Abstract
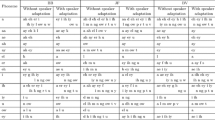
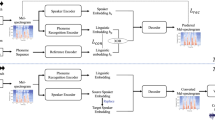
Data augmentation is an essential component in building a dysarthric speech recognition system, as speech data collection from dysarthric speakers with varying degree of disorder is difficult. Dysarthric speech recognition systems are mostly built for isolated words as most of the low intelligible dysarthric speakers are fluent in speaking words in isolation. However, mild and moderate dysarthric speakers can formulate few phrases up to 5 words. Data augmentation procedures for continuous dysarthric speech are yet to be explored. In the current work, virtual microphone array synthesis and multi-resolution feature extraction-based data augmentation (VM-MRFE) proposed by the authors Mariya Celin et al. (IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 14(2):346–354, 2020) is used to augment continuous dysarthric speech. The current work proposes a transfer learning-based speaker-dependent ASR system (isolated and continuous) for 15 dysarthric speakers from UA corpus and 20 dysarthric speakers from the SSN-Tamil Dysarthric Speech developed by the authors. The conventional speed and volume perturbation-based data augmentation is carried out for comparison. It is observed that for isolated word recognition the combination of speed & volume perturbation and the proposed VM-MRFE-based technique showed a reduction in WER of up to 29.98%, whereas for continuous speech the proposed VM-MRFE provided a reduction in WER by 24.95% over the conventional speed and volume perturbation-based data augmentation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available in the LDC repository, under the name “The SSNCE Database of Tamil Dysarthric speech” [https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC2021S04]
References
M. Arcienega, A. Drygajlo, J. Malsano, Robust phase shift estimation in noise for microphone arrays with virtual sensors, in Proceedings of the 10th IEEE European Signal Processing Conference, pp. 1–4 (2000)
S.L. Christina, P. Vijayalakshmi, T. Nagarajan, Hmm-based speech recognition system for the dysarthric speech evaluation of articulatory subsystem, in 2012 International Conference on Recent Trends in Information Technology, pp. 54–59 (2012)
M. Dhanalakshmi, T.A. Mariya Celin, T. Nagarajan, P. Vijayalakshmi, Speech-input speech-output communication for dysarthric speakers using HMM-based speech recognition and adaptive synthesis system. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37(2), 674–703 (2018)
R. Frank, N. Aravind Kumar, W. Talya, The TORGO database of acoustic and articulatory speech from speakers with dysarthria. Lang. Resour. Eval. 46(4), 523–541 (2012)
M. Geng, X. Xie, S. Liu, J. Yu, S. Hu, X. Liu, H. Meng, Investigation of data augmentation techniques for disordered speech recognition. Interspeech 2020, 696–700 (2020)
J. Harvill, D. Issa, M. Hasegawa-Johnson, C. Yoo, Synthesis of new words for improved dysarthric speech recognition on an expanded vocabulary, in ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 6428–6432. IEEE (2021)
K. Heejin, M. Hasegawa-Johnson, A. Perlman, J. Gunderson, T.S. Huang, K. Watkin, S. Frame, Dysarthric speech database for universal access research, in Proceedings of the 9th Annual Conference of International Speech Communication Association, pp. 1741–1744 (2008)
Y. Jiao, M. Tu, V. Berisha, J. Liss, Simulating dysarthric speech for training data augmentation in clinical speech applications, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 6009–6013 (2018)
R.J. Manuel, A. Montalvo, J.R. Calvo, A Survey of the Effects of Data Augmentation for Automatic Speech Recognition Systems, in Iberoamerican Congress on Pattern Recognition. (Springer, Cham, 2019), pp. 669–678
S.R. Mani Sekhar, K. Gaurav, B. Akshay, K. Singh, Dysarthric-speech detection using transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. ICT Express (2021)
T.A. Mariya Celin, G. Anushiya Rachel, T. Nagarajan, P. Vijayalakshmi, A weighted speaker-specific confusion transducer-based augmentative and alternative speech communication aid for dysarthric speakers. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 27(2), 187–197 (2018)
T.A. Mariya Celin, T. Nagarajan, P. Vijayalakshmi, Data augmentation using virtual microphone array synthesis and multi-resolution feature extraction for isolated word dysarthric speech recognition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 14(2), 346–354 (2020)
T.A. Mariya Celin, T. Nagarajan, P. Vijayalakshmi, Dysarthric speech corpus in Tamil for rehabilitation research, in Proceedings of IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), pp. 2610–2613 (2016)
S. Mohammad, M.T. Johnson, R. Soleymanpour, J. Berry, Synthesizing dysarthric speech using multi-talker TTS for dysarthric speech recognition, in ICASSP, pp. 1–5 (2022)
M.A.S. Priyanka, V.S. Solomi, P. Vijayalakshmi, T. Nagarajan, Multiresolution feature extraction (MRFE) based speech recognition system, in Proceedings of IEEE International Conference Recent Trends Information Technology, pp. 152–156 (2013)
SoX, audio manipulation tool. Accessed May, 2021. http://sox.sourceforge.net/
R. Takashima, T. Takiguchi, Y. Ariki, Two-step acoustic model adaptation for dysarthric speech recognition, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 6104–6108 (2020)
K. Tom, V. Peddinti, D. Povey, S. Khudanpur, Audio augmentation for speech recognition, in INTERSPEECH, pp. 3586–3589 (2015)
B. Vachhani, C. Bhat, S.K. Kopparapu, Data augmentation using healthy speech for dysarthric speech recognition. Interspeech 2018, 471–475 (2018)
P. Vijayalakshmi, T.A. Mariya Celin, T. Nagarajan, The SSNCE Database of Tamil Dysarthric Speech. LDC2021S04, Web Download, Philadelphia: Linguistic Data Consortium (2021)
P. Vijayalakshmi, M. Ramasubba Reddy, Assessment of dysarthric speech and an analysis on velopharyngeal incompetence, in Proceedings of 2006 International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 3759–3762 (2006)
P. Vijayalakshmi, M. Ramasubba Reddy, D. O’Shaughnessy, Assessment of articulatory sub-systems of dysarthric speech using an isolated-style phoneme recognition system, in Ninth International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (2006)
F. Xiong, B. Jon, Z. Yue, H. Christensen, Source domain data selection for improved transfer learning targeting dysarthric speech recognition, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 7424–7428 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Institute of Empowerment of Persons with Multiple Disabilities (NIEPMD), for their constant support in collecting dysarthric speech data
Funding
The Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, for funding the project on Speech-Input Speech-Output Communication Aid (SISOCA) for speakers with Cerebral palsy, Ref. No. SEED/TIDE/027/2016/G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mariya Celin, T.A., Vijayalakshmi, P. & Nagarajan, T. Data Augmentation Techniques for Transfer Learning-Based Continuous Dysarthric Speech Recognition. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 601–622 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02156-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02156-7