Abstract
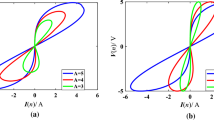
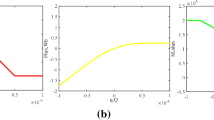
This paper analyzes the fingerprint characteristics of a memristor model and proves that this memristor model conforms to the definition of generalized memristor. Using this memristor model, a new class of memristive circuit is built. A new memristive system is obtained through the mathematical modeling of the memristive circuit. The equilibrium points and stability of the new memristive system are analyzed by mathematical theory, and the complex dynamic behavior of the system under different parameters is analyzed by using simulation tools such as phase diagram, bifurcation diagram, Lyapunov exponent spectrum and time-domain waveform. Through simulation, it is found that this system can have quasi-periodic, periodic, chaotic and hyperchaotic attractors and wing-variable phenomenon under the change of parameters. The sensitivity of hyperchaos and chaos to the change of initial value is studied, and the phenomena of chaotic bursting and periodic bursting are observed. For physical verification, the hardware implementation of digital circuit based on FPGA is given. The experimental results are consistent with the numerical simulation ones, which prove its physical realizability.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
H. Bao, A.H. Hu, W.B. Liu, B.C. Bao, Hidden bursting firings and bifurcation mechanisms in memristive neuron model with threshold electromagnetic induction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(2), 502–511 (2020)
H. Chang, Y.X. Li, G.R. Chen, A novel memristor-based dynamical system with multi-wing attractors and symmetric periodic bursting. Chaos Interdiscipl. J. Nonlinear Sci. 30(4), 043110 (2020)
H. Chang, Y.X. Li, G.R. Chen, F. Yuan, Extreme Multistability and Complex Dynamics of a Memristor-Based Chaotic System. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos. 30(8), 2030019 (2020)
L.O. Chua, S.M. Kang, Memristive devices and systems. Proc. IEEE 64(2), 209–223 (1976)
S.J. Cang, A.G. Wu, Z.H. Wang, W. Xue, Z.Q. Chen, Birth of one-to-four-wing chaotic attractors in a class of simplest three-dimensional continuous memristive systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 83(4), 1987–2001 (2015)
N. Khan, P. Muthukumar, Transient chaos, synchronization and digital image enhancement technique based on a novel 5D fractional-order hyperchaotic memristive system. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 41(4), 2266–2289 (2022)
C.L. Li, H.D. Li, W.W. Xie, J.R. Du, A S-type bistable locally active memristor model and its analog implementation in an oscillator circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 106(1), 1041–1058 (2021)
L.A. Magrini, M. Oliveira, E.E.N. Macau, I.Z. Kiss, Synchronization in populations of electrochemical bursting oscillators with chaotic slow dynamics. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 31(5), 053125 (2021)
R.W. Newcomb, N. El-Leithy, Chaos generation using binary hysteresis. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 5(3), 321–341 (1986)
Q.Z. Wan, Z.D. Yan, F. Li, J. Liu, S.M. Chen, Multistable dynamics in a Hopfield neural network under electromagnetic radiation and dual bias currents. Nonlinear Dyn. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07544-x
Q.Z. Wan, Z.D. Yan, F. Li, S.M. Chen, J. Liu, Complex dynamics in a Hopfield neural network under electromagnetic induction and electromagnetic radiation. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 32(7), 073107 (2022)
H.G. Wu, B.C. Bao, Z. Liu, Q. Xu, P. Jiang, Chaotic and periodic bursting phenomena in a memristive Wien-bridge oscillator. Nonlinear Dyn. 83(1–2), 893–903 (2015)
F. Yu, Z.N. Zhang, H. Shen, Y.Y. Huang, S. Cai, S.C. Du, FPGA implementation and image encryption application of a new PRNG based on a memristive Hopfield neural network with a special activation gradient. Chin. Phys. B 31(2), 20505 (2022)
X.Y. Zhong, M.F. Peng, M. Shahidehpour, Creation and circuit implementation of two-to-eight-wing chaotic attractors using a 3D memristor-based system. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 47(5), 686–701 (2019)
S. Zhang, C.B. Li, J.H. Zheng, X.P. Wang, Z.G. Zeng, G.R. Chen, Generating any number of diversified hidden attractors via memristor coupling. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 68(12), 4945–4956 (2021)
Z.D. Zhang, B.B. Liu, Q.S. Bi, Non-smooth bifurcations on the bursting oscillations in a dynamic system with two timescales. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(1), 195–203 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61901169) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (Grant No. 2019JJ40190).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, Q., Li, F., Liu, J. et al. A New Memristive System with Chaotic and Periodic Bursting and Its FPGA Implementation. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 623–637 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02136-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02136-x