Abstract
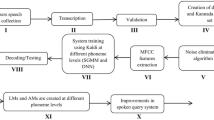
This work explores the significance of source information for speech enhancement resulting in better phoneme recognition of speech with background music segments. Standard procedure for speech enhancement in noisy conditions involves sequential processing in terms of the temporal, spectral and perceptual methods. This work follows the same sequential processing but with the additional modification of studying the effect of source, particularly in the temporal and perceptual-based enhancement techniques for enhancing speech with background music segments. The source information is studied in terms of the epoch locations and epoch strength, obtained after passing the sum of the mean and standard deviation of the component envelopes computed across frequencies obtained using the single frequency filter (SFF), through a zero frequency filter (ZFF). This method of obtaining epoch locations and epoch strength will be termed as SFF-ZFF in this work. The enhanced segments are passed through a phoneme recognizer built using Gaussian mixture model-hidden Markov model (GMM-HMM), subspace Gaussian mixture model-hidden Markov model (SGMM-HMM) and deep neural network-hidden Markov model (DNN-HMM) system, where the models are trained on clean speech. The enhanced audio files show a better phone error rate than the degraded audio files, which means that performing enhancement in terms of the source information is significant for the speech with background music regions.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Aneeja, B. Yegnanarayana, Single frequency filtering approach for discriminating speech and nonspeech. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 23(4), 705–717 (2015)
M. Berouti, R. Schwartz, J. Makhoul, Enhancement of speech corrupted by acoustic noise. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP’79, vol. 4 (IEEE, 1979), pp. 208–211
S. Boll, Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 27(2), 113–120 (1979)
O. Cappé, Elimination of the musical noise phenomenon with the Ephraim and Malah noise suppressor. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2(2), 345–349 (1994)
K.T. Deepak, S.R.M. Prasanna, Foreground speech segmentation and enhancement using glottal closure instants and mel cepstral coefficients. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 24(7), 1204–1218 (2016)
M. Dendrinos, S. Bakamidis, G. Carayannis, Speech enhancement from noise: a regenerative approach. Speech Commun. 10(1), 45–57 (1991)
Y. Ephraim, A Bayesian estimation approach for speech enhancement using hidden Markov models. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 40(4), 725–735 (1992)
Y. Ephraim, D. Malah, Speech enhancement using a minimum-mean square error short-time spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 32(6), 1109–1121 (1984)
Y. Ephraim, D. Malah, Speech enhancement using a minimum mean-square error log-spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 33(2), 443–445 (1985)
Y. Ephraim, H.L. Van Trees, A signal subspace approach for speech enhancement. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 3(4), 251–266 (1995)
G. Fant, Speech Sounds and Features (The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1973)
S.H. Jensen, P.C. Hansen, S.D. Hansen, J.A. Sorensen, Reduction of broad-band noise in speech by truncated QSVD. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 3(6), 439–448 (1995)
S.R. Kadiri, B. Yegnanarayana, Epoch extraction from emotional speech using single frequency filtering approach. Speech Commun. 86, 52–63 (2017)
S. Kamath, P. Loizou, A multi-band spectral subtraction method for enhancing speech corrupted by colored noise. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing, vol. 4. (Citeseer, 2002), pp. 4164–4164
B.K. Khonglah, S.R.M. Prasanna, Speech/music classification using speech-specific features. Digit. Signal Process. 48, 71–83 (2016)
P. Krishnamoorthy, S.R.M. Prasanna, Reverberant speech enhancement by temporal and spectral processing. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 17(2), 253–266 (2009)
P. Krishnamoorthy, S.R.M. Prasanna, Enhancement of noisy speech by temporal and spectral processing. Speech Commun. 53(2), 154–174 (2011)
R. Martin, Speech enhancement based on minimum mean-square error estimation and supergaussian priors. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 13(5), 845–856 (2005)
R. McAulay, M. Malpass, Speech enhancement using a soft-decision noise suppression filter. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 28(2), 137–145 (1980)
K.S.R. Murthy, B. Yegnanarayana, Epoch extraction from speech signals. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 16, 1602–1613 (2008)
D. Povey, A. Ghoshal, G. Boulianne, L. Burget, O. Glembek, N. Goel, M. Hannemann, P. Motlicek, Y. Qian, P. Schwarz, et al., The kaldi speech recognition toolkit. In: IEEE 2011 Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, EPFL-CONF-192584 (IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2011)
D. Povey, X. Zhang, S. Khudanpur, Parallel training of dnns with natural gradient and parameter averaging. arXiv preprint arXiv:1410.7455 (2014)
S. Shahnawazuddin, D. Thotappa, A. Dey, S. Imani, S.R.M. Prasanna, R. Sinha, Improvements in IITG Assamese spoken query system: Background noise suppression and alternate acoustic modeling. J. Signal Process. Syst. 88, 91–102 (2016)
K. Tokuda, T. Kobayashi, T. Masuko, S. Imai, Mel-generalized cepstral analysis—a unified approach to speech spectral estimation. In: ICSLP (1994)
S.V. Vaseghi, Advanced Digital Signal Processing and Noise Reduction (Wiley, New York, 2008)
K. Veselỳ, A. Ghoshal, L. Burget, D. Povey, Sequence-discriminative training of deep neural networks. In: Interspeech (2013), pp. 2345–2349
C.M. Vikram, S.M. Mahadeva Prasanna, Epoch extraction from telephone quality speech using single pole filter. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. (ASLP) 25(3), 624–636 (2017)
D. Wang, J. Lim, The unimportance of phase in speech enhancement. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 30(4), 679–681 (1982)
B. Yegnanarayana, C. Avendano, H. Hermansky, P.S. Murthy, Speech enhancement using linear prediction residual. Speech Commun. 28(1), 25–42 (1999)
Acknowledgements
This work is part of the project titled Multi-modal Broadcast Analytics: Structured Evidence Visualization for Events of Security Concern funded by the e-Security division of the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khonglah, B.K., Dey, A. & Prasanna, S.R.M. Speech Enhancement Using Source Information for Phoneme Recognition of Speech with Background Music. Circuits Syst Signal Process 38, 643–663 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0873-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0873-x