Abstract
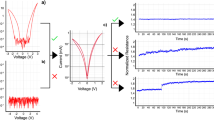
The memristor and the memristive systems have represented a challenge to be incorporated into a simulation procedure in order to carry out novel applications. The discovery of the physical memristor by the HP Labs has caused widespread interest for modeling the memristive behavior in order to combine this new fundamental circuit element with traditional devices. DC domain analysis represents a fundamental stage in the circuit simulators because the DC operating points are used as starting points in other analysis domains. In this work, the DC response of mathematical memristive systems is explored in order to recognize different scenarios according to the nature of the memristive variable. The piecewise linear formulation has been used in order to establish the memristive phenomenon in the device. As a result of this exploration, a novel DC modeling methodology for memristive systems is introduced. This methodology is capable of generating current–voltage branch relationships that represent the memristive behavior of the device. The memristive model proposed is characterized in order to determinate the impact of the variables on the memristive behavior. Moreover, the existence of multiple DC operation points (MOPs) is treated and the conditions for the occurrence of MOPs are established by two cases of study. Finally, the new contributions of this work compared to previous work are presented and discussed.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Adhikari, M. Sah, H. Kim, L. Chua, Three fingerprints of memristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 60(11), 3008–3021 (2013)
R. Burden, J. Faires, Numerical Analysis (Cengage Learning, Boston, 2004)
L. Chua, Memristor—the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18(5), 507–519 (1971)
L. Chua, A.-C. Deng, Canonical piecewise-linear modeling. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 33(5), 511–525 (1986)
L. Chua, S.M. Kang, Memristive devices and systems. Proc. IEEE 64(2), 209–223 (1976)
L. Chua, S.M. Kang, Section-wise piecewise-linear functions: canonical representation, properties, and applications. Proc. IEEE 65(6), 915–929 (1977)
L. Chua, P. Lin, Computer-Aided Analysis of Electronic Circuits: Algorithms and Computational Techniques. Prentice-Hall Series in Electrical and Computer Engineering (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1975)
L. Chua, A. Ushida, A switching-parameter algorithm for finding multiple solutions of nonlinear resistive circuits. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 4(3), 215–239 (1976)
G. Diaz-Arango, A. Sarmiento-Reyes, L. Hernández-Martínez, H. Vázquez-Leal, D. D. Lopez-Hernandez, A. Marín-Hernández, Path optimization for terrestrial robots using homotopy path planning method, in 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) (2015), pp. 2824–2827
A. Emelyanov, V. Demin, I. Antropov, G. Tselikov, Z. Lavrukhina, P. Kashkarov, Effect of the thickness of the \(\text{ tio }_{x}/\text{ tio }_{2}\) layers on their memristor properties. Tech. Phys. 60(1), 112–115 (2015). ISSN 1063-7842
K. Eshraghian, K. Rok Cho, O. Kavehei, S.-K. Kang, D. Abbott, S.-M. S. Kang, Memristor MOS content addressable memory (MCAM): hybrid architecture for future high performance search engines. ArXiv e-prints (2010)
E. Gale, B. de Lacy Costello, V. Erokhin, A. Adamatzky, The short-term memory (d.c. response) of the memristor demonstrates the causes of the memristor frequency effect. ArXiv e-prints (2014)
S.H. Jo, T. Chang, I. Ebong, B.B. Bhadviya, P. Mazumder, W. Lu, Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett 10(4), 1297–1301 (2010)
G. Liu, L. Fang, N. Li, B. cai Sui, Z. K. Duan, New behavioral modeling method for crossbar-based memristor, in 2010 Asia Pacific Conference on Postgraduate Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PrimeAsia) (2010), pp. 356–359
G. Martinsen, S. Grimnes, C. Lutken, G. Johnsen, Memristance in human skin. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 224(1), 012071 (2010)
A. Mazady, M. Anwar, Memristor: Part II-DC, transient, and RF analysis. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 61(4), 1062–1070 (2014)
J. Ogrodzki, Circuit Simulation Methods and Algorithms. Electronic Engineering Systems (Taylor & Francis, New York, 1994)
Y.V. Pershin, S. La Fontaine, M. Di Ventra, Memristive model of amoeba learning. Phys. Rev. E 80, 021926 (2009)
A. Radwan, M. Zidan, K. Salama, HP memristor mathematical model for periodic signals and DC, in 2010 53rd IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS) (2010), pp. 861–864
G.S. Rose, J. Rajendran, H. Manem, R. Karri, R.E. Pino, Leveraging memristive systems in the construction of digital logic circuits. Proc. IEEE 100(6), 2033–2049 (2012). ISSN 0018-9219
A. Schwarz, Computer-aided design of microelectronic circuits and systems: general introduction and analog-circuit aspects, in Computer-Aided Design of Microelectronic Circuits and Systems: Fundamentals, Methods, and Tools (Academic Press, Cambridge, 1987)
S. Shin, L. Zheng, G. Weickhardt, S. Cho, S.-M. Kang, Compact circuit model and hardware emulation for floating memristor devices. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 13(2), 42–55 (2013)
D.B. Strukov, G.S. Snider, D.R. Stewart, R.S. Williams, The missing memristor found. Nature 453(7191), 80–83 (2008)
D. Torres-Muñoz, H. Vázquez-Leal, L. Hernández-Martínez, A. Sarmiento-Reyes, Improved spherical continuation algorithm with application to the double-bounded homotopy (dbh). Comput. Appl. Math. 33(1), 147–161 (2014)
D. Torres-Muñoz, L. Hernández-Martínez, H. Vázquez-Leal, Spherical continuation algorithm with spheres of variable radius to trace homotopy curves. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 2(3), 421–433 (2016)
W. Tzong-Mou, Solving the nonlinear equations by the Newton-homotopy continuation method with adjustable auxiliary homotopy function. Appl. Math. Comput. 173(1), 383–388 (2006)
A. Ushida, Y. Yamagami, Y. Nishio, I. Kinouchi, Y. Inoue, An efficient algorithm for finding multiple DC solutions based on the spice-oriented Newton homotopy method. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 21(3), 337–348 (2002)
R. Waser, M. Aono, Nanoionics-based resistive switching memories. Nat. Mater. 6(11), 833–840 (2007)
S. Wolfram, The MATHEMATICA ® Book, Version 4 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1999)
J.J. Yang, M.D. Pickett, X. Li, D.A.A. Ohlberg, R.S. Williams, D.R. Stewart, Memristive switching mechanism for metal/oxide/metal nanodevices. Nature 3(7), 429–433 (2008)
Y. Yilmaz, P. Mazumder, Image processing by a programmable grid comprising quantum dots and memristors. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 12(6), 879–887 (2013). ISSN 1536-125X
L. Zhang, Z. Chen, J. Joshua Yang, B. Wysocki, N. McDonald, Y. Chen, A compact modeling of \(\text{ TiO }_{2}-\text{ TiO }_{2-x}\) memristor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102(15), 153503–153503-4 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández-Mejía, C., Torres-Muñoz, D. & Vázquez-Leal, H. Exploring a Novel Methodology for DC Analysis in Memristive Circuits with Multiple Operating Points. Circuits Syst Signal Process 37, 2227–2249 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0677-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0677-4