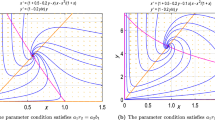
Abstract
Synchronized maturation has been extensively studied in biological science on its evolutionary advantages. This paper is devoted to the study of the spatial dynamics of species growth with annually synchronous emergence of adults by formulating an impulsive reaction–diffusion model. With the aid of the discrete-time semiflow generated by the 1-year solution map, we establish the existence of the spreading speed and traveling waves for the model on an unbounded spatial domain. It turns out that the spreading speed coincides with the minimal speed of traveling waves, regardless of the monotonicity of the birth rate function. We also investigate the model on a bounded domain with a lethal exterior to determine the critical domain size to reserve species persistence. Numerical simulations are illustrated to confirm the analytical results and to explore the effects of the emergence maturation delay on the spatial dynamics of the population distribution. In particular, the relationship between the spreading speed and the emergence maturation delay is found to be counterintuitively variable.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altwegg, R.: Trait-mediated indirect effects and complex life-cycles in two European frogs. Evol. Ecol. Res. 4, 519–536 (2002)
Borowsky, R., Diffley, J.: Synchronized maturation and breeding in natural populations of Xiphophorus variatus (Poeciliidae). Environ. Biol. Fish. 6, 49–58 (1981)
Coville, J., Dupaigne, L.: On a nonlocal equation arising in population dynamics. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. A 137, 727–755 (2007)
Fang, J., Gourley, S., Lou, Y.: Stage-structured models of intra-and inter-specific competition within age classes. J. Differ. Equ. 260, 1918–1953 (2016)
Fazly, M., Lewis, M., Wang, H.: On impulsive reaction–diffusion models in higher dimensions. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 77, 224–246 (2017)
Fazly, M., Lewis, M., Wang, H.: Analysis of propagation for impulsive reaction–diffusion models. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 80, 521–542 (2020)
Gourley, S., Ruan, S.: A delay equation model for oviposition habitat selection by mosquitoes. J. Math. Biol. 65, 1125–1148 (2012)
Hoppensteadt, F.C., Keller, J.B.: Synchronization of periodical cicada emergences. Science 194, 335–337 (1976)
Hsu, S.-B., Zhao, X.-Q.: Spreading speeds and traveling waves for nonmonotone integrodifference equations. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 40, 776–789 (2008)
Jin, W., Smith, H.L., Thieme, H.R.: Persistence and critical domain size for diffusing populations with two sexes and short reproductive season. J. Dyn. Differ. Equ. 28, 689–705 (2016)
Jin, W., Thieme, H.R.: Persistence and extinction of diffusing populations with two sexes and short reproductive season. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 19, 3209–3218 (2014)
Kao, C.-Y., Lou, Y., Shen, W.: Random dispersal vs. nonlocal dispersal. Discre. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 26, 551–596 (2010)
Lewis, M.A., Li, B.: Spreading speed, traveling wave, and minimal domain size in impulsive reaction–diffusion models. Bull. Math. Biol. 74, 2383–2402 (2012)
Li, W.T., Wang, J.B., Zhao, X.-Q.: Spatial dynamics of a nonlocal dispersal population model in a shifting environment. J. Nonlinear Sci. 28, 1189–1219 (2018)
Liang, J., Yan, Q., Xiang, C., Tang, S.: A reaction–diffusion population growth equation with multiple pulse perturbations. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 74, 122–137 (2019)
Liang, X., Yi, Y., Zhao, X.-Q.: Spreading speeds and traveling waves for periodic evolution systems. J. Differ. Equ. 231, 57–77 (2006)
Liang, X., Zhao, X.-Q.: Asymptotic speeds of spread and traveling waves for monotone semiflows with applications. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 60, 1–40 (2007)
Lin, Y., Wang, Q.-R.: Spreading speed and traveling wave solutions in impulsive reaction–diffusion models. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 23, 185–191 (2015)
Lu, J., Guan, Z.: Numerical Solutions of Partial Differential Equations, 2nd edn. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing (2004)
Mohring, M.B., Wernberg, T., Kendrick, G.A., et al.: Reproductive synchrony in a habitat-forming kelp and its relationship with environmental conditions. Mar. Biol. 160, 119–126 (2013)
Peng, R., Zhao, X.-Q.: The diffusive logistic model with a free boundary and seasonal succession. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 33, 2007–2031 (2013)
Riehl, C.: Reproductive synchrony. In: Vonk, J., Shackelford, T. (eds.) Encyclopedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior. Springer, Cham (2018)
Santos, R.G., Pinheiro, H.T., Martins, A.S., et al.: The anti-predator role of within-nest emergence synchrony in sea turtle hatchlings. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 283, 20160697 (2016)
Shlesinger, T., Loya, Y.: Breakdown in spawning synchrony: a silent threat to coral persistence. Science 365, 1002–1007 (2019)
Smith, H.L.: Monotone dynamical systems: an introduction to the theory of competitive and cooperative systems. In: Mathematical Surveys and Monographs, vol. 41. American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI (1995)
Taylor, C.M., Hastings, A.: Allee effects in biological invasions. Ecol. Lett. 8, 895–908 (2005)
Veprauskas, A.: Synchrony and the dynamic dichotomy in a class of matrix population models. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 78, 2491–2510 (2018)
Veprauskas, A., Cushing, J.M.: A juvenile-adult population model: climate change, cannibalism, reproductive synchrony, and strong Allee effects. J. Biol. Dyn. 11, 1–24 (2017)
Wang, Z., Wang, H.: Persistence and propagation of a PDE and discrete-time map hybrid animal movement model with habitat shift driven by climate change. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 80, 2608–2630 (2020)
Williams, K.S., Smith, K.G., Stephen, F.M.: Emergence of 13-Yr periodical cicadas (Cicadidae: Magicicada): phenology, mortality, and predators satiation. Ecology 74, 1143–1152 (1993)
Wu, R., Zhao, X.-Q.: Spatial invasion of a birth pulse population with nonlocal dispersal. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 79, 1075–1097 (2019)
Wu, R., Zhao, X.-Q.: The evolution dynamics of an impulsive hybrid population model with spatial heterogeneity. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 107, 106181 (2022)
Yu, X., Zhao, X.-Q.: A periodic reaction–advection–diffusion model for a stream population. J. Differ. Equ. 258, 3037–3062 (2015)
Zhang, L., Liu, K., Lou, Y., Wang, Z.-C.: Spatial dynamics of a nonlocal model with periodic delay and competition. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 31, 1070–1100 (2020)
Zhao, X.-Q.: Dynamical Systems in Population Biology, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to two anonymous referees for their valuable comments which led to improvements of our original manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Philip K. Maini.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This research was supported in part by the NSF of China [11971369, 12071393], the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities [JB210711], the General Research Fund from The Hong Kong Research Grants Council [15304821], and the NSERC of Canada [RGPIN-2019-05648].
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Z., Lou, Y. & Zhao, XQ. Spatial Dynamics of Species with Annually Synchronized Emergence of Adults. J Nonlinear Sci 32, 78 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00332-022-09836-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00332-022-09836-3
Keywords
- Impulsive reaction–diffusion model
- Maturation delay
- Traveling waves
- Spreading speed
- Critical domain size