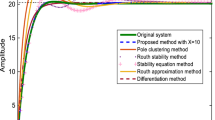
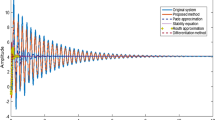
Abstract
A new model diminution technique is proposed for the reduction of complexity of higher order linear dynamical systems. In this proposed method, a generalized pole clustering technique is used for obtaining the denominator polynomial of the lower order plant and the numerator polynomial is evaluated by applying the Padé approximation technique. The generalized pole clustering algorithm promises the preservation of stability and dominant poles of the actual system in the reduced order plant. The performance error indices such as integral square error (ISE), integral absolute error (IAE), integral time weighted absolute error (ITAE) and relative integral square error (RISE) are used to validate the proposed technique. By using the transfer function of the simplified order plant, the PID and lead/lag compensators are designed by using a moment matching algorithm. This controller is applied to the original large scale system and the response of the closed loop system is matching with the response of the desired reference model.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
A.B.H. Adamou-Mitiche, L. Mitiche, Multivariable systems model reduction based on the dominant modes and Genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64(2), 1617–1619 (2017)
H. Aridhi, M.H. Zaki, S. Tahar, Enhancing model Order Reduction for Nonlinear Analog Circuit Simulation. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 24(3), 1–14 (2016)
N. Ashoor, V. Singh, A note on lower order modelling. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 27(5), 1124–1126 (1982)
J.C. Basilio, S.R. Matos, Design of PI and PID controllers with transient performance specification. IEEE Trans. Educ. 45(4), 364–370 (2002)
R. Bhatt, G. Parmar, R. Gupta, A. Sikander, Application of stochastic fractal search in approximation and control of LTI systems. Microsyst. Technol. 25(1), 105–114 (2019)
D. Binion, X. Chen, Coupled electrothermal–mechanical analysis for MEMS via model order reduction. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 46(12), 1068–1076 (2010)
T.C. Chen, C.Y. Chang, K.W. Han, Model reduction using the stability-equation method and the Padé approximation method. J. Franklin Inst. 309(6), 473–490 (1980)
T.C. Chen, C.Y. Chang, K.W. Han, Reduction of transfer functions by the stability-equation method. J. Franklin Inst. 308(4), 389–404 (1979)
T.C. Chen, C.Y. Chang, K.W. Han, Model reduction using the stability-equation method and the continued fraction method. Int. J. Control 32(1), 81–94 (1980)
A. Chu, H. Chiang, Constructing analytical energy functions for lossless network-reduction power system models; framework and new developments. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 18(1), 1–16 (1999)
S.R. Desai, R. Prasad, A new approach to order reduction using stability equation and big bang big crunch optimization. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 1(1), 20–27 (2013)
K.V. Fernando, H. Nicholson, Singular perturbational model reduction of balanced systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 27(2), 466–468 (1982)
A. Ghafoor, M. Imran, Passivity preserving frequency weighted model order reduction technique. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(11), 4388–4400 (2017)
A.N. Gorban, Model reduction in chemical dynamics : slow invariant manifolds, singular perturbations, thermodynamic estimates, and analysis of reaction graph. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 21, 48–59 (2018)
R. Goyal, P. Girish, A. Sikander, A new approach for simplification and control of linear time invariant systems. Microsyst. Technol. 25, 599–607 (2019)
A. Graham, R.C. Lathrop, The synthesis of ‘optimum’ transient response: Criteria and standard forms. Trans. Am. Inst. Electr. Eng. Part II: Appl. Ind. 72(5), 273–288 (1953)
G. Gu, All optimal Hankel-norm approximations and their L∞ error bounds in discrete-time. Int. J. Control 78(6), 408–423 (2005)
Y. Gu, N. Bottrell, T.C. Green, Reduced-order models for representing converters in power system studies. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33(4), 3644–3654 (2017)
P. Gutman, C.F. Mannerfelt, P. Molander, Contributions to the model reduction problem. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 27(2), 454–455 (1982)
C. Hsieh, P.C. Hwang, Model reduction of continuous-time systems using a modified Routh approximation method. IEE Proc. 136(1), 151–156 (1989)
C. Huang, K. Zhang, X. Dai, W. Tang, A modified balanced truncation method and its application to model reduction of power system, in Proceedings on IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, pp. 1–5 (2013)
M. Hutton, B. Friedland, Routh approximations for reducing order of linear, time-invariant systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 20(3), 329–337 (1975)
T.C. Ionescu, A. Astolfi, Nonlinear moment matching-based model order reduction. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 61(10), 2837–2847 (2016)
T. Ishizaki, H. Sandberg, K. Kashima, J. Imura, K. Aihara, Dissipativity-preserving model reduction for large-scale distributed control systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 60(4), 1023–1037 (2015)
J.P. Liu, X.B. Shu, H. Kanazawa, K. Imaoka, A.G. Mikkola, X. Ren, A model order reduction method for the simulation of gear contacts based on Arbitrary Lagrangian Eulerian formulation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 338(1), 68–96 (2018)
M. Jamshidi, Large-Scale Systems: Modeling, Control, and Fuzzy Logic, 1st edn. (Prentice Hall PTR, Upper Saddle River, 1998)
R. Komarasamy, N. Albhonso, G. Gurusamy, Order reduction of linear systems with an improved pole clustering. J. Vib. Control 18(12), 1876–1885 (2011)
D.K. Kranthi, S.K. Nagar, J.P. Tiwari, A new algorithm for model order reduction of interval systems. Bonfring Int. J. Data Min. 3(1), 6–11 (2013)
V. Krishnamurthy, V. Seshadri, Model reduction using the Routh stability criterion. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 23(4), 729–731 (1978)
D. Kumar, S.K. Nagar, Model reduction by extended minimal degree optimal Hankel norm approximation. Appl. Math. Model. 38(11–12), 2922–2933 (2014)
D. Kumar, J.P. Tiwari, S.K. Nagar, Reducing order of large-scale systems by extended balanced singular perturbation approximation. Int. J. Autom. Control 6(1), 21–38 (2012)
V. Kumar, J.P. Tiwari, Order reducing of linear system using clustering method factor division algorithm. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Syst. 3(5), 3–6 (2012)
D. Kun, E.L. Shengbo, L. Sisi, L. Zhaojian, Aggregation-based thermal model reduction, in Automotive Air Conditioning (Springer, Basel, 2016), pp. 29–49
T.N. Lucas, Factor division: a useful algorithm in model reduction. IEE Proc. D Control Theory Appl. 130(6), 362–364 (1983)
B.C. Moore, Principal component analysis in linear systems: controllability, observability, and model reduction. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 26(1), 17–32 (1981)
S. Mukherjee, R.C. Mittal, Model order reduction using response-matching technique. J. Franklin Inst. 342, 503–519 (2005)
A. Narwal, R. Prasad, A novel order reduction approach for LTI systems using cuckoo search optimization and stability equation. IETE J. Res. 62(2), 154–163 (2016)
A. Narwal, R. Prasad, Optimization of LTI systems using modified clustering algorithm. IETE Tech. Rev. 34(2), 201–213 (2017)
A. Narwal, R. Prasad, Order reduction of LTI systems and their qualitative comparison. IETE Tech. Rev. 34(6), 655–663 (2017)
J. Pal, Stable reduced order Padé approximants using Routh Hurwitz array. Electron. Lett. 15(8), 225–226 (1979)
Y. Paquay, O. Brüls, C. Geuzaine, Nonlinear interpolation on manifold of reduced-order models in magnetodynamic problems. IEEE Trans. Magn. 52(3), 18–21 (2016)
G. Parmar, R. Prasad, S. Mukherjee, Order reduction by least-squares methods about general point ‘a.’ Int. J. Electron. Commun. Eng. 1(2), 268–255 (2007)
G. Parmar, S. Mukherjee, R. Prasad, System reduction using eigen spectrum analysis and Padé approximation technique. Int. J. Comput. Math. 84(12), 1871–1880 (2007)
G. Parmar, S. Mukherjee, R. Prasad, System reduction using factor division algorithm and eigen spectrum analysis. Appl. Math. Model. 31(11), 2542–2552 (2007)
W.C. Peterson, A.H. Nassar, On the synthesis of optimum linear feedback control systems. J. Franklin Inst. 306(3), 237–256 (1978)
B. Philip, J. Pal, An evolutionary computation based approach for reduced order modelling of linear systems, in IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research, 2010, Coimbatore, India, pp. 1–8 (2010)
A. Pierquin, T. Henneron, S. Clenet, Data-driven model-order reduction for magnetostatic problem coupled with data-driven model order reduction for magnetostatic problem coupled with circuit equations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 54(3), 1–4 (2018)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, Failure of Padé approximation and time moment matching techniques in reduced order modelling, in Proceedings 3rd IEEE International Conference for Convergence in Technology, Pune, India, pp. 1–4 (2018)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, Model order reduction by using the balanced truncation and factor division methods. IETE J. Res. 65(6), 827–842 (2018)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, Order reduction of linear dynamic systems by improved Routh approximation method. IETE J. Res. 65(5), 702–715 (2018)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, Order reduction of linear dynamic systems with an improved Routh stability method, in Proceedings IEEE International Conference on Control, Power, Communication and Computing Technologies, Kerala, India, pp. 362–367 (2018)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, Reduced order modelling of linear time invariant systems using the factor division method to allow retention of dominant modes. IETE Tech. Rev. 36(5), 449–462 (2018)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, A new model order reduction method for the design of compensator by using moment matching algorithm. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 42(3), 472–484 (2019)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, A new model reduction method for the linear dynamic systems and its application for the design of compensator. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 39(5), 2328–2348 (2019)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, Model reduction of linear systems by using improved Mihailov stability criterion, in Proceedings 11th IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN), Hawaii, USA, pp. 1–6 (2019)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, Order reduction in linear dynamical systems by using improved balanced realization technique. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38(11), 5298–5303 (2019)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, Reduced-order modelling of LTI systems by using Routh approximation and factor division methods. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38(7), 3340–3355 (2019)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, A novel order reduction method for linear dynamic systems and its application for designing of PID and lead / lag compensators. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 43(5), 1226–1238 (2021)
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, Model reduction using the balanced truncation method and the Padé approximation method. IETE Tech. Rev. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/02564602.2020.1842257
A.K. Prajapati, R. Prasad, J. Pal, Contribution of time moments and Markov parameters in reduced order modeling, in Proceedings 3rd IEEE International Conference for Convergence in Technology, Pune, India, pp. 1–7 (2018)
A.K. Prajapati, V.G.D. Rayudu, A. Sikander, R. Prasad, A new technique for the reduced-order modelling of linear dynamic systems and design of controller. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 39(10), 4849–4867 (2020)
R. Prasad, Padé type model order reduction for multivariable systems using Routh approximation. Comput. Electr. Eng. 26(6), 445–459 (2000)
M. Rydel, R. Stanisławski, A new frequency weighted Fourier-based method for model order. Automatica 88, 107–112 (2018)
M.G. Safonov, R.Y. Chiang, A Schur method for balanced-truncation model reduction. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 34(7), 729–733 (1989)
G. Scarciotti, A. Astolfi, Model reduction of neutral linear and nonlinear time-invariant time-delay systems with discrete and distributed delays. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 61(6), 1–14 (2016)
Y. Shamash, Stable reduced-order models using Padé-type approximation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 19(5), 615–616 (1974)
Y. Shamash, Linear system reduction using Padé approximation to allow retention of dominant modes. Int. J. Control 21(2), 257–272 (1975)
Y. Shamash, Model reduction using the Routh stability criterion and the Padé approximation technique. Int. J. Control 21(3), 475–484 (1975)
Y. Shamash, Truncation method of reduction: a viable alternative. Electron. Lett. 17(2), 97–99 (1981)
T. Shimotani, Y. Sato, T. Sato, H. Igarashi, Fast finite-element analysis of motors using block model order reduction. IEEE Trans. Magn. 52(3), 3–6 (2016)
A. Sikander, R. Prasad, Linear time-invariant system reduction using a mixed methods approach. Appl. Math. Model. 39(16), 4848–4858 (2015)
A. Sikander, R. Prasad, A new technique for reduced-order modelling of linear time-invariant system. IETE J. Res. 63(3), 316–324 (2017)
A. Sikander, R. Prasad, New technique for system simplification using Cuckoo search and ESA. Sadhana – Acad. Proc. Eng. Sci. 42(9), 1453–1458 (2017)
J. Singh, C.B. Vishwakarma, K. Chatterjee, Biased reduction method by combining improved modified pole clustering and improved Padé approximations. Appl. Math. Model. 40(2), 1418–1426 (2016)
N. Singh, R. Prasad, H.O. Gupta, Reduction of linear dynamic systems using Routh Hurwitz array and factor division method. IETE J. Educ. 47(1), 25–29 (2006)
A.K. Sinha, J, Pal, Simulation based reduced order modelling using a clustering technique. Comput. Electr. Eng. 16(3), 159–169 (1990)
H.N. Soloklo, M.M. Farsangi, Model order reduction by using Legendre expansion and harmony search algorithm. Majlesi J. Electr. Eng. 9(1), 25–35 (2015)
S.K. Tiwari, G. Kaur, Model reduction by new clustering method and frequency response matching. J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst. 28(1), 78–85 (2017)
S.K. Tiwari, G. Kaur, Improved reduced-order modeling using clustering method with dominant pole retention. IETE J. Res. 66(1), 42–52 (2018)
D. Tong, Q. Chen, Delay and its time-derivative-dependent model reduction for neutral-type control system. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(6), 2542–2557 (2017)
D. Tong, W. Zhou, A. Dai, H. Wang, X. Mou, Y. Xu, H∞ model reduction for the distillation column linear system. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(10), 3287–3297 (2014)
D.R. Towill, Transfer Function Techniques for Control Engineers (First Edit. IliffeBooks Ltd., London, 1970)
M.K. Transtrum, A.T. Sari, A.M. Stankovi, Measurement-directed reduction of dynamic models in power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 32(3), 2243–2253 (2017)
C.B. Vishwakarma, R. Prasad, Clustering method for reducing order of linear system using Padé approximation. IETE J. Res. 54(5), 326–330 (2008)
C.B. Vishwakarma, R. Prasad, Order reduction using modified pole clustering and Padé approximations. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 5(8), 1003–1007 (2011)
C.B. Vishwakarma, R. Prasad, MIMO system reduction using modified pole clustering and Genetic Algorithm. Modell. Simul. Eng. 2009(1), 1–5 (2009)
C.B. Vishwakarma, R. Prasad, Time domain model order reduction using Hankel matrix approach. J. Franklin Inst. 351(6), 3445–3456 (2014)
P. Vorobev, P. Huang, M.A. Hosani, J.L. Kirtley, K. Turitsyn, High-fidelity model order reduction for microgrids stability assessment. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 33(1), 874–887 (2018)
B.W. Wan, Linear model reduction using Mihailov criterion and Padé approximation technique. Int. J. Control 33(6), 1073–1089 (1981)
Q. Wang, Y. Wang, E.Y. Lam, N. Wong, Model order reduction for neutral systems by moment matching. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(3), 1039–1063 (2013)
X. Wang, M. Yu, C. Wang, Structure-preserving-based model-order reduction of parameterized interconnect systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37(1), 19–48 (2018)
W. Zhou, D. Tong, H. Lu, Q. Zhong, J. Fang, Time-delay dependent H∞ model reduction for uncertain stochastic systems : continuous-time case. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 30(5), 941–961 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prajapati, A.K., Prasad, R. A New Generalized Pole Clustering-Based Model Reduction Technique and Its Application for Design of Controllers. Circuits Syst Signal Process 41, 1497–1529 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01860-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01860-0