Abstract.
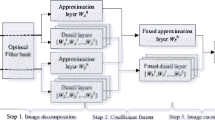
This paper presents an image fusion method based on a new class of wavelet - nonseparable wavelet with compact support, linear phase, orthogonality, and dilation matrix \(\left( {{\begin{array}{*{20}c} 2 \hfill & 0 \hfill \\ 0 \hfill & 2 \hfill \\ \end{array}}} \right)\). We first construct a 6 x 6 nonseparable wavelet filter bank. Using these filters the images involved are decomposed into nonseparable wavelet pyramids. Then the following fusion algorithm is proposed: for the low-frequency part, we select the average of the low-frequency subimages from both sensors. For every high-frequency subimage of each level, we select the absolute value of each pixel of the high-frequency subimage to form a new subimage, and the variance of each image patch over a 3 x 3 window in the new subimages is computed as an activity measurement. If the variance of the 3 x 3 window in one new subimage is greater than the variance of the corresponding 3 x 3 window in the other new subimage, then the center pixel value of the 3 x 3 window is selected as a new pixel value of the fused image. A new fused image is then reconstructed. The performance of the method is evaluated using entropy, root mean square error, and peak-to-peak signal-to-noise ratio. The experimental results show that this method has good vision effect. Because the nonseparable wavelet transform can extract more details from source images, all the features in the source images can be seen in the fused image, and the fused image can extract more information from the source images.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hall DL (1997) An introduction to multi-sensor fusion. Proc IEEE 85(1):6-23
Toet A (1990) Hierachical image fusion. Mach Vis Appl 3(1):1-11
Li H, Manjunath BS, Mitra SK (1995) Multi-sensor image fusion using the wavelet transform. Graph Model Image Process 57(3):235-245
Chipman LJ, Orr TM, Graham LN (1995) Wavelets and image fusion. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on image processing, 3:248-251
Daubechies I (1990) The wavelet transform, time-frequency localization and signal analysis. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 36(5):961-1003
Chui (1995) An introduction to wavelets. Academic, San Diego, Chap 5
Daubechies I (1992) Ten lectures on wavelets. Capital City Press, Montpellier, VT, Chap 8
Kovačević J, Vetterli M (1992) Non-separable multidimensional perfect reconstruction filter bank and wavelet bases for \(\mathbb R^n\). IEEE Trans Inf Theory 38(2):533-555
Lai MJ, Roach D (1999) Nonseparable symmetric wavelets with short support. In: Proceedings of the SPIE conference on wavelet applications in signal and image processing VII, 3813:132-146
Jun L, Zhongjian L (1997) Data fusion for remote sensing imagery based on feature. China J Image Graph 2(2):103-107 (in Chinese)
Guixi L, Wanhai Y (2001) A multiscale contrast, pyramid-based image fusion scheme and its performance evaluation. Acta Optica Sinica 21(11):1336-1342 (in Chinese)
Daubechies I (1992) Ten lectures on wavelets. Capital City Press, Montpelier, VT, pp 194-202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received: 5 July 2003, Accepted: 29 November 2004, Published online: 25 February 2005
This research was support by NSFC under project 60085002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bin, L., Jiaxiong, P. Image fusion method based on nonseparable wavelets. Machine Vision and Applications 16, 189–196 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-004-0171-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-004-0171-4