Abstract
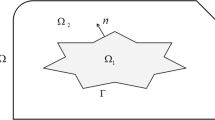
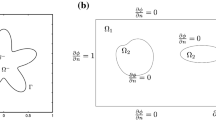
In the current paper, two numerical methods are proposed for the numerical solution of two- and three-dimensional elliptic partial differential equations (PDEs) with regular interfaces. The proposed methods are based on meshless collocation and Haar wavelet collocation. Numerical tests are performed to check accuracy and robustness of the proposed methods. Numerical results of the proposed methods are measured in terms of \(L_{\infty }\) error norm to show their better accuracy than the existing methods.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Z, Ito K (2001) Maximum principle preserving schemes for interface problems with discontinuous coefficients. SIAM J Sci Comput 23:339–361
Baruch G, Fibich G, Tsynkov S, Turkel E (2009) Fourth order schemes for time-harmonic wave equations with discontinuous coefficients. Commun Comput Phys 5:442–455
Li Z, McTigue D, Heine J (1997) A numerical method for diffusive transport with moving boundaries and discontinuous material properties. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 21:653–662
Li Z, Wang D, Zou J (1998) Theoretical and numerical analysis on a thermo-elastic system with discontinuities. Comput Appl Math 92:37–58
Linnick MN, Fasel HF (2005) A high-order immersed interface method for simulating unsteady incompressible flows on irregular domains. J Comput Phys 204:157–192
Liu X, Sideris TC (2003) Convergence of the ghost fluid method for elliptic equations with interfaces. Math Comput 72:1731–1746
Rutka V, Li Z (2008) An explicit jump immersed interface method for two-phase Navier–Stokes equations with interfaces. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197:2317–2328
Zhou YC, Zhao S, Feig M, Wei GW (2006) High order matched interface and boundary method for elliptic equations with discontinuous coefficients and singular sources. J Comput Phys 213:1–30
Xu S, Wang ZJ (2006) Systematic derivation of jump conditions for the immersed interface method in three-dimensional flow simulation. SIAM J Sci Comput 27:1948–1980
Wiegmann A, Bube K (1998) The immersed interface method for nonlinear differential equations with discontinuous coefficients and singular sources. SIAM J Numer Anal 35:177–200
LeVeque RJ, Li Z (1994) The immersed interface method for elliptic equations with discontinuous coefficients and singular sources. SIAM J Numer Anal 31:1019–1044
Li Z, Ito K (2006) The immersed interface method: numerical solutions of PDEs involving interfaces and irregular domains. In: Frontiers in applied mathematics, vol 33. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. (SIAM), Philadelphia
Calhoun D (2002) A cartesian grid method for solving the streamfunction-vorticity equation in irregular regions. J Comput Phys 176:231–275
Li Z, Wang C (2003) A fast finite difference method for solving Navier–Stokes equations on irregular domains. J Commun Math Sci 1:180–196
Russell D, Wang ZJ (2003) A cartesian grid method for modeling multiple moving irregular objects in 2D incompressible viscous flow. J Comput Phys 191:177–205
Bell JB, Colella P, Glaz HM (1989) A second-order projection method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. J Comput Phys 85:257–283
Kan J (1986) A second-order accurate pressure-correction scheme for viscous incompressible flow. SIAM J Sci Comput 7:870–891
Kim J, Moin P (1985) Application of a fractional-step method to incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. J Comput Phys 59:308–323
Dahmen W, Kurdila A, Oswald P (1997) Multiscale wavelet methods for partial differential equations. Academic Press, New York
Siraj-ul-Islam, Aziz I, Haq F (2010) A comparative study of numerical integration based on Haar wavelets and hybrid functions. Comput Math Appl 59:2026–2036
Aziz I, Siraj-ul-Islam, Khan W (2011) Quadrature rules for numerical integration based on Haar wavelets and hybrid functions. Comput Math Appl 61:2770–2781
Dehghan M, Lakestani M (2008) Numerical solution of nonlinear system of second-order boundary value problems using cubic B-spline scaling functions. Int J Comput Math 85:1455–1461
Siraj-ul-Islam, Aziz I, Šarlar B (2010) The numerical solution of second-order boundary-value problems by collocation method with the Haar wavelets. Math Comput Model 52:1577–1590
Comincioli V, Naldi G, Scapolla T (2000) A wavelet-based method for numerical solution of nonlinear evolution equations. Appl Numer Math 33:291–297
Wu JL (2009) A wavelet operational method for solving fractional partial differential equations numerically. Appl Math Comput 214:31–40
Diaz L, Martin M, Vampa V (2009) Daubechies wavelet beam and plate finite elements. Finite Elem Anal Des 45:200–209
Zhu X, Lei G, Pan G (1997) On application of fast and adaptive Battle–Lemarie wavelets to modeling of multiple lossy transmission lines. J Comput Phys 132:299–311
Babolian E, Fattahzdeh F (2007) Numerical solution of differential equations by using Chebyshev wavelet operational matrix of integration. Appl Math Comput 188:417–426
Banifatemi E, Razzaghi M, Yousefi S (2007) Two-dimensional Legendre wavelets method for the mixed Volterra–Fredholm integral equations. J Vib Control 13:1667–1675
Lepik U (2007) Numerical solution of evolution equations by the Haar wavelet method. Appl Math Comput 185:695–704
Chen C, Hsiao C (1997) Haar wavelet method for solving lumped and distributed-parameter systems. IEE Proc Control Theory Appl 144:87–94
Kansa EJ (1990) Multiquadrics—a scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid-dynamics—I surface approximations and partial derivative estimates. Comput Math Appl 19:127–145
Franke C, Schaback R (1998) Convergence order estimates of meshless collocation methods using radial basis functions. Adv Comput Math 8:381–399
Chinchapatnam P, Djidjeli K, Nair P (2006) Unsymmetric and symmetric meshless schemes for the unsteady convection–diffusion equation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195:2432–2453
Franke C, Schaback R (1998) Solving partial differential equations by collocation with radial basis functions. Appl Math Comput 93:72–82
Siraj-ul-Islam, Ahmad I (2016) A comparative analysis of local meshless formulation for multi-asset option models. Eng Anal Bound Elem 65:159–176
Siraj-ul-Islam, Singh V, Kumar S (2017) Estimation of dispersion in an open channel from an elevated source using an upwind local meshless method. Int J Comput Methods 14:1750009
Bellman RE, Kalaba RE (1965) Quasilinearization and non-linear boundary value problems. American Elsevier, New York
Feng X, Li Z (2012) Simplified immersed interface methods for elliptic interface problems with straight interfaces. Numer Methods Partial Differ Eqs 28:188–203
Majak J, Shvartsman BS, Kirs M, Pohlak M, Herranen H (2015) Convergence theorem for the Haar wavelet based discretization method. Compos Struct 126:227–232
Majak J, Shvartsman BS, Kurjust K, Mikola M, Haavajoe A, Pohlak M (2015) On the accuracy of the Haar wavelet discretization method. Compos Part B Eng 80:321–327
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haider, N., Aziz, I. & Siraj-ul-Islam Numerical solution of 2D and 3D elliptic-type interface models with regular interfaces. Engineering with Computers 35, 1081–1102 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-018-0652-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-018-0652-0