Abstract
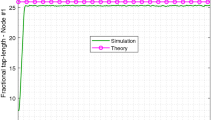
Estimation in a cooperative and distributed manner in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) has considered much attention in recent years. When this distributed estimation is performed adaptively, the concept of adaptive networks will develop. In such networks, proper selection of the unknown parameter length is an issue in itself. A deficient filter length results in an additional steady-state error while selecting a large length will impose a more computational load on the nodes, which is critical in sensor networks due to the lack of energy resources. This motivates the use of variable tap-length adaptive filters in the context of the adaptive networks. This has been achieved in adaptive networks using the distributed fractional tap-length (FT) algorithm. This algorithm requires proper selection of the length adaptation parameters, such as error width and length adaptation step-size. This paper proposes an automatic method for selecting these parameters. In the proposed method, these parameters are adapted based on the estimated gradient vector. The proposed method is fully distributed and presented in a diffusion strategy. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm has both the advantage of fast length convergence and an unbiased steady-state tap-length.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S.E. Abadi, Z. Saffari, Distributed estimation over an adaptive diffusion network based on the family of affine projection algorithms. In: 6th International Symposium on Telecommunications (IST), pp. 607–611 (2012)
R. Abdolee, B. Champagne, Centralized adaptation for parameter estimation over wireless sensor networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 19(9), 1624–1627 (2015)
S.N. Adnani, M.A. Tinati, G. Azarnia, T.Y. Rezaii, Energy-efficient data reconstruction algorithm for spatially- and temporally correlated data in wireless sensor networks. IET Signal Process. 12(8), 1053–1062 (2018)
M.T. Akhtar, S. Ahmed, A robust normalized variable tap-length normalized fractional lms algorithm. In: 2016 IEEE 59th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), pp. 1–4. IEEE (2016)
F. Albu, The constrained stability least mean square algorithm for active noise control. In: 2018 IEEE International Black Sea Conference on Communications and Networking (BlackSeaCom), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2018)
F. Albu, C. Paleologu, S. Ciochina, New variable step size affine projection algorithms. In: 2012 9th International Conference on Communications (COMM), pp. 63–66. IEEE (2012)
S.A. Alghunaim, E. Ryu, K. Yuan, A.H. Sayed, Decentralized proximal gradient algorithms with linear convergence rates. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control pp. 1–1 (2020)
S.A. Alghunaim, K. Yuan, A.H. Sayed, A proximal diffusion strategy for multi-agent optimization with sparse affine constraints. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control pp. 1–1 (2019)
G. Azarnia, M.A. Tinati, Steady-state analysis of the deficient length incremental lms adaptive networks. Circuits, Syst. Signal Process. 34(9), 2893–2910 (2015)
G. Azarnia, M.A. Tinati, Steady-state analysis of the deficient length incremental lms adaptive networks with noisy links. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 69(1), 153–162 (2015)
G. Azarnia, M.A. Tinati, T.Y. Rezaii, Cooperative and distributed algorithm for compressed sensing recovery in wsns. IET Signal Process. 12(3), 346–357 (2018)
G. Azarnia, M.A. Tinati, T.Y. Rezaii, Generic cooperative and distributed algorithm for recovery of signals with the same sparsity profile in wireless sensor networks: a non-convex approach. J. Supercomput. 75(5), 2315–2340 (2019)
G. Azarnia, M.A. Tinati, A.A. Sharifi, H. Shiri, Incremental and diffusion compressive sensing strategies over distributed networks. Digital Signal Processing 101, 102732 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2020.102732. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1051200420300774
X. Cao, K.J.R. Liu, Decentralized sparse multitask rls over networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65(23), 6217–6232 (2017)
F.S. Cattivelli, C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion recursive least-squares for distributed estimation over adaptive networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(5), 1865–1877 (2008)
S. Chen, Y. Liu, Robust distributed parameter estimation of nonlinear systems with missing data over networks. IEEE Trans. Aerospace Electron. Syst. 56(3), 2228–2244 (2020)
M. Ferrer, M. de Diego, G. Piñero, A. Gonzalez, Active noise control over adaptive distributed networks. Signal Proces. 107, 82–95 (2015)
Y. Han, M. Wang, M. Liu, An improved variable tap-length algorithm with adaptive parameters. Digital Signal Process. 74, 111–118 (2018)
A. Kar, T. Padhi, B. Majhi, M.N.S. Swamy, Analysing the impact of system dimension on the performance of a variable-tap-length adaptive algorithm. Appl. Acoustics 150, 207–215 (2019)
C. Li, S. Huang, Y. Liu, Z. Zhang, Distributed jointly sparse multitask learning over networks. IEEE Trans. Cybernet. 48(1), 151–164 (2018)
L. Li, J. Feng, J. He, J.A. Chambers, A distributed variable tap-length algorithm within diffusion adaptive networks. AASRI Procedia 5, 77 – 84 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aasri.2013.10.061. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212671613000620. 2013 AASRI Conference on Parallel and Distributed Computing and Systems
L. Li, Y. Zhang, J.A. Chambers, Variable length adaptive filtering within incremental learning algorithms for distributed networks. In: 2008 42nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, pp. 225–229 (2008)
N. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhao, Y. Hao, An improved variable tap-length LMS algorithm. Signal Process. 89(5), 908–912 (2009)
Z. Li, W. Shi, M. Yan, A decentralized proximal-gradient method with network independent step-sizes and separated convergence rates. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 67(17), 4494–4506 (2019)
Z. Liu, Variable tap-length linear equaliser with variable tap-length adaptation step-size. Electron. Lett. 50(8), 587–589 (2014)
C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion least-mean squares over adaptive networks: Formulation and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(7), 3122–3136 (2008)
K. Mayyas, H.A. AbuSeba, A new variable length nlms adaptive algorithm. Digital Signal Process. 34, 82–91 (2014)
C. Paleologu, J. Benesty, S. Ciochina, A variable step-size affine projection algorithm designed for acoustic echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Audio, Speech, and Language Process. 16(8), 1466–1478 (2008)
S.H. Pauline, D. Samiappan, R. Kumar, A. Anand, A. Kar, Variable tap-length non-parametric variable step-size NLMS adaptive filtering algorithm for acoustic echo cancellation. Appl. Acoustics 159, 107074 (2020)
A. Rastegarnia, Reduced-communication diffusion rls for distributed estimation over multi-agent networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Exp. Briefs 67(1), 177–181 (2020)
F. Riera-Palou, J.M. Noras, D.G.M. Cruickshank, Linear equalisers, with dynamic and automatic length selection. Electron. Lett. 37(25), 1553–1554 (2001)
M.O.B. Saeed, A. Zerguine, An incremental variable step-size LMS algorithm for adaptive networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs pp. 1–1 (2019)
K. Shravan Kumar, N.V. George, Polynomial sparse adaptive estimation in distributed networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs 65(3), 401–405 (2018)
N. Takahashi, I. Yamada, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion least-mean squares with adaptive combiners: Formulation and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Proces. 58(9), 4795–4810 (2010)
Y. Wei, Z. Yan, Variable tap-length lms algorithm with adaptive step size. Circuits, Syst. Signal Process. 36(7), 2815–2827 (2017)
S. Xu, R.C. de Lamare, H.V. Poor, Distributed estimation over sensor networks based on distributed conjugate gradient strategies. IET Signal Process. 10(3), 291–301 (2016)
G. Yu, C.F.N. Cowan, An lms style variable tap-length algorithm for structure adaptation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(7), 2400–2407 (2005)
G. Yuantao, T. Kun, C. Huijuan, Lms algorithm with gradient descent filter length. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11(3), 305–307 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azarnia, G. Diffusion Fractional Tap-length Algorithm with Adaptive Error Width and Step-size . Circuits Syst Signal Process 41, 321–345 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01778-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01778-7