Abstract
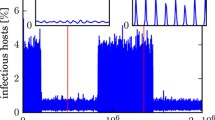
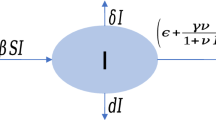
This paper is concerned with complex dynamical behaviors of a simple unified SIR and HIV disease model with a convex incidence and four real parameters. Due to the complex nature of the disease dynamics, our goal is to explore bifurcations including multistable states, limit cycles, and homoclinic loops in the whole parameter space. The first contribution is the proof of the existence of multiple limit cycles giving rise from Hopf bifurcation, which further induces bistable or tristable states because of the coexistence of stable equilibria and periodic motion. Next, we propose that the existence of Bogdanov–Takens (BT) bifurcation yields the bifurcation of homoclinic loops, which provides a new mechanism for generating disease recurrence, for example, the relapse–remission, viral blip cycles in HIV infection. Last, we present a novel method for the derivation of the normal forms of codimension two and three BT bifurcations. The method is based on the simplest normal form theory from Yu’s previous works.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boie, S., Kirk, V., Sneyd, J., Wechselberger, M.: Effects of quasi-steady-state reduction on biophysical models with oscillations. J. Theor. Biol. 393, 16–31 (2016)
Dumortier, F., Roussarie, R., Sotomayor, J.: Generic 3-parameter family of vector feilds on the plane, unfolding a singularity with nilpotent linear part. The cusp case of codimension 3. Ergod. Theory Dyn. Syst. 7(3), 375–413 (1987)
Earn, D.J.D., Rohani, P., Bolker, B.M., Grenfell, B.T.: A simple model for complex dynamical transitions in epidemics. Science 287(5453), 667–670 (2000)
Flach, E.H., Schnell, S.: Use and abuse of the quasi-steady-state approximation. IEEE Proc. Syst. Biol. 153(4), 187–191 (2006)
Gazor, M., Yu, P.: Formal decomposition method and parametric normal form. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 20, 3415–3487 (2010)
Gazor, M., Yu, P.: Spectral sequences and parametric normal forms. J. Differ. Equ. 252, 1003–1031 (2012)
Gazor, M., Moazeni, M.: Parametric normal forms for Bogdanov–Takens singularity; the generalized saddle-node case. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 35, 205–224 (2015)
Griffin D. E.: Immune Responses during measles virus infection. In: Measles Virus (Eds ter Meulen, Volker and Billeter, Martin A.) pp. 117–134, Springer, Berlin (1995)
Guckenheimer, J., Holmes, P.: Nonlinear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems, and Bifurcations of Vector Fields, 4th edn. Springer, New York (1993)
Han, M., Yu, P.: Normal Forms, Melnikov Functions and Bifurcations of Limit Cycles. Sringer, New York (2012)
Hethcote, H.W., van den Driessche, P.: Some epidemiological models with nonlinear incidence. J. Math. Biol. 29(3), 271–287 (1991)
Korobeinikov, A., Maini, P.K.: Non-linear incidence and stability of infectious disease models. Math. Med. Biol. 22, 113–128 (2005)
Korobeinikov, A., Shchepakina, E., Sobolev, V.: Paradox of enrichment and system order reduction: bacteriophages dynamics as case study. Math. Med. Biol. 33(3), 359–369 (2005)
Li, C., Rousseau, C.: A system with three limit cycles appearing in a Hopf bifurcation and dying in a homoclinic bifurcation: the cusp of order 4. J. Differ. Equ. 79, 132–167 (1989)
Liu, W., Levin, S., Iwasa, Y.: Influence of nonlinear incidence rates upon the behavior of SIRS epidemiological models. J. Math. Biol. 23, 187–204 (1986)
Tian, Y., Yu, P.: Bifurcation of small limit cycles in cubic integrable systems using higher-order analysis. J. Differ. Equ. 264(9), 5950–5976 (2018)
van Gaalen, R.D., Wahl, L.M.: Reconciling conflicting clinical studies of antioxidant supplementation as HIV therapy: a mathematical approach. BMC Public Health 9, 1–18 (2009)
Wang, J.J., Zhang, J.Z., Jin, Z.: Analysis of an SIR model with bilinear incidence rate. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 11(4), 2390–2402 (2010)
Yu, P.: Computation of normal forms via a perturbation technique. J. Sound Vib. 211, 19–38 (1998)
Yu, P.: Simplest normal forms of Hopf and generalized Hopf bifurcations. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 9, 1917–1939 (1999)
Yu, P., Leung, A.Y.L.: The simplest normal form of Hopf bifurcation. Nonlinearity 16, 277–300 (2003)
Yu, P., Zhang, W., Wahl, L.M.: Dynamical analysis and simulation of a 2-dimensional disease model with convex incidence. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 37, 163–192 (2016)
Zhang, W., Wahl, L.M., Yu, P.: Conditions for transient viremia in deterministic in-host models: viral blips need no exogenous trigger. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 73, 853–881 (2013)
Zhang, W., Wahl, L.M., Yu, P.: Viral blips may not need a trigger: how transient viremia can arise in deterministic in-host models. SIAM Rev. 56, 127–155 (2014)
Zhang, W., Wahl, L.M., Yu, P.: Modelling and analysis of recurrent autoimmune disease. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 74, 1998–2025 (2014)
Zhang, W., Wahl, L.M., Yu, P.: Backward bifurcation underlies rich dynamics in simple disease models. J. Math. Biol. 73, 947–976 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (No. R2686A02). The comments and suggestions, received from two anonymous reviewers, for improving this manuscript are greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Paul Newton.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, P., Zhang, W. Complex Dynamics in a Unified SIR and HIV Disease Model: A Bifurcation Theory Approach. J Nonlinear Sci 29, 2447–2500 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00332-019-09550-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00332-019-09550-7
Keywords
- A unified SIR and HIV disease model
- Recurrent infection
- Stability
- Hopf bifurcation
- Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation
- Limit cycle
- Homoclnic orbit
- The simplest normal form