Abstract
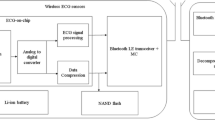
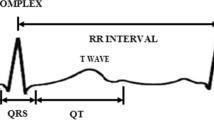
A digital electrocardiogram (ECG) detector with low power consumption and high performance based on biorthogonal 2.2 wavelet transform and applicable for the modern implantable cardiac pacemakers is proposed in the present work. Biorthogonal 2.2 wavelet transform is chosen due to its high SNR, less number of coefficients, resemblance of shape with ECG wave and ability to increase QRS complex detection performance. Architecture of the proposed ECG detector includes modified biorthogonal 2.2 wavelet filter bank and a modified soft threshold-based QRS complex detector. Three low-pass filters and one high-pass filter with pipelined architecture are used which are lesser than the earlier designed detectors. Various blocks of proposed detector are designed to denoise the input ECG signal and then to find the correct location of R-wave. Verilog hardware description language for design entry, Modelsim embedded in Xilinx ISE v.14.1 for simulation, Virtex-6 FPGAs for synthesis and Xilinx ISE tools are used to measure the performance, area and power of the proposed ECG detector and its constituent blocks. A low detection error rate of 0.13%, positive predictivity (\(\hbox {P}^{+}\)) of 99.94% and sensitivity (\(\hbox {S}_{\mathrm{e}}\)) of 99.92% are achieved for the proposed ECG detector which are better compared to the previous results. Also, it consumes only 20 mW of total power at 50 KHz and shows the overall delay of 18.924 ns which makes it useful for the low power and high-performance applications.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
V.X. Afonso, W.J. Tompkins, T.Q. Nguyen, S. Luo, ECG beat detection using filter banks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 46, 192–202 (1999)
Bhavtosh, D. Berwal, Y. Kumar, High performance QRS complex detector for wearable ECG system using multi scaled product with booth multiplier and soft threshold algorithm, IEEE ICSC-15, 204–209 (2015)
G.M. Friesen, T.C. Jannett, M.A. Jadallah, S.L. Yates, S.R. Quint, H.T. Nagle, A comparison of the noise sensitivity of nine QRS detection algorithms. IEEE Trans. Biomedical Engineering 37(1), 85–98 (1990)
R.X. Gao, R. Yan, Wavelets: Theory and Applications for Manufacturing. Springer Science and Business Media publication, ISBN 978 1 4419 1544 3, (2010)
F. Gritzali, G. Frangakis, G. Papakonstantinou, Detection of the P and T waves in an ECG. Comput. Biomed. Res. 22, 83–91 (1989)
P.S. Hamilton, W.J. Tompkins, Quantitative investigation of QRS detection rules using the MIT-BIH arrhythmai database. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 12, 1157–1187 (1986)
Y.H. Hu, W.J. Tompkins, J.L. Urrusti, V.X. Afonso, Applications of artificial neural networks for ECG signal detection and classification. J. Electrocardiol. 26(Suppl.), 66–73 (1993)
S. Kadambe, R. Murray, G.F.B. Bartels, Wavelet transform-based QRS complex detector. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 46, 838–848 (1999)
B.U. Kohler, C. Hennig, R. Orglmeister, The principles of software QRS detection. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 21(1), 42–57 (2002)
B.U. Kohler, C. Hennig, R. Orglmeister, QRS detection using zero crossing counts. Prog. Biomed. Res. 8(3), 138–145 (2003)
C. Li, C. Zheng, C. Tai, Detection of ECG characteristic pointsusing wavelet transforms. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 42, 21–28 (1995)
Y.J. Min, H.K. Kim, Y.R. Kang, G.S. Kim, J. Park, S.W. Kim, Design of wavelet-based ECG detector for implantable cardiac pacemakers. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 7(4), 426–436 (2013)
T. Pan, L. Zhang, S. Zhou, Detection of ECG characteristic points using biorthogonl spline wavelet. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. Inform. 2, 858–863 (2010)
E. Pietka, Feature extraction in computerized approach to the ECG analysis. Pattern Recog. 24, 139–146 (1991)
R. Poli, S. Cagnoni, G. Valli, Genetic design of optimum linear and nonlinear QRS detectors. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 42, 1137–1141 (1995)
J.N. Rodrigues, T. Olsson, L. Sornmo, V. Owall, Digital implementation of a wavelet-based event detector for cardiac pacemakers. IEEE Trans. Syst. I 52(12), 2686–2698 (2005). Reg. Papers
R.S. Sanders, M.T. Lee, Implantable pacemakers. Proc. IEEE 84(3), 480–486 (1996)
M.G. Strintzis, G. Stalidis, X. Magnisalis, N. Maglaveras, Use of neural networks for electrocardiogram (ECG) feature extraction, recognition and classification. Neural Netw. World 3(4), 313–327 (1992)
Y. Sun, S. Suppappola, T.A. Wrublewski, Microcontroller-based real-time QRS detection. Biomed. Instrum. Technol. 26(6), 477–484 (1992)
Y. Sun, K.L. Chan, S.M. Krishan, Characteristic wave detection ECG signal using morphological transform BMC Cardiovasular. Disorders 5(1), 28 (2005)
P.E. Trahanias, An approach to QRS complex detection using mathematical morphology. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 40(2), 201–205 (1993)
G. Vijaya, V. Kumar, H.K. Verma, ANN-based QRS-complex analysis of ECG. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 22(4), 160–167 (1998)
H.W. Wang, Y.L. Lai, M.C. Hou, S.H. Lin, B.S. Yen, Y.C. Huang, L.C. Chou, S.Y. Hsu, S.C. Huang, M.Y. Jan, A \(\pm 6\) ms- accuracy, \(0.68\text{mm}^{2}\) and \(2.21\,{\upmu \text{ W }}\) QRS detection ASIC, in Proc. IEEE Circuits Syst. Symp., Paris, France, pp. 1372-1375 (2010)
L.L. Wang, T.Y. Chen, Q. Fang, S.Y. Lee, Implementation of a wireless ECG acquisition SOC for IEEE 802.15.4 (ZigBee) applications. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Infom. 19(1), 247–255 (2015)
L.S.Y. Wong, S. Hossain, A. Ta, J. Edvinsson, D.H. Rivas, H. Naas, A very low-power CMOS mixed-signal IC for implantable pacemaker applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 39(12), 2446–2456 (2004)
Q. Xue, Y.H. Hu, W.J. Tompkins, Neural-network-based adaptive matched filtering for QRS detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 39, 317–329 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Berwal, D. & Kumar, Y. Design of High-Performance ECG Detector for Implantable Cardiac Pacemaker Systems using Biorthogonal Wavelet Transform. Circuits Syst Signal Process 37, 3995–4014 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0754-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0754-3