Abstract
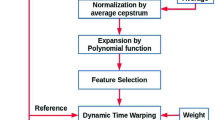
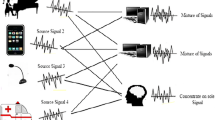
A high-performance speaker verification system from codec-distorted speech is developed and implemented in this paper. Apriori knowledge of the type of the speech codec is utilized in this. Code excited linear prediction-based codec which is one of the most commonly used codecs in mobile communications is assumed here. A novel method is developed by applying the concepts of feature switching and affine transform for the design and implementation of the proposed speaker verification system. In this system, best feature set for each speaker is identified during training phase from affine transformed speech features to make feature selection more robust. Mel frequency cepstral coefficients and modified power normalized cepstral coefficients are identified as features for feature switching. Feature switching is done using direct method in feature level itself and an indirect method in the i-vector framework. During testing phase, best feature set of the claimed speaker is extracted from the codec-distorted speech and affine transform is applied to reflect the feature space during training. Speaker verification is performed using this affine transformed feature set. Classifiers based on Gaussian mixture model-universal background model and i-vector are used for verification. The performance of the proposed system is tested using two databases, namely TIMIT and VoxCeleb1. For both databases with the above two classifiers, we could achieve very low equal error rate when compared with the other competitive methods available in the literature. Hence, the proposed system is a very good candidate for critical applications like forensic speaker verification.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
References
K. Amino, T. Arai, Speaker-dependent characteristics of the nasals. Forensic Sci. Int. 185(1–3), 21–28 (2009)
T. Asha, M. Saranya, D.K. Pandia, S. Madikeri, H.A. Murthy, Feature switching in the i-vector framework for speaker verification, in Fifteenth Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (2014)
M.S. Athulya, P.S. Sathidevi, Speaker verification from codec distorted speech for forensic investigation through serial combination of classifiers. Digit. Investig. 25, 70–77 (2018)
L. Besacier, S. Grassi, A. Dufaux, M. Ansorge, F. Pellandini. GSM speech coding and speaker recognition, in 2000 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37100), vol. 2, pp. II1085–II1088. IEEE (2000)
O. Büyük, L.M. Arslan, Combining log-spectral mean subtraction at different frequency resolutions for handset-channel compensation in single utterance speaker verification. IET Signal Proc. 6(9), 824–828 (2012)
J.K. Chaitanya, R. Janakiraman, H.A. Murthy, Kl divergence based feature switching in the linguistic search space for automatic speech recognition, in 2010 National Conference On Communications (NCC), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2010)
Q. Dan, Y. Honggang, T. Hui, W. Bingxi, Two schemes for automatic speaker recognition over voip, in 2008 IEEE Pacific-Asia Workshop on Computational Intelligence and Industrial Application, vol. 2, pp. 695–699. IEEE (2008)
S. Davis, P. Mermelstein, Comparison of parametric representations for monosyllabic word recognition in continuously spoken sentences. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 28(4), 357–366 (1980)
M. Debyeche, A. Krobba, A. Amrouche, Effect of GSM speech coding on the performance of speaker recognition system, in 10th International Conference on Information Science, Signal Processing and their Applications (ISSPA 2010), pp. 137–140. IEEE (2010)
R. Dunn, T. Quatieri, D. Reynolds, J. Campbell, Speaker recognition from coded speech and the effects of score normalization, in Conference Record of Thirty-Fifth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (Cat. No. 01CH37256), vol. 2, pp. 1562–1567. IEEE (2001)
W. Eric, M.W. Mak, S.Y. Kung, Speaker verification from coded telephone speech using stochastic feature transformation and handset identification, in Pacific-Rim Conference on Multimedia, pp. 598–606. Springer (2002)
W. Fakhr, A. AbdelSalam, N. Hamdy, Enhancement of mismatched conditions in speaker recognition for multimedia applications, in 2004 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, vol. 1, pp. I–377. IEEE (2004)
J.S. Garofolo, Timit acoustic-phonetic continuous speech corpus. https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC93S1/. Accessed 05 July 2018
J.S. Garofolo, Timit acoustic phonetic continuous speech corpus. Linguistic Data Consortium, 1993 (1993)
S. Grassi, L. Besacier, A. Dufaux, M. Ansorge, F. Pellandini, Influence of GSM speech coding on the performance of text-independent speaker recognition, in 2000 10th European Signal Processing Conference, pp. 1–4. IEEE (2000)
B.J. Guillemin, C.I. Watson, Impact of the GSM AMR speech codec on formant information important to forensic speaker identification, in Proceedings of the 11th Australian International Conference on Speech Science & Technology, pp. 483–488 (2006)
P. Henderson, Sammon mapping. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 18(11–13), 1307–1316 (1997)
M.E. Houle, H.P. Kriegel, P. Kröger, E. Schubert, A. Zimek, Can shared-neighbor distances defeat the curse of dimensionality? in International Conference on Scientific and Statistical Database Management, pp. 482–500. Springer (2010)
M. Hunt, M. Lennig, P. Mermelstein, Experiments in syllable-based recognition of continuous speech, in ICASSP’80. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, vol. 5, pp. 880–883. Citeseer (1980)
E.T. Imen, A.A. Imen, M. Debyeche, Framework for VOIP speech database generation and a comparaison of different features extraction methodes for speaker identification on VOIP, in 2015 3rd International Conference on Control, Engineering & Information Technology (CEIT), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2015)
R. Jarina, J. Polackỳ, P. Počta, M. Chmulík, Automatic speaker verification on narrowband and wideband lossy coded clean speech. IET Biometrics 6(4), 276–281 (2017)
T. Jiang, B. Gao, J. Han, Speaker identification and verification from audio coded speech in matched and mismatched conditions, in 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), pp. 2199–2204. IEEE (2009)
C. Kim, R.M. Stern, Power-normalized cepstral coefficients (PNCC) for robust speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. (TASLP) 24(7), 1315–1329 (2016)
Lawrence, R. Fundamentals of Speech Recognition. Pearson Education India (2008)
R. Mammone, X. Zhang: Robust speech processing with affine transform replicated data (2000). US Patent 6,038,528
R.J. Mammone, X. Zhang, R.P. Ramachandran, Robust speaker recognition: a feature-based approach. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 13(5), 58 (1996)
R.W. Mudrowsky, R.P. Ramachandran, S.S. Shetty, The affine transform and feature fusion for robust speaker identification in the presence of speech coding distortion, in 2010 IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems, pp. 1063–1066. IEEE (2010)
A. Nagrani, J.S. Chung, A. Zisserman, The voxceleb1 dataset. http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/data/voxceleb/vox1.html. Accessed 05 July 2020
A. Nagrani, J.S. Chung, A. Zisserman, Voxceleb: a large-scale speaker identification dataset. In: INTERSPEECH (2017)
N. Nandan, G. Saha, On the performance of IP and mobile based automatic speaker verification, in 2012 National Conference on Communications (NCC), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2012)
R. Padmanabhan, R.M. Hegde, H.A. Murthy, Dynamic selection of magnitude and phase based acoustic feature streams for speaker verification, in 2009 17th European Signal Processing Conference, pp. 1244–1248. IEEE (2009)
R. Padmanabhan, H.A. Murthy, Acoustic feature diversity and speaker verification, in Eleventh Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (2010)
M. Petracca, A. Servetti, J. De Martin, Performance analysis of compressed-domain automatic speaker recognition as a function of speech coding technique and bit rate, in 2006 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, pp. 1393–1396. IEEE (2006)
M. Phythian, J. Ingram, S. Sridharan, Effects of speech coding on text-dependent speaker recognition, in TENCON’97 Brisbane-Australia. Proceedings of IEEE TENCON’97. IEEE Region 10 Annual Conference. Speech and Image Technologies for Computing and Telecommunications (Cat. No. 97CH36162), vol. 1, pp. 137–140. IEEE (1997)
J. Polacky, R. Jarina, M. Chmulik, Assessment of automatic speaker verification on lossy transcoded speech, in 2016 4th International Conference on Biometrics and Forensics (IWBF), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2016)
J. Polacky, P. Pocta, R. Jarina, An impact of narrowband speech codec mismatch on a performance of GMM-UBM speaker recognition over telecommunication channel. Commun. Sci. Lett. Univ. Zilina 18(1), 23–28 (2016)
J. Polacky, P. Pocta, R. Jarina, An impact of wideband speech codec mismatch on a performance of GMM-UBM speaker verification over telecommunication channel, in 2016 ELEKTRO, pp. 77–82. IEEE (2016)
T.F. Quatieri, E. Singer, R.B. Dunn, D.A. Reynolds, J.P. Campbell, Speaker and Language Recognition Using Speech Codec Parameters. Tech. rep, Massachusetts Inst of Tech Lexington Lincoln Lab (1999)
D.A. Reynolds, T.F. Quatieri, R.B. Dunn, Speaker verification using adapted gaussian mixture models. Digit. Signal Proc. 10(1–3), 19–41 (2000)
D.A. Reynolds, R.C. Rose, Robust text-independent speaker identification using gaussian mixture speaker models. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 3(1), 72–83 (1995)
M. Saranya, R. Padmanabhan, H.A. Murthy, Feature-switching: Dynamic feature selection for an i-vector based speaker verification system. Speech Commun. 93, 53–62 (2017)
J. Silovsky, P. Cerva, J. Zdansky, Assessment of speaker recognition on lossy codecs used for transmission of speech, in Proceedings ELMAR-2011, pp. 205–208. IEEE (2011)
D. Snyder, D. Garcia-Romero, D. Povey, S. Khudanpur, Deep neural network embeddings for text-independent speaker verification, in Interspeech, pp. 999–1003 (2017)
D. Snyder, D. Garcia-Romero, G. Sell, D. Povey, S. Khudanpur, X-vectors: Robust DNN embeddings for speaker recognition, in 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 5329–5333. IEEE (2018)
D. Snyder, P. Ghahremani, D. Povey, D. Garcia-Romero, Y. Carmiel, S. Khudanpur, Deep neural network-based speaker embeddings for end-to-end speaker verification, in 2016 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), pp. 165–170. IEEE (2016)
A. Stauffer, A.D. Lawson, Speaker Recognition on Lossy Compressed Speech Using the Speex Codec Tech. rep, Research Associates for Defense Conversion (RADC) Marcy NY (2009)
A.K. Vuppala, K.S. Rao, S. Chakrabarti, Effect of speech coding on speaker identification, in 2010 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), pp. 1–4. IEEE (2010)
N. Wang, L. Wang, Robust speaker recognition based on multi-stream features, in 2016 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-China (ICCE-China), pp. 1–4. IEEE (2016)
X. Wang, J. Lin, Applying speaker recognition on VOIP auditing, in 2007 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, vol. 6, pp. 3577–3581. IEEE (2007)
D. Yessad, A. Amrouche, Fusion strategies for distributed speaker recognition using residual signal based g729 resynthesized speech, in Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Information Fusion, pp. 432–437. IEEE (2013)
E.W. Yu, M.W. Mak, C.H. Sit, S.Y. Kung: Speaker verification based on g. 729 and g. 723.1 coder parameters and handset mismatch compensation, in Eighth European Conference on Speech Communication and Technology (2003)
V. Zue, S. Seneff, J. Glass, Speech database development at MIT: timit and beyond. Speech Commun. 9(4), 351–356 (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Athulya, M.S., Sathidevi, P.S. Speaker Verification from Codec-Distorted Speech Through Combination of Affine Transform and Feature Switching. Circuits Syst Signal Process 40, 6016–6034 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01747-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01747-0