Abstract
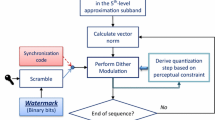
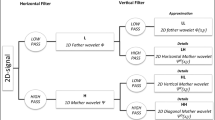
This paper reports two schemes aimed at enhancing the performance of an algorithm based on rational dither modulation (RDM) for the blind watermarking of audio signals. The enhanced algorithm operates in a 4th-level approximation subband, which is obtained through discrete wavelet transform (DWT) decomposition. The first scheme involves the application of a two-tap FIR lowpass filter to mask the noise induced by watermarking, while the second scheme is meant to compensate for distortion introduced by vector modulation. These two schemes make it possible for the DWT-RDM algorithm to formulate audio watermarking with a payload capacity of 689 bits per second. The embedding process is organized as parametric vector operations, which allow the implantation of binary bits into DWT coefficient vectors using two variables, respectively, corresponding to lowpass filtering and distortion compensation. Experiments aimed at evaluating the quality of the resulting audio files indicated an improvement in average ODG score from \(-0.33\) to \(-0.26\). Furthermore, we observed a noticeable reduction in the bit error rates when conducting robustness tests against attacks, such as brumm addition, zero crossing, noise corruption, echo addition, MPEG-1 layer 3 compression, and time shifting.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Bassia, I. Pitas, N. Nikolaidis, Robust audio watermarking in the time domain. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 3(2), 232–241 (2001)
W. Bender, D. Gruhl, N. Morimoto, A. Lu, Techniques for data hiding. IBM Syst. J. 35(3.4), 313–336 (1996)
V. Bhat K, I. Sengupta, A. Das, An adaptive audio watermarking based on the singular value decomposition in the wavelet domain. Digit. Signal Proc. 20(6), 1547–1558 (2010)
V. Bhat K, I. Sengupta, A. Das, A new audio watermarking scheme based on singular value decomposition and quantization. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 30(5), 915–927 (2011)
B. Chen, G.W. Wornell, Quantization index modulation: a class of provably good methods for digital watermarking and information embedding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 47(4), 1423–1443 (2001)
S.-T. Chen, H.-N. Huang, C.-J. Chen, K.-K. Tseng, S.-Y. Tu, Adaptive audio watermarking via the optimization point of view on the wavelet-based entropy. Digit. Signal Proc. 23(3), 971–980 (2013)
N. Cvejic, T. Seppänen, Digital Audio Watermarking Techniques and Technologies: Applications and Benchmarks (Information Science Reference, Hershey, 2008)
I. Daubechies, Ten Lectures on Wavelets (Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, PA, 1992)
P.K. Dhar, T. Shimamura, Blind SVD-based audio watermarking using entropy and log-polar transformation. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 20, 74–83 (2015)
J.J. Garcia-Hernandez, M. Nakano-Miyatake, H. Perez-Meana, Data hiding in audio signal using Rational Dither Modulation. IEICE Electron. Express 5(7), 217–222 (2008)
M. Hasler, Y.L. Maistrenko, An introduction to the synchronization of chaotic systems: coupled skew tent maps. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 44(10), 856–866 (1997)
X. He, Watermarking in Audio: Key Techniques and Technologies (Cambria Press, Youngstown, 2008)
H.-T. Hu, W.-H. Chen, A dual cepstrum-based watermarking scheme with self-synchronization. Sig. Process. 92(4), 1109–1116 (2012)
H.-T. Hu, L.-Y. Hsu, Robust, transparent and high-capacity audio watermarking in DCT domain. Sig. Process. 109, 226–235 (2015)
H.-T. Hu, L.-Y. Hsu, A DWT-based rational dither modulation scheme for effective blind audio watermarking. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(2), 553–572 (2016)
H.-T. Hu, L.-Y. Hsu, H.-H. Chou, Variable-dimensional vector modulation for perceptual-based DWT blind audio watermarking with adjustable payload capacity. Digit. Signal Proc. 31, 115–123 (2014)
ITU Radiocommunication Sector Recommendation, BS.1387, Method for objective Measurements of Perceived Audio Quality (ITU-R, 1998)
P. Kabal, An Examination and Interpretation of ITU-R BS.1387: Perceptual Evaluation of Audio Quality. TSP Lab Technical Report, Department Electrical and Computer Engineering, McGill University, Montreal (2002)
N.K. Kalantari, S.M. Ahadi, A logarithmic quantization index modulation for perceptually better data hiding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(6), 1504–1517 (2010)
S. Katzenbeisser, F.A.P. Petitcolas, in Information Hiding Techniques for Steganography and Digital Watermarking/Stefan Katzenbeisser, ed. by F.A.P. Petitcolas (Artech House, Boston, 2000)
C. Kiho, Y. Hwan Sik, K. Nam Soo, Robust data hiding for MCLT based acoustic data transmission. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(7), 679–682 (2010)
B. Lei, I.Y. Soon, F. Zhou, Z. Li, H. Lei, A robust audio watermarking scheme based on lifting wavelet transform and singular value decomposition. Signal Process. 92(9), 1985–2001 (2012)
B.Y. Lei, I.Y. Soon, Z. Li, Blind and robust audio watermarking scheme based on SVD–DCT. Signal Process. 91(8), 1973–1984 (2011)
W. Li, X. Xue, P. Lu, Localized audio watermarking technique robust against time-scale modification. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 8(1), 60–69 (2006)
X. Li, H.H. Yu, in IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, New York, NY, USA. Transparent and robust audio data hiding in cepstrum domain (2000), pp. 397–400
W.-N. Lie, L.-C. Chang, Robust and high-quality time-domain audio watermarking based on low-frequency amplitude modification. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 8(1), 46–59 (2006)
S.C. Liu, S.D. Lin, BCH code-based robust audio watermarking in cepstrum domain. J. Inf. Sci. Eng. 22(3), 535–543 (2006)
D. Megías, J. Serra-Ruiz, M. Fallahpour, Efficient self-synchronised blind audio watermarking system based on time domain and FFT amplitude modification. Sig. Process. 90(12), 3078–3092 (2010)
P. Moulin, R. Koetter, Data-hiding codes. Proc. IEEE 93(12), 2083–2126 (2005)
H. Peng, B. Li, X. Luo, J. Wang, Z. Zhang, A learning-based audio watermarking scheme using kernel Fisher discriminant analysis. Digit. Signal Proc. 23(1), 382–389 (2013)
R. Tachibana, S. Shimizu, S. Kobayashi, T. Nakamura, An audio watermarking method using a two-dimensional pseudo-random array. Sig. Process. 82(10), 1455–1469 (2002)
S.V. Vaseghi, Multimedia Signal Processing: Theory and Applications in Speech, Music and Communications (Wiley, Chichester, 2007)
V.S. Verma, R.K. Jha, A. Ojha, Digital watermark extraction using support vector machine with principal component analysis based feature reduction. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 31, 75–85 (2015)
V.S. Verma, R.K. Jha, A. Ojha, Significant region based robust watermarking scheme in lifting wavelet transform domain. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(21), 8184–8197 (2015)
X.-Y. Wang, P.-P. Niu, H.-Y. Yang, A robust digital audio watermarking based on statistics characteristics. Pattern Recogn. 42(11), 3057–3064 (2009)
X.-Y. Wang, H. Zhao, A novel synchronization invariant audio watermarking scheme based on DWT and DCT. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(12), 4835–4840 (2006)
X. Wang, P. Wang, P. Zhang, S. Xu, H. Yang, A norm-space, adaptive, and blind audio watermarking algorithm by discrete wavelet transform. Signal Process. 93(4), 913–922 (2013)
X. Wang, P. Wang, P. Zhang, S. Xu, H. Yang, A blind audio watermarking algorithm by logarithmic quantization index modulation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 71(3), 1157–1177 (2014)
X.Y. Wang, Q.L. Shi, S.M. Wang, H.Y. Yang, A blind robust digital watermarking using invariant exponent moments. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 70(4), 416–426 (2016)
S. Wu, J. Huang, D. Huang, Y.Q. Shi, Efficiently self-synchronized audio watermarking for assured audio data transmission. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 51(1), 69–76 (2005)
S. Xiang, Audio watermarking robust against D/A and A/D conversions. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2011(1), 1–14 (2011)
I.-K. Yeo, H.J. Kim, Modified patchwork algorithm: a novel audio watermarking scheme. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 11(4), 381–386 (2003)
E. Zwicker, E. Terhardt, Analytical expressions for critical-band rate and critical bandwidth as a function of frequency. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 68(5), 1523–1525 (1980)
Acknowledgments
This research work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, ROC under Grant MOST 104-2221-E-197-023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, HT., Hsu, LY. Supplementary Schemes to Enhance the Performance of DWT-RDM-Based Blind Audio Watermarking. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 1890–1911 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0383-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0383-7