Abstract
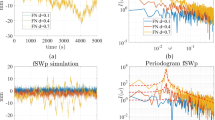
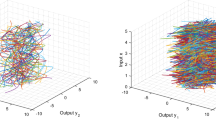
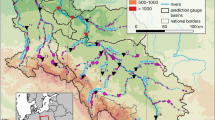
The Bayesian nonparametric (BNP) approach is an effective tool for building flexible spatio-temporal probability models. Despite the flexibility and attractiveness of this approach, the resulting spatio-temporal models become computationally demanding when datasets are large. This paper develops a class of computationally efficient and easy to implement BNP models for large spatio-temporal data. To be more specific, we introduce a random distribution for the spatio-temporal effects based on a stick-breaking construction in which the atoms are modeled in terms of a basis system. In this framework, a low rank basis approximation and a vector autoregressive process are used to model spatial and temporal dependencies, respectively. We demonstrate that the proposed model is an extension of the Gaussian low rank model with similar computational complexity, hence it offers great scalability for large spatio-temporal data. Through a simulation study, we assess the performance of the proposed model. For illustration, we then analyze a set of data comprised of precipitation measurements.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandyopadhyay S, Rao SS (2017) A test for stationarity for irregularly spaced spatial data. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Method) 79(1):95–123
Banerjee S, Gelfand AE, Finley AO, Sang H (2008) Gaussian predictive process models for large spatial data sets. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 70(4):825–848
Banerjee S, Finley AO, Waldmann P, Ericsson T (2010) Hierarchical spatial process models for multiple traits in large genetic trials. J Am Stat Assoc 105(490):506–521
Bradley JR, Cressie N, Shi T (2011) Selection of rank and basis functions in the spatial random effects model. In: Proceedings of the 2011 joint statistical meetings. American Statistical Association, Alexandria, pp 3393–3406
Bradley JR, Cressie N, Shi T (2015) Comparing and selecting spatial predictors using local criteria. Test 24(1):1–28
Bradley JR, Cressie N, Shi T (2016) A comparison of spatial predictors when datasets could be very large. Stat Surv 10:100–131
Canale A, Scarpa B (2016) Bayesian nonparametric location–scale–shape mixtures. Test 25(1):113–130
Carter CK, Kohn R (1994) On Gibbs sampling for state space models. Biometrika 81:541–553
Cavatti Vieira C, Loschi RH, Duarte D (2015) Nonparametric mixtures based on skew-normal distributions: an application to density estimation. Commun Stat Theory Methods 44(8):1552–1570
Cressie N, Johannesson G (2008) Fixed rank kriging for very large spatial data sets. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 70(1):209–226
Cressie N, Shi T, Kang EL (2010) Fixed rank filtering for spatio-temporal data. J Comput Graph Stat 19(3):724–745
Di Lucca MA, Guglielmi A, Müller P, Quintana FA (2013) A simple class of Bayesian nonparametric autoregression models. Bayesian Anal (Online) 8(1):63
Duan JA, Guindani M, Gelfand AE (2007) Generalized spatial Dirichlet process models. Biometrika 94(4):809–825
Escobar MD, West M (1995) Bayesian density estimation and inference using mixtures. J Am Stat Assoc 90(430):577–588
Finley AO, Banerjee S, Gelfand AE (2012) Bayesian dynamic modeling for large space–time datasets using Gaussian predictive processes, vol 14. Springer, Berlin
Frühwirth-Schnatter S (1994) Data augmentation and dynamic linear models. J Time Ser Anal 15(2):183–202
Furrer R, Genton MG, Nychka D (2006) Covariance tapering for interpolation of large spatial datasets. J Comput Graph Stat 15(3):502–523
Gelfand AE, Kottas A, MacEachern SN (2005) Bayesian nonparametric spatial modeling with Dirichlet process mixing. J Am Stat Assoc 100(471):1021–1035
Gelfand AE, Diggle P, Guttorp P, Fuentes M (eds) (2010) Handbook of spatial statistics. CRC Press, Cambridge
Gelfand AE, Banerjee S, Finley A (2012) Spatial design for knot selection in knot-based dimension reduction models. In: Mateu JM, Mueller W (eds) Spatio-temporal design: Advances in efficient data acquisition. Wiley, pp 142–169
Ghosal S, Ghosh JK, Ramamoorthi RV (1999) Posterior consistency of Dirichlet mixtures in density estimation. Ann Stat 27(1):143–158
Griffin JE, Steel MF (2011) Stick-breaking autoregressive processes. J Econom 162(2):383–396
Gutiérrez L, Mena RH, Ruggiero M (2016) A time dependent bayesian nonparametric model for air quality analysis. Comput Stat Data Anal 95:161–175
Hanson T, Johnson WO (2002) Modeling regression error with a mixture of Polya trees. J Am Stat Assoc 97(460):1020–1033
Hastings WK (1970) Monte Carlo sampling methods using Markov chains and their applications. Biometrika 57:97–109
Heaton MJ, Katzfuss M, Berrett C, Nychka DW (2014) Constructing valid spatial processes on the sphere using kernel convolutions. Environmetrics 25:2–15
Higdon D (1998) A process-convolution approach to modelling temperatures in the North Atlantic Ocean. Environ Ecol Stat 5(2):173–190
Hosseinpouri M, Khaledi MJ (2019) An area-specific stick breaking process for spatial data. Stat Pap 60(1):199–221
Kalli M, Griffin JE (2018) Bayesian nonparametric vector autoregressive models. J Econom 203(2):267–282
Kalli M, Griffin JE, Walker SG (2011) Slice sampling mixture models. Stat Comput 21(1):93–105
Kang EL, Cressie N, Shi T (2010) Using temporal variability to improve spatial mapping with application to satellite data. Can J Stat 38(2):271–289
Katzfuss M (2013) Bayesian nonstationary spatial modeling for very large datasets. Environmetrics 24(3):189–200
Katzfuss M, Cressie N (2011) Bayesian hierarchical spatio-temporal smoothing for very large datasets. Environmetrics 23(1):94–107
Kaufman L, Rousseeuw P (1990) Finding groups in data, vol 16. Wiley, New York
Lemos RT, Sanso B (2009) A spatio-temporal model for mean, anomaly, and trend fields of North Atlantic sea surface temperature. J Am Stat Assoc 104(485):5–18
Metropolis N, Rosenbluth AW, Rosenbluth MN, Teller AH, Teller E (1953) Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines. J Chem Phys 21(6):1087–1092
Nieto-Barajas LE, Contreras-Cristán A (2014) A Bayesian nonparametric approach for time series clustering. Bayesian Anal 9(1):147–170
Nieto-Barajas L, Müller P, Ji Y, Lu Y, Mills G (2008) Time series dependent Dirichlet process. Preprint
Nguyen H, Cressie N, Braverman A (2012) Spatial statistical data fusion for remote sensing applications. J Am Stat Assoc 107(499):1004–1018
Pati D, Dunson DB, Tokdar ST (2013) Posterior consistency in conditional distribution estimation. J Multivar Anal 116:456–472
Petrone S, Guindani M, Gelfand AE (2009) Hybrid Dirichlet mixture models for functional data. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 71(4):755–782
Reich BJ, Fuentes M (2007) A multivariate semiparametric Bayesian spatial modeling framework for hurricane surface wind fields. Ann Appl Stat 1:249–264
Reich BJ, Fuentes M (2012) Nonparametric Bayesian models for a spatial covariance. Stat Methodol 9(1–2):265–274
Rue H, Held L (2005) Gaussian Markov random fields: theory and applications. CRC Press, Cambridge
Rue H, Tjelmeland H (2002) Fitting Gaussian Markov random fields to Gaussian fields. Scand J Stat 29(1):31–49
Sahr K, White D, Kimerling AJ (2003) Geodesic discrete global grid systems. Cartogr Geogr Inf Sci 30(2):121–134
Schörgendorfer A, Branscum AJ, Hanson TE (2013) A Bayesian goodness of fit test and semiparametric generalization of logistic regression with measurement data. Biometrics 69(2):508–519
Spiegelhalter DJ, Best NG, Carlin BP, van der Linde A (2002) Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit (with Discussion). J Roy Stat Soc B 64:583–639
Stein ML (2014) Limitations on low rank approximations for covariance matrices of spatial data. Spat Stat 8:1–19
Stein ML, Chi Z, Welty LJ (2004) Approximating likelihoods for large spatial data sets. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 66(2):275–296
Vecchia AV (1988) Estimation and model identification for continuous spatial processes. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Methodol) 50(2):297–312
Walker SG (2007) Sampling the Dirichlet mixture model with slices. Commun Stat Simul Comput 36(1):45–54
Walker SG, Mallick BK (1999) Semiparametric accelerated life time model. Biometrics 55:477–483
Warren J, Fuentes M, Herring A, Langlois P (2012) Bayesian spatial–temporal model for cardiac congenital anomalies and ambient air pollution risk assessment. Environmetrics 23(8):673–684
West M, Harrison J (1997) Bayesian forecasting and dynamic models, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Xu K, Wikle CK, Fox NI (2005) A kernel-based spatio-temporal dynamical model for nowcasting weather radar reflectivities. J Am Stat Assoc 100(472):1133–1144
Acknowledgements
The Editor, and two referees are gratefully acknowledged. Their precise comments and constructive suggestions have substantially improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barzegar, Z., Rivaz, F. A scalable Bayesian nonparametric model for large spatio-temporal data. Comput Stat 35, 153–173 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-019-00905-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-019-00905-y