. Yavari, High-speed three-stage operational transconductance amplifiers for switched-capacitor circuits, in Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering, 2014, pp. 413–417
S. Golabi, M. Yavari, Design of CMOS three-stage amplifiers for fast-settling switched-capacitor circuits. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 80(2), 195–208 (2014)
J.H. Huijsing, D. Linebarger, Low-voltage operational amplifier with rail-to-rail input and output ranges. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 20(6), 1144–1150 (1986)
S.H. Lewis, H.S. Fetterman, G.F. Gross et al., A 10-b 20-Msample/s analog-to-digital converter. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 27(3), 351–358 (1992)
R. Nguyen, B. Murmann, The design of fast-settling three-stage amplifiers using the open-loop damping factor as a design parameter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 57(6), 1244–1254 (2010)
G. Palumbo, S. Pennisi, Design methodology and advances in nested-Miller compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 49(7), 893–903 (2002)
X. Peng, W. Sansen, Nested feed-forward Gm-stage and nulling resistor plus nested-Miller compensation for multistage amplifiers, in Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, 2002, pp. 329–332
X. Peng, W. Sansen, AC boosting compensation scheme for low-power multistage amplifiers. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 39(11), 2074–2079 (2004)
X. Peng, W. Sansen, L. Hou et al., Impedance adapting compensation for low-power multistage amplifiers. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 46(2), 445–451 (2011)
X. Peng, W. Sansen, Transconductance with capacitances feedback compensation for multistage amplifiers. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 40(7), 1514–1520 (2005)
X. Qu, Z.-K. Zhou, B. Zhang, Embedded capacitor multiplier gain boosting compensation for large-capacitive-load three-stage amplifier with slew rate enhancement. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 79(3), 543–553 (2014)
V. Saxena, R.J. Baker, Indirect compensation techniques for three-stage CMOS op-amps, in International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2009, pp. 9–12
V. Saxena, R.J. Baker, Indirect compensation techniques for three-stage fully-differential op-amps, in International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2010, pp. 588–591
V. Saxena, S. Balagopal, R.J. Baker, Systematic design of three-stage op-amps using split-length compensation, in International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2011, pp. 1–4
V. Saxena, S. Balagopal, R.J. Baker, Indirect feedback compensation of CMOS op-amps, in Workshop on Microelectronics and Electron Devices, 2006, pp. 2–4
S. Seth, B. Murmann, Settling time and noise optimization of a three-stage operational transconductance amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 60(5), 1168–1174 (2013)
B.D. Sahoo, B. Razavi, A 12-bit 200-MHz CMOS ADC. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 44(4), 2366–2380 (2009)
M. Taherzadeh-Sani, A. Hamoui, A 1-V process-insensitive current-scalable two-stage opamp with enhanced DC gain and settling behavior in 65-nm digital CMOS. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 46(3), 660–668 (2011)
F. You, S. Embabi, E. Sanchez-Sinencio, Multistage amplifier topologies with nested Gm-C compensation. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 32(12), 2000–2011 (1997)
W. Yan, R. Kolm, H. Zimmermann, Efficient four-stage frequency compensation for low-voltage amplifiers, in International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2008, pp. 2278–2281
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61234002, 61322405, 61574103 and 61574105)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, C., Zhu, Z. & Yang, Y. A Fast-Settling Three-Stage Amplifier Using Regular Miller Plus Reversed Indirect Compensation. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 795–810 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0314-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0314-7