Abstract
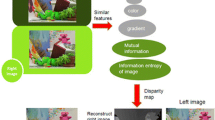
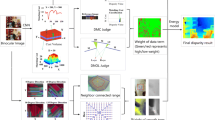
The saliency of a given image region for stereo matching is measured by the Kullback–Leibler divergence from the conditional probability density function (pdf) for the matching region to a pdf for the background. If the region has a high saliency, then there is a high probability that the correct matching region can be found. The Kullback–Leibler divergence is directly estimated from the samples without an intermediate estimation of the pdfs. Experiments with the stereo images in the Middlebury database show that the proposed estimation of the Kullback–Leibler divergence is faster than the estimation based on parametric models for the pdfs, with no loss of accuracy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Itti, L., Koch, C., Niebur, E.: A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 20(11), 1254–1259 (1998)
Wang, L., Xue, J., Zheng, N., Hua, G.: Automatic salient object extraction with contextual cue. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2011, pp. 105–112
Goferman, S., Zelnik-Manor, L., Tal, A.: Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 34(10), 1915–1926 (2012)
Itti, L.: Automatic foveation for video compression using a neurobiological model of visual attention. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 13(10), 1304–1318 (2004)
Harris, C., Stephens, M.: A combined corner and edge detector, In: Alvey Vision Conference, Vol. 15, Manchester, UK, pp. 147–151 (1988)
Mikolajczyk, K., Schmid, C.: Scale & affine invariant interest point detectors. International Journal of Computer Vision 60(1), 63–86 (2004)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision 60(2), 91–110 (2004)
Matas, J., Chum, O., Urban, M., Pajdla, T.: Robust wide baseline stereo from maximally stable extremal regions, In: British Machine Vision Conference, Vol. 1, pp. 384–393 (2002)
Kadir, T., Brady, M.: Saliency, scale and image description. International Journal of Computer Vision 45(2), 83–105 (2001)
Hou, X., Zhang, L.: Saliency detection: A spectral residual approach, In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Achanta, R., Hemami, S., Estrada, F., Susstrunk, S.: Frequency-tuned salient region detection, In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1597–1604 (2009)
Harel, J., Koch, C., Perona, P.: Graph-based visual saliency, in: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 545–552 (2006)
Gao, D., Han, S., Vasconcelos, N.: Discriminant saliency, the detection of suspicious coincidences, and applications to visual recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 31(6), 989–1005 (2009)
Mudge, T., Turney, J., Volz, R.: Automatic generation of salient features for the recognition of partially occluded parts. Robotica 5(2), 117–127 (1987)
Walker, K. N., Cootes, T. F., Taylor, C. J.: Locating salient object features., in: BMVC, Vol. 98, Citeseer, pp. 557–566 (1998)
Yang, J., Yang, M.-H.: Top-down visual saliency via joint crf and dictionary learning, In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2296–2303 (2012)
Maybank, S.J.: A probabilistic definition of salient regions for image matching. Neurocomputing 1(11), 1254–1259 (2013)
Wang, Q., Kulkarni, S.R., Verdú, S.: Divergence estimation of continuous distributions based on data-dependent partitions. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 51(9), 3064–3074 (2005)
Hirschmuller, H., Scharstein, D.: Evaluation of cost functions for stereo matching, In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Gao, D., Vasconcelos, N.: Discriminant saliency for visual recognition from cluttered scenes, In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 481–488 (2004)
Buccigrossi, R.W., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image compression via joint statistical characterization in the wavelet domain. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 8(12), 1688–1701 (1999)
Vasconcelos, M., Vasconcelos, N.: Natural image statistics and low-complexity feature selection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 31(2), 228–244 (2009)
Moreno, P. J., Ho, P. P., Vasconcelos, N.: A kullback-leibler divergence based kernel for svm classification in multimedia applications, In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1385–1392 (2003)
Olsen, P. A., Dharanipragada, S.: An efficient integrated gender detection scheme and time mediated averaging of gender dependent acoustic models, In: European Conference on Speech Communication and Technology, pp. 2509–2512 (2003)
Goldberger, J., Gordon, S., Greenspan, H.: An efficient image similarity measure based on approximations of kl-divergence between two gaussian mixtures, In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 487–493 (2003)
Kullback, S., Leibler, R.A.: On information and sufficiency. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics 22(1), 79–86 (1951)
Hershey, J. R., Olsen, P. A.: Approximating the kullback leibler divergence between gaussian mixture models, In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vol. 4, pp. 317–320 (2007)
Nguyen, X., Wainwright, M.J., Jordan, M.I.: Estimating divergence functionals and the likelihood ratio by convex risk minimization. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 56(11), 5847–5861 (2010)
Wang, Q., Kulkarni, S.R., Verdú, S.: Divergence estimation for multidimensional densities via k-nearest-neighbor distances. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 55(5), 2392–2405 (2009)
Scharstein, D., Szeliski, R.: A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. International Journal of Computer Vision 47(1–3), 7–42 (2002)
Scharstein, D., Pal, C.: Learning conditional random fields for stereo, in: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Liu, C., Yuen, J., Torralba, A.: Sift flow: Dense correspondence across scenes and its applications. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 33(5), 978–994 (2011). doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2010.147
Ke, Y., Sukthankar, R.: Pca-sift: a more distinctive representation for local image descriptors, In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vol. 2, 2004, pp. II-506-II-513 Vol. 2. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2004.1315206
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, J., Maybank, S.J. & Zhang, Y. Stereo matching-based definition of saliency via sample-based Kullback–Leibler divergence estimation. Machine Vision and Applications 26, 607–618 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-015-0685-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-015-0685-y