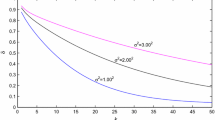
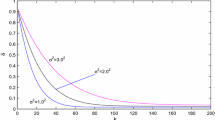
Abstract
Bilinear systems are a special class of nonlinear systems. Some systems can be described by using bilinear models. This paper considers the parameter identification problems of bilinear stochastic systems. The difficulty of identification is that the model structure of the bilinear systems includes the products of the states and inputs. To this point, this paper gives the input–output representation of the bilinear systems through eliminating the state variables in the model and derives a least squares algorithm and a multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for identifying the parameters of bilinear systems based on the least squares principle and the multi-innovation identification theory. The simulation results indicate that the proposed algorithms are effective for identifying bilinear systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Alfi, Particle swarm optimization algorithm with dynamic inertia weight for online parameter identification applied to Lorenz chaotic system. Int. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 8(2), 1191–1203 (2012)
A. Alfi, PSO with adaptive mutation and inertia weight and its application in parameter estimation of dynamic systems. Acta Autom. Sin. 37(5), 541–549 (2011)
A. Alfi, M.M. Fateh, Identification of nonlinear systems using modified particle swarm optimization: a hydraulic suspension system. J. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 46(6), 871–887 (2011)
A. Alfi, M.M. Fateh, Intelligent identification and control using improved fuzzy particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(10), 12312–12317 (2011)
A. Alfi, H. Modares, System identification and control using adaptive particle swarm optimization. Appl. Math. Model. 35, 1210–1221 (2011)
A. Arab, A. Alfi, An adaptive gradient descent-based local search in memetic algorithm for solving engineering optimization problems. Inf. Sci. 299, 117–142 (2015)
Z.X. Cao, Y. Yang, J.Y. Lu, F.R. Gao, Constrained two dimensional recursive least squares model identification for batch processes. J. Process Control 24(6), 871–879 (2014)
X. Cao, D.Q. Zhu, S.X. Yang, Multi-AUV target search based on bioinspired neurodynamics model in 3-D underwater environments. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2016). doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2482501
H.B. Chen, Y.S. Xiao, Hierarchical gradient parameter estimation algorithm for Hammerstein nonlinear systems using the key term separation principle. Appl. Math. Comput. 247, 1202–1210 (2014)
Z.Z. Chu, D.Q. Zhu, S.X. Yang, Observer-based adaptive neural network trajectory tracking control for remotely operated Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2016). doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2544786
H. Dai, N.K. Sinha, Robust recursive least-squares method with modified weights for bilinear system identification. IEE Proc. Part D 136(3), 122–126 (1989)
A. Darabi, A. Alfi, B. Kiumarsi, H. Modares, Employing adaptive PSO algorithm for parameter estimation of an exciter machine. J. Dyn. Syst-T ASME 134(1). doi:10.1115/1.4005371, (2012)
F. Ding, System Identification—New Theory and Methods (Science Press, Beijing, 2013)
F. Ding, K.P. Deng, X.M. Liu, Decomposition based Newton iterative identification method for a Hammerstein nonlinear FIR system with ARMA noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(9), 2881–2893 (2014)
F. Ding, X.M. Liu, Y. Gu, An auxiliary model based least squares algorithm for a dual-rate state space system with time-delay using the data filtering. J. Franklin Inst. 353(2), 398–408 (2016)
F. Ding, X.M. Liu, M.M. Liu, The recursive least squares identification algorithm for a class of Wiener nonlinear systems. J. Franklin Inst. 353(7), 1518–1526 (2016)
F. Ding, X.M. Liu, X.Y. Ma, Kalman state filtering based least squares iterative parameter estimation for observer canonical state space systems using decomposition. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 301, 135–143 (2016)
F. Ding, X.H. Wang, Q.J. Chen, Y.S. Xiao, Recursive least squares parameter estimation for a class of output nonlinear systems based on the model decomposition. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35, (2016). doi:10.1007/s00034-015-0190-6
F. Fnaiech, L. Ljung, Recursive identification of bilinear systems. Int. J. Control 45(2), 453–470 (1987)
S. Gibson, A. Wills, B. Ninness, Maximum-likelihood parameter estimation of bilinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 50(10), 1581–1596 (2005)
Y.B. Hu, Iterative and recursive least squares estimation algorithms for moving average systems. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 34, 12–19 (2013)
Y.B. Hu, B.L. Liu, Q. Zhou, A multi-innovation generalized extended stochastic gradient algorithm for output nonlinear autoregressive moving average systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 247, 218–224 (2014)
Y. Ji, X.M. Liu, New criteria for the robust impulsive synchronization of uncertain chaotic delayed nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(1), 1–9 (2015)
Y. Ji, X.M. Liu, Unified synchronization criteria for hybrid switching-impulsive dynamical networks. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 34(5), 1499–1517 (2015)
S.X. Jing, T.H. Pan, Z.M. Li, Recursive bayesian algorithm with covariance resetting for identification of Box–Jenkins systems with non-uniformly sampled input data. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 16, 1–14 (2015)
V.R. Karanam, P.A. Frick, R.R. Mohler, Bilinear system identification by Walsh functions. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 23, 709–713 (1978)
G.Q. Li, C.Y. Wen, A.M. Zhang, Fixed point iteration in identifying bilinear models. Syst. Control Lett. 83, 28–37 (2015)
P. Lopes dos Santos, J.A. Ramos, J.L. Martins de Carvalho, Identification of a Benchmark Wiener–Hammerstein: a bilinear and Hammerstein–Bilinear model approach. Control Eng. Pract. 20, 1156–1164 (2012)
H. Modares, A. Alfi, M.N. Sistani, Parameter estimation of bilinear systems based on an adaptive particle swarm optimization. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 23, 1105–1111 (2010)
Y. Mousavi, A. Alfi, A memetic algorithm applied to trajectory control by tuning of fractional order proportional–integral–derivative controllers. Appl. Soft. Comput. 36, 599–617 (2015)
B.Q. Mu, J. Guo, L.Y. Wang, G. Yin, L.J. Xu, W.X. Zheng, Identification of linear continuous-time systems under irregular and random output sampling. Automatica 60, 100–114 (2015)
J. Na, X.M. Ren, Y.Q. Xia, Adaptive parameter identification of linear SISO systems with unknown time-delay. Syst. Control Lett. 66, 43–50 (2014)
D.Q. Wang, Hierarchical parameter estimation for a class of MIMO Hammerstein systems based on the reframed models. Appl. Math. Lett. 57, 13–19 (2016)
D.Q. Wang, Least squares-based recursive and iterative estimation for output error moving average systems using data filtering. IET Control Theory Appl. 5(14), 1648–1657 (2011)
D.W. Wang, F. Ding, Parameter estimation algorithms for multivariable Hammerstein CARMA systems. Inf. Sci. 355, 237–248 (2016)
Y.J. Wang, F. Ding, Novel data filtering based parameter identification for multiple-input multiple-output systems using the auxiliary model. Automatica (2016). doi:10.1016/j.automatica.2016.05.024
Y.J. Wang, F. Ding, The filtering based iterative identification for multivariable systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 10(8), 894–902 (2016)
Y.J. Wang, F. Ding, The auxiliary model based hierarchical gradient algorithms and convergence analysis using the filtering technique. Signal Process. 128, 212–221 (2016)
Y.J. Wang, F. Ding, Recursive least squares algorithm and gradient algorithm for Hammerstein–Wiener systems using the data filtering. Nonlinear Dyn. 84(2), 1045–1053 (2016)
X.H. Wang, F. Ding, Modelling and multi-innovation parameter identification for Hammerstein nonlinear state space systems using the filtering technique. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst. 22(2), 113–140 (2016)
X.H. Wang, F. Ding, Recursive parameter and state estimation for an input nonlinear state space system using the hierarchical identification principle. Signal Process. 117, 208–218 (2015)
C. Wang, T. Tang, Recursive least squares estimation algorithm applied to a class of linear-in-parameters output error moving average systems. Appl. Math. Lett. 29, 36–41 (2014)
D.Q. Wang, W. Zhang, Improved least squares identification algorithm for multivariable Hammerstein systems. J. Franklin Inst. Eng. Appl. Math. 352(11), 5292–5370 (2015)
W.G. Zhang, Decomposition based least squares iterative estimation for output error moving average systems. Eng. Comput. 31(4), 709–725 (2014)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61273194). The author is grateful to her Master Supervisor Professor Feng Ding and the main idea of this paper comes from him and his books “System Identification—New Theory and Methods, Science Press, Beijing, 2013,” “System Identification—Performances Analysis for Identification Methods, Science Press, Beijing, 2014” and “System Identification—Multi-Innovation Identification Theory and Methods, Science Press, Beijing, 2016.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, D. Recursive Least Squares and Multi-innovation Gradient Estimation Algorithms for Bilinear Stochastic Systems. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 1052–1065 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0337-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0337-0