Abstract
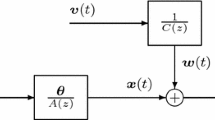
This paper studies the parameter estimation algorithms of multivariate equation-error autoregressive systems. By using the decomposition technique, the multivariate equation-error autoregressive system is decomposed into two subsystems, and a decomposition-based generalized stochastic gradient algorithm is deduced for estimating the parameters of these two subsystems. In order to further improve the parameter accuracy, a decomposition-based multi-innovation generalized stochastic gradient algorithm is developed by means of the multi-innovation theory. The simulation results confirm that these two algorithms are effective.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Atitallah, S. Bedoui, K. Abderrahim, Multistage for identification of Wiener time delay systems based on hierarchical gradient approach. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst. 23(2), 222–239 (2017)
X. Cao, D.Q. Zhu, Multi-AUV task assignment and path planning with ocean current based on biological inspired self-organizing map and velocity synthesis algorithm. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 23(1), 31–39 (2017)
X. Cao, D.Q. Zhu, S.X. Yang, Multi-AUV target search based on bioinspired neurodynamics model in 3-D underwater environments. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(11), 2364–2374 (2016)
J. Chen, B. Jiang, Modified stochastic gradient parameter estimation algorithms for a nonlinear two-variable difference system. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 14(6), 1493–1500 (2016)
Z.Z. Chu, D.Q. Zhu, S.X. Yang, Adaptive sliding mode control for depth trajectory tracking of remotely operated vehicle with thruster nonlinearity. J. Navig. 70(1), 149–164 (2017)
Z.Z. Chu, D.Q. Zhu, S.X. Yang, Observer-based adaptive neural network trajectory tracking control for remotely operated vehicle. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(7), 1633–1645 (2017)
F. Ding, X.H. Wang, L. Mao, L. Xu, Joint state and multi-innovation parameter estimation for time-delay linear systems and its convergence based on the Kalman filtering. Digital Signal Process. 62, 211–223 (2017)
F. Ding, F.F. Wang, L. Xu, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, Parameter estimation for pseudo-linear systems using the auxiliary model and the decomposition technique. IET Control Theory Appl. 11(3), 390–400 (2017)
F. Ding, F.F. Wang, L. Xu, M.H. Wu, Decomposition based least squares iterative identification algorithm for multivariate pseudo-linear ARMA systems using the data filtering. J. Franklin Inst. 354(3), 1321–1339 (2017)
F. Ding, L. Xu, Q.M. Zhu, Performance analysis of the generalised projection identification for time-varying systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 10(18), 2506–2514 (2016)
L. Feng, M.H. Wu, Q.X. Li et al., Array factor forming for image reconstruction of one-dimensional nonuniform aperture synthesis radiometers. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 13(2), 237–241 (2016)
G.C. Goodwin, K.S. Sin, Adaptive Filtering, Prediction and Control (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1984)
Y. Ji, X.M. Liu, Unified synchronization criteria for hybrid switching-impulsive dynamical networks. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 34(5), 1499–1517 (2015)
K. Katahira, How hierarchical models improve point estimates of model parameters at the individual level. J. Math. Psychol. 73, 37–58 (2016)
M.H. Li, X.M. Liu, F. Ding, The gradient based iterative estimation algorithms for bilinear systems with autoregressive noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. (2017). doi:10.1007/s00034-017-0527-4
M.H. Li, X.M. Liu, F. Ding, Least-squares-based iterative and gradient-based iterative estimation algorithms for bilinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(1), 197–211 (2017)
M.H. Li, X.M. Liu, F. Ding, The maximum likelihood least squares based iterative estimation algorithm for bilinear systems with autoregressive noise. J. Franklin Inst. 354(12), 4861–4881 (2017)
H. Li, Y. Shi, W. Yan, On neighbor information utilization in distributed receding horizon control for consensus-seeking. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 46(9), 2019–2027 (2016)
H. Li, Y. Shi, W. Yan, Distributed receding horizon control of constrained nonlinear vehicle formations with guaranteed \(\gamma \)-gain stability. Automatica 68, 148–154 (2016)
H. Li, W.S. Yan, Y. Shi, Continuous-time model predictive control of under-actuated spacecraft with bounded control torques. Automatica 75, 144–153 (2016)
J.H. Li, W.X. Zheng, J.P. Gu, L. Hua, Parameter estimation algorithms for Hammerstein output error systems using Levenberg–Marquardt optimization method with varying interval measurements. J. Franklin Inst. 354(1), 316–331 (2017)
R.R. Liu, E.X. Zheng, S. Chang, S.Y. Bei, L.C. Zhang, Hierarchical stochastic gradient identification for non-uniformly sampling Hammerstein systems with colored noise. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 31(6), 425–430 (2016)
P. Ma, F. Ding, New gradient based identification methods for multivariate pseudo-linear systems using the multi-innovation and the data filtering. J. Franklin Inst. 354(3), 1568–1583 (2017)
P. Ma, F. Ding, A. Alsaedi, T. Hayat, Recursive least squares identification methods for multivariate pseudo-linear systems using the data filtering. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. (2017). doi:10.1007/s11045-017-0491-y
H. Mahnaz, Adaptive neural dynamic surface control of MIMO nonlinear time delay systems with time-varying actuator failures. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 31(2), 275–296 (2017)
Y.W. Mao, F. Ding, Multi-innovation stochastic gradient identification for Hammerstein controlled autoregressive autoregressive systems based on the filtering technique. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(3), 1745–1755 (2015)
D.D. Meng, Recursive least squares and multi-innovation gradient estimation algorithms for bilinear stochastic systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(3), 1052–1065 (2017)
J. Na, G. Herrmann, K.Q. Zhang, Improving transient performance of adaptive control via a modified reference model and novel adaptation. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 27(8), 1351–1372 (2017)
J. Na, J. Yang, X. Wu, Y. Guo, Robust adaptive parameter estimation of sinusoidal signals. Automatica 53, 376–384 (2015)
J. Na, J. Yang, X.M. Ren, Y. Guo, Robust adaptive estimation of nonlinear system with time-varying parameters. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 29(8), 1055–1072 (2015)
J. Na, M.N. Mahyuddin, G. Herrmann, X.M. Ren, P. Barber, Robust adaptive finite-time parameter estimation and control for robotic systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 25(16), 3045–3071 (2015)
J. Pan, X. Jiang, X.K. Wan, W. Ding, A filtering based multi-innovation extended stochastic gradient algorithm for multivariable control systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 15(3), 1189–1197 (2017)
J. Pan, X.H. Yang, H.F. Cai, B.X. Mu, Image noise smoothing using a modified Kalman filter. Neurocomputing 173, 1625–1629 (2016)
X.K. Wan, Y. Li, C. Xia, M.H. Wu, J. Liang, N. Wang, A T-wave alternans assessment method based on least squares curve fitting technique. Measurement 86, 93–100 (2016)
X.H. Wang, F. Ding, Convergence of the recursive identification algorithms for multivariate pseudo-linear regressive systems. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 30(6), 824–842 (2016)
D.Q. Wang, Y.P. Gao, Recursive maximum likelihood identification method for a multivariable controlled autoregressive moving average system. IMA J. Math. Control Inf. 33(4), 1015–1031 (2016)
D.Q. Wang, L. Mao, F. Ding, Recasted models-based hierarchical extended stochastic gradient method for MIMO nonlinear systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 11(4), 476–485 (2017)
D.Q. Wang, Z. Zhang, J.Y. Yuan, Maximum likelihood estimation method for dual-rate Hammerstein systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 15(2), 698–705 (2017)
F.Q. Wen, X.D. Xiong, J. Su, Z.J. Zhang, Angle estimation for bistatic MIMO radar in the presence of spatial colored noise. Signal Process. 134, 261–267 (2017)
F.Q. Wen, X.D. Xiong, Z.J. Zhang, Angle and mutual coupling estimation in bistatic MIMO radar based on PARAFAC decomposition. Digital Signal Process. 65, 1–10 (2017)
W. Wout, D.S. Gert, D. Christof, G. Patrick, Operational modal parameter estimation of MIMO systems using transmissibility functions. Automatica 50(2), 559–564 (2014)
L. Xu, A proportional differential control method for a time-delay system using the Taylor expansion approximation. Appl. Math. Comput. 236, 391–399 (2014)
L. Xu, Application of the Newton iteration algorithm to the parameter estimation for dynamical systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 288, 33–43 (2015)
L. Xu, L. Chen, W.L. Xiong, Parameter estimation and controller design for dynamic systems from the step responses based on the Newton iteration. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(3), 2155–2163 (2015)
L. Xu, The damping iterative parameter identification method for dynamical systems based on the sine signal measurement. Signal Process. 120, 660–667 (2016)
L. Xu, F. Ding, Parameter estimation algorithms for dynamical response signals based on the multi-innovation theory and the hierarchical principle. IET Signal Process. 11(2), 228–237 (2017)
L. Xu, F. Ding, Recursive least squares and multi-innovation stochastic gradient parameter estimation methods for signal modeling. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(4), 1735–1753 (2017)
L. Xu, F. Ding, Y. Gu, A. Alsaedi, T. Hayat, A multi-innovation state and parameter estimation algorithm for a state space system with d-step state-delay. Signal Process. 140, 97–103 (2017)
L.X. Yang, J. Fang, H.B. Li, B. Zeng, An iterative reweighted method for tucker decomposition of incomplete tensors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(18), 4817–4829 (2016)
N. Zhao, M.H. Wu, J.J. Chen, Android-based mobile educational platform for speech signal processing. Int. J. Electr. Eng. Educ. 54(1), 3–16 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61273194) and the 111 Project (B12018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, P., Ding, F., Alsaedi, A. et al. Decomposition-Based Gradient Estimation Algorithms for Multivariate Equation-Error Autoregressive Systems Using the Multi-innovation Theory. Circuits Syst Signal Process 37, 1846–1862 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0644-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0644-0