Abstract
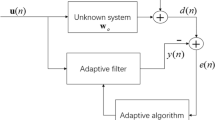
In active noise control (ANC) systems, the primary path may exhibit nonlinear impulse responses. Conventional linear ANC controllers based on a filtered-x least mean square (FxLMS) algorithm exhibit performance degradation when compensating for nonlinear distortions of the primary path. Several nonlinear active noise control algorithms, including Volterra filtered-x least mean square (VFxLMS) and filtered-s least mean square (FsLMS), have been utilized to overcome this nonlinear effect. However, the performance still needs to be improved when the reference noise is mixed with multiple narrowband signals and additional Gaussian white noise. Over the last several years, kernel adaptive filters have exhibited powerful capabilities in multiple signal processing domains. When kernel adaptive filters are introduced into the ANC system, a great challenge is to compensate for the inherent delay caused by the secondary path. Due to the implicit mapping of the kernel method, it is difficult to filter the reference signal in the high-dimensional feature space. In this paper, an approximate method is proposed in which the filtered reference signal is mapped to the high-dimensional feature space. In addition, a kernel filtered-x least mean square (KFxLMS) algorithm is developed for an ANC system with a nonlinear primary path. Simulation experiments demonstrate that the performance of the proposed KFxLMS algorithm is better than that of the FxLMS, VFxLMS, and FsLMS algorithms.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Aronszajn, Theory of reproducing kernels. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 68(3), 337–404 (1950)
M. Aslam, M. Raja, A new adaptive strategy to improve online secondary path modeling in active noise control systems using fractional signal processing approach. Signal Process. 107((C)), 433–443 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.04.012
H. Bao, I. Panahi, Active noise control based on kernel least-mean-square algorithm, in 2009 Conference Record of the Forty-Third Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, pp. 642–644 (2009)
S. Behera, D. Das, B. Subudhi, Adaptive nonlinear active noise control algorithm for active headrest with moving error microphones. Appl. Acoust. 123, 9–19 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2017.03.002
J. Chen, W. Gao, C. Richard, J. Bermudez, Convergence analysis of kernel LMS algorithm with pre-tuned dictionary, in 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 7243–7247 (2014)
I. Constantin, R. Lengelle, Performance analysis of kernel adaptive filters based on LMS algorithm. Procedia Comput. Sci. 20(2), 39–45 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2013.09.236
H. Dai, Y. Huang, J. Wang, L. Yang, Resource optimization in heterogeneous cloud radio access networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 22(3), 494–497 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2787676
D. Das, S. Mohapatra, A. Routray, T. Basu, Filtered-s LMS algorithm for multichannel active control of nonlinear noise processes. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 14(5), 1875–1880 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSA.2005.858543
D. Das, D. Moreau, B. Cazzolato, Nonlinear active noise control for headrest using virtual microphone control. Control Eng. Pract. 21(4), 544–555 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conengprac.2012.11.007
D. Das, G. Panda, Active mitigation of nonlinear noise processes using a novel filtered-s LMS algorithm. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 12(3), 313–322 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSA.2003.822741
W. Gao, J. Chen, C. Richard, J. Huang, Online dictionary learning for kernel LMS analysis and forward-backward splitting algorithm. Statistics 62(11), 2765–2777 (2013)
N. George, G. Panda, A robust filtered-s LMS algorithm for nonlinear active noise control. Appl. Acoust. 73(8), 836–841 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2012.02.005
J. Gil-Cacho, M. Signoretto, T. Waterschoot, M. Moonen, Nonlinear acoustic echo cancellation based on a sliding-window leaky kernel affine projection algorithm. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 21(9), 1867–1878 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2013.2260742
P. Kumar, K. Prabhu, D. Das, Block filtered-s least mean square algorithm for active control of non-linear noise systems. IET Signal Proc. 4(2), 168–180 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-spr.2008.0157
S. Kuo, D. Morgan, Active Noise Control Systems: Algorithms and DSP Implementations, 1st edn. (Wiley, New York, 1995)
S. Kuo, H. Wu, Nonlinear adaptive bilinear filters for active noise control systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 52(3), 617–624 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2004.842429
C. Li, Y. Li, K. Song, L. Yang, Energy efficient design for multiuser downlink energy and uplink information transfer in 5g. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 59(2), 1–8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-015-5510-8
C. Li, K. Song, D. Wang, F. Zheng, L. Yang, Optimal remote radio head selection for cloud radio access networks. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 59(10), 102315 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-016-0060-y
C. Li, X. Wang, L. Yang, W. Zhu, A joint source and relay power allocation scheme for a class of mimo relay systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57(12), 4852–4860 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2009.2027409
T. Li, J. Jiang, Filtered-x second-order Volterra adaptive algorithms. Electron. Lett. 33(8), 671–672 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:19970477
T. Li, J. Jiang, Adaptive Volterra filters for active control of nonlinear noise processes. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 49(8), 1667–1676 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1109/78.934136
S.H.W. Liu, J.C. Principe, Kernel Adaptive Filtering: A Comprehensive Introduction (Wiley, Hoboken, 2010)
W. Liu, P. Pokharel, J. Principe, The kernel least-mean-square algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(2), 543–554 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2007.907881
L. Lu, H. Zhao, Improved filtered-x least mean kurtosis algorithm for active noise control. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(4), 1586–1603 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0379-3
L. Luo, J. Sun, B. Huang, D. Quoc, Efficient combination of feedforward and feedback structures for nonlinear narrowband active noise control. Signal Process. 128, 494–503 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.05.014
Y. Nakajima, M. Yukawa, Nonlinear channel equalization by multi-kernel adaptive filter, in 2012 IEEE 13th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), pp. 384–388 (2012)
W. Parreira, J. Bermudez, C. Richard, J. Tourneret, Stochastic behavior analysis of the gaussian kernel least-mean-square algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(5), 2208–2222 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2012.2186132
V. Patel, V. Gandhi, S. Heda, N. George, Design of adaptive exponential functional link network-based nonlinear filters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 63(9), 1434–1442 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2016.2572091
A. Rahimi, B. Recht, Random features for large-scale kernel machines, in International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1177–1184 (2007)
G. Sicuranza, A. Carini, A generalized FLANN filter for nonlinear active noise control. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(8), 2412–2417 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2011.2136336
W. Tan, M. Matthaiou, S. Jin, X. Li, Spectral efficiency of dft-based processing hybrid architectures in massive mimo. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 6(5), 586–589 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/LWC.2017.2719036
N. Thai, X. Wu, J. Na, Y. Guo, N. Tin, P. Le, Adaptive variable step-size neural controller for nonlinear feedback active noise control systems. Appl. Acoust. 116, 337–347 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.09.022
S. Zhao, B. Chen, P. Zhu, J. Ncipe, Adaptive RSOV filter using the FELMS algorithm for nonlinear active noise control systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 34(1), 378–392 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2012.06.020
H. Zhao, X. Zeng, Z. He, S. Yu, B. Chen, Improved functional link artificial neural network via convex combination for nonlinear active noise control. Appl. Soft Comput. 42((C)), 351–359 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.01.051
H. Zhao, X. Zeng, Z. He, S. Yu, B. Chen, Improved functional link artificial neural network via convex combination for nonlinear active noise control. Appl. Soft Comput. 42((C)), 351–359 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.01.051
S. Zhao, B. Chen, P. Zhu, J. Ncipe, Fixed budget quantized kernel least-mean-square algorithm. Signal Process. 93(9), 2759–2770 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.02.012
D. Zhou, V. DeBrunner, Efficient adaptive nonlinear filters for nonlinear active noise control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 54(3), 669–681 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2006.887636
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Sun, C. & Jiang, S. Kernel Filtered-x LMS Algorithm for Active Noise Control System with Nonlinear Primary Path. Circuits Syst Signal Process 37, 5576–5594 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0832-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0832-6