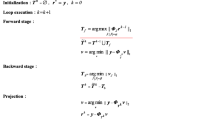Abstract
In recent years, compressed sensing has received considerable attention from the signal processing community because of its ability to represent sparse signals with a number of samples much less than that is required by the Nyquist sampling theorem. \(\ell _{1}\)-minimization is a powerful tool for sparse signal reconstruction from few measured samples, but its computational complexity is a burden for real applications. Recently, a number of greedy algorithms based on orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) have been proposed, and they have near \(\ell _{1}\)-minimization performance with much less processing time. In this work, a new OMP-type two-stage sparse signal reconstruction algorithm, namely data-driven forward–backward pursuit (DD-FBP), is proposed. It is based on a former work called forward–backward pursuit (FBP). DD-FBP iteratively expands and shrinks the estimated support set, and these constitute the forward and backward stages. In DD-FBP, unlike FBP, the forward and backward step sizes are not constants, but they are dependent on the correlation and projection values, respectively, which are calculated in each iteration. The recovery performance by using noiseless and noisy sparse signal ensembles, as well as a natural sparse image, indicates that DD-FBP surpasses the other methods in terms of success rate and processing time.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Antoniadis, J. Bigot, T. Saapatinas, Wavelet estimators in non-parametric regression: a comparative simulation study. J. Stat. Softw. 6, 1–83 (2001)
A. Beck, M. Teboulle, A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J Imag. Sci. 2, 183–202 (2009)
J.D. Blanchard, M. Cermak, D. Hanle, Y. Jing, Greedy algorithms for joint sparse recovery. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62, 1694–1704 (2014)
T. Blumensath, M.E. Davies, Stagewise weak gradient pursuits. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57, 4333–4346 (2009)
J.K. Bradley, A. Kyrola, D. Bickson, C. Guestrin, Parallel coordinate descent for \(\ell 1\)-regularized loss minimization, in Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML (2011)
E. Candes, J. Romberg, \(\ell _{1}\)-MAGIC: Recovery of sparse signals via convex programming. Technical report, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, 2005
E. Candes, J. Romberg, T. Tao, Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 52, 489–509 (2006)
S.S. Chen, D.L. Donoho, M.A. Saunders, Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 20, 33–61 (1998)
W. Dai, O. Milenkovic, Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing signal reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 55, 2230–2249 (2009)
J.F. Determe, J. Louveaux, L. Jacques, F. Horlin, On the exact recovery condition of simultaneous orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23, 164–168 (2016)
D.L. Donoho, Compressive sensing. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 52, 1289–1306 (2006)
D.L. Donoho, Y. Tsaig, I. Drori, J.L. Starck, Sparse solution of underdetermined systems of linear equations by stagewise orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 58, 1094–1121 (2012)
M.A.T. Figueiredo, R.D. Nowak, S.J. Wright, Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction: application to compressed sensing and other inverse problems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 1, 586–597 (2007)
J. Friedman, T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J. Statist. Softw. 33, 1 (2010)
E.T. Hale, W. Yin, Y. Zhang, A fixed-point continuation method for \(\ell _{1}\)-minimization: methodology and convergence. SIAM J. Optim. 19, 1107–1130 (2008)
N.B. Karahanoglu, H. Erdogan, Compressed sensing signal recovery via forward–backward pursuit. Digit. Signal Proc. 23, 1539–1548 (2013)
J. Kim, H. Park, Fast active-set-type algorithms for l1-regularized linear regression, in Proceedings of the 13 \(^{th}\) International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, AISTAD (2010)
S.J. Kim, K. Koh, M. Lustig, S. Boyd, D. Gorinevsky, An interior-point method for large-scale \(\ell _{1}\)-regularized least squares. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 1, 606–617 (2007)
E. Liu, V.N. Temlyakov, The orthogonal super greedy algorithm and applications in compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 58, 2040–2047 (2012)
A. Maleki, D.L. Donoho, Optimally tuned iterative reconstruction algorithms for compressed sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 4, 330–341 (2010)
B.K. Natarajan, Sparse approximate solutions to linear systems. SIAM J. Comput. 24, 227–234 (1995)
D. Needell, J.A. Tropp, CoSaMP: iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 26, 301–321 (2008)
D. Needell, R. Vershynin, Signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements via regularized orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 4, 310–316 (2010)
M.R. Osborne, B. Presnell, B. Turlach, A new approach to variable selection in least squares problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 20, 389–403 (2000)
G. Papageorgiou, P. Bouboulis, S. Theodoridis, Robust linear regression analysis—a greedy approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63, 3872–3887 (2015)
Y.C. Pati, R. Rezaiifar, P.S. Krishnaprasad, Orthogonal matching pursuit: Recursive function approximation with applications to wavelet decomposition, in Proceedings of 27th Asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers, (1993)
S. Shalev-Shwartz, N. Srebro, T. Zhang, Trading accuracy for sparsity in optimization problems with sparsity constraint. SIAM J. Optim. 20, 2807–2832 (2010)
R. Tibshirani, Regression shrinkage and selection via the LASSO. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 58, 267–288 (1996)
J.A. Tropp, A.C. Gilbert, Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 53, 4655–4666 (2007)
J.A. Tropp, S.J. Wright, Computational methods for sparse solution of linear inverse problems. Proc. IEEE 98, 948–958 (2010)
J. Wang, B. Shim, On recovery limit of orthogonal matching pursuit using restricted isometry property. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60, 4973–4976 (2012)
J. Wang, S. Kwon, B. Shim, Generalized orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60, 6202–6216 (2012)
J. Wang, S. Kwon, P. Li, B. Shim, Recovery of sparse signals via generalized orthogonal matching pursuit: a new analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64, 1076–1089 (2016)
Z.J. Xiang, H. Xu, P.J. Ramadge, Learning sparse representations of high dimensional data on large scale dictionaries, in Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS (2012)
L. Xiao, T. Zhang, A proximal-gradient homotopy method for the sparse least-squares problem. SIAM J. Optim. 23, 1062–1091 (2013)
M. Yaghoobi, D. Wu, M.E. Davies, Fast non-negative orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22, 1229–1233 (2015)
S. Yun, K.C. Toh, A coordinate gradient descent method for \(\ell _{1}\)-regularized convex minimization. Comput. Optim. Appl. 48, 273–307 (2011)
W.J. Zeng, H.C. So, X. Jiang, Outlier-robust greedy pursuit algorithms in \(\ell _{p}\)-space for sparse approximation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64, 60–75 (2016)
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the reviewers and the editor for their invaluable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kara, F. Data-Driven Forward–Backward Pursuit for Sparse Signal Reconstruction. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 2402–2419 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0416-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0416-2