Abstract
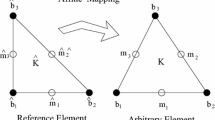
In this paper numerical solution of 3D convection–diffusion problems both with high Reynolds (Re) numbers and variable coefficients are investigated via a meshless method based on polynomial basis. It is well known that using polynomial basis directly for solving partial differential equations may be unsafe due to ill-conditioned resultant coefficients matrix that formed after discretization process. Therefore to get rid of highly ill-conditioned coefficient matrix we took advantage of multiple-scale method which is essentially based on the idea of equating norm of each column of resultant coefficients matrix. Through this approach we can reduce the condition number greatly. The proposed method is a truly meshless method since there is no need for meshing or any node connectivity and implementation of the method is simple and straightforward. The performance of the proposed method is measured by four test problems in both regular and irregular computational domains. Numerical results corroborate efficiency of meshless multiple-scale polynomial method for 3D convection–diffusion problems as well show its stability in case of large noise effect.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J (1998) An explicit fourth-order compact finite difference scheme for three dimensional convection-diffusion equation. Commun Numer Meth Eng 14:263–280
Roache P (1972) Computational fluid dynamics. Hermosa Press, Albuquerque
Gupta MM, Zhang J (2000) High accuracy multigrid solution of the 3D convection diffusion equation. Appl Math Comput 113:249–274
Dehghan M (2004) Numerical solution of the three-dimensional advection-diffusion equation. Appl Math Comput 150:5–19
Dehghan M, Mohebbi A (2008) High-order compact boundary value method for the solution of unsteady convection–diffusion problems. Math Comput Simul 79:683–699
Dehghan M (2006) Finite difference procedures for solving a problem arising in modeling and design of certain optoelectronic devices. Math Comput Simul 71(1):16–30
Oruç Ö (2018) A new numerical treatment based on Lucas polynomials for 1D and 2D sinh-Gordon equation. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 57:14–25
Oruç Ö, Bulut F, Esen A (2015) A haar wavelet-finite difference hybrid method for the numerical solution of the modified burgers’ equation. J Math Chem 53(7):1592–1607
Shivanian E (2014) Analysis of meshless local and spectral meshless radial point interpolation (MLRPI and SMRPI) on 3-D nonlinear wave equations. Ocean Eng 89(1):173–188
Shivanian E (2016) Spectral meshless radial point interpolation (SMRPI) method to two-dimensional fractional telegraph equation. Math Methods Appl Sci 39(7):1820–1835
Shivanian E, Jafarabadi A (2018) Time fractional modified anomalous sub-diffusion equation with a nonlinear source term through locally applied meshless radial point interpolation. Mod Phys Lett B 32(22):1850251
Shivanian E (2015) A new spectral meshless radial point interpolation (SMRPI) method: a well-behaved alternative to the meshless weak forms. Eng Anal Bound Elem 54:1–12
Fatahi H, Saberi-Nadjafi J, Shivanian E (2016) A new spectral meshless radial point interpolation (SMRPI) method for the two-dimensional Fredholm integral equations on general domains with error analysis. J Comput Appl Math 294:196–209
Dehghan M (2007) Time-splitting procedures for the solution of the two-dimensional transport equation. Kybernetes 36(5/6):791–805
Dehghan M (2005) Quasi-implicit and two-level explicit finite-difference procedures for solving the one-dimensional advection equation. Appl Math Comput 167(1):46–67
Dehghan M (2004) Numerical solution of the three-dimensional advection-diffusion equation. Appl Math Comput 150(1):5–19
Dehghan M (2004) Weighted finite difference techniques for the one-dimensional advection-diffusion equation. Appl Math Comput 147(2):307–319
Dehghan M (2005) On the numerical solution of the one-dimensional convection-diffusion equation. Math probl eng 1:61–74
Wang C, He M, Sun P (2016) A new combined finite element-upwind finite volume method for convection-dominated diffusion problems. Numer Methods Partial Differ Equ 32:799–818
Varanasi C, Murthy JY, Sanjay Mathur (2012) Numerical schemes for the convection-diffusion equation using a meshless finite-difference method. Numer Heat Tr, Part B-Fund 62(1):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/10407790.2012.687976
Vertnik R, Šarler B (2006) Meshless local radial basis function collocation method for convective-diffusive solid–liquid phase change problems. Int J Numer Method Heat 16(5):617–640. https://doi.org/10.1108/09615530610669148
Safdari-Vaighani A, Heryudono A, Larsson E (2015) A radial basis function partition of unity collocation method for convection-diffusion equations arising in financial applications. J Sci Comput 64(2):341–367
Ge YB, Tian ZF, Zhang J (2013) An exponential high-order compact ADI method for 3d unsteady convection–diffusion problems. Numer Methods Partial Differ Equ 29:186–205
Kalita JC, Dalal DC, Dass AK (2002) A class of higher order compact schemes for the unsteady two-dimensional convection–diffusion equation with variable convection coefficients. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 38:1111–1131
Tian ZF, Dai SQ (2007) High-order compact exponential finite difference methods for convection–diffusion type problems. J Comput Phys 220:952–974
Tian ZF, Yu PX (2011) A high-order exponential scheme for solving 1D unsteady convection–diffusion equations. J Comput Appl Math 235:2477–2491
Ma Y, Ge Y (2010) A high order finite difference method with Richardson extrapolation for 3D convection diffusion equation. Appl Math Comput 215:3408–3417
Dai R, Wang Y, Zhang J (2013) Fast and high accuracy multiscale multigrid method with multiple coarse grid updating strategy for the 3D convection–diffusion equation. Comput Math Appl 66:542–559
Wang K, Wang H (2018) Stability and error estimates of a new high-order compact ADI method for the unsteady 3D convection–diffusion equation. Appl Math Comput 331:140–159
Liu GR, Liu MB, Li S (2004) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: a mesh free method. Comput Mech 33(6):491–491
Belytschko T, Lu YY, Gu L (1994) Element free Galerkin methods. Int J Numer Methods Eng 37:229–256
Onate E, Idelsohn S, Zienkiewicz OC, Taylor RL (1996) A finite point method in computational mechanics. Application to convective transport and fluid flow. Int J Numer Methods Eng 39:3839–3866
Ilati M, Dehghan M (2017) Application of direct meshless local Petrov-Galerkin (DMLPG) method for some Turing-type models. Eng Comput 33(1):107–124
Shivanian E (2013) Analysis of meshless local radial point interpolation (MLRPI) on a nonlinear partial integro-differential equation arising in population dynamics. Eng Anal Bound Elem 37(12):1693–1702
Shivanian E (2015) Meshless local Petrov-Galerkin (MLPG) method for three-dimensional nonlinear wave equations via moving least squares approximation. Eng Anal Bound Elem 50:249–257
Shivanian E (2016) On the convergence analysis, stability, and implementation of meshless local radial point interpolation on a class of three-dimensional wave equations. Int J Numer Methods Eng 105(2):83–110
Shivanian E, Khodabandehlo HR (2014) Meshless local radial point interpolation (MLRPI) on the telegraph equation with purely integral conditions. Phys J Plus 129:241. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2014-14241-9
Kansa EJ (1990) Multiquadrics—a scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid dynamics—II. Comput Math Appl 19(8/9):147–61
Cheng AHD (2007) Radial basis function collocation method. In: Computational mechanics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-75999-7_20
Hu HY, Li ZC, Cheng AH-D (2005) Radial basis collocation methods for elliptic boundary value problems. Comput Math Appl 50:289–320
Jankowska MA, Karageorghis A, Chen CS (2018) Improved Kansa RBF method for the solution of nonlinear boundary value problems. Eng Anal Bound Elem 87:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2017.11.012
Dehghan M, Shokri A (2007) A numerical method for two-dimensional Schrodinger equation using collocation and radial basis functions. Comput Math Appl 54:136–146
Dehghan M, Mohammadi V (2014) The numerical solution of Fokker-Planck equation with radial basis functions (RBFs) based on the meshless technique of Kansa’s approach and Galerkin method. Eng Anal Bound Elem 47:38–63
Sarra SA (2012) A local radial basis function method for advection–diffusion–reaction equations on complexly shaped domains. Appl Math Comput 218:9853–9865
Dehghan M, Abbaszadeh M, Mohebbi A (2014) The numerical solution of nonlinear high dimensional generalized Benjamin–Bona–Mahony–Burgers equation via the meshless method of radial basis functions. Comput Math Appl 68:212–237
Xiong J, Jiang P, Zheng H, Chen CS (2018) A high accurate simulation of thin plate problems by using the method of approximate particular solutions with high order polynomial basis. Eng Anal Bound Elem 94:153–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2018.06.009
Lin J, Chen CS, Wang F, Dangal T (2017) Method of particular solutions using polynomial basis functions for the simulation of plate bending vibration problems. Appl Math Model 49:452–469
Li X, Dangal T, Lei B (2018) Localized method of approximate particular solutions with polynomial basis functions. Eng Anal Bound Elem 97:16–22
Liu GR, Gu YT (2003) A meshfree method: meshfree weak strong (MWS) form method, for 2-D solids. Comput Mech 33:2–14
Liu GR, Wu YL, Ding H (2004) Meshfree weak strong (MWS) form method and its application to incompressible flow problems. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 46(10):1025–1047
Gu YT, Liu GR (2005) A meshfree weak-strong (MWS) form method for time dependent problems. Comput Mech 35:134–145
Dehghan M, Ghesmati A (2010) Combination of meshless local weak and strong (MLWS) forms to solve the two dimensional hyperbolic telegraph equation. Eng Anal Bound Elem 34(4):324–336
Dehghan M, Abbaszadeh M, Mohebbi A (2015) The use of interpolating element-free Galerkin technique for solving 2D generalized Benjamin–Bona–Mahony–Burgers and regularized long-wave equations on non-rectangular domains with error estimate. J Comput Appl Math 286:211–231
Trobec R, Kosec G, Šterk M, Šarler B (2012) Comparison of local weak and strong form meshless methods for 2-D diffusion equation. Eng Anal Bound Elem 36:310–321
Garg S, Pant M (2018) Meshfree methods: a comprehensive review of applications. Int J Comput Meth. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219876218300015
Liu CS, Kuo CL (2016) A multiple-scale Pascal polynomial triangle solving elliptic equations and inverse Cauchy problems. Eng Anal Bound Elem 62:35–43
Liu CS, Young DL (2016) A multiple-scale Pascal polynomial for 2D Stokes and inverse Cauchy-Stokes problems. J Comput Phys 312:1–13
Chang CW (2016) A new meshless method for solving steady-state nonlinear heat conduction problems in arbitrary plane domain. Eng Anal Bound Elem 70:56–71
Liu G, Ma W, Ma H, Zhu L (2018) A multiple-scale higher order polynomial collocation method for 2D and 3D elliptic partial differential equations with variable coefficients. Appl Math Comput 331:430–444
Wang M, Watson D, Li M (2018) The method of particular solutions with polynomial basis functions for solving axisymmetric problems. Eng Anal Bound Elem 90:39–46
Oruç Ö (2019) Numerical solution of two-dimensional Berger equation in deflection of thin plates via a meshless method based on multiple-scale Pascal polynomials. Appl Math Model. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.04.022
Liu CS, Wang F, Qu W (2018) Fast solving the cauchy problems of poisson equation in an arbitrary three-dimensional domain. CMES-Comp Model Eng 114(3):351–380
Schöberl J (1997) NETGEN an advancing front 2D/3D-mesh generator based on abstract rules. Comput Vis Sci 1(1):41–52
Logg A, Wells GN (2010) DOLFIN: automated finite element computing. ACM Trans Math Softw 37(2):1–28
Oliphant Travis E (2007) Python for scientific computing. Comput Sci Eng 9(3):10–20
Meurer A, Smith CP, Paprocki M, Čertík O, Kirpichev SB, Rocklin M, Kumar A, Ivanov S, Moore JK, Singh S, Rathnayake T, Vig S, Granger BE, Muller RP, Bonazzi F, Gupta H, Vats S, Johansson F, Pedregosa F, Curry MJ, Terrel AR, Roučka Š, Saboo A, Fernando I, Kulal S, Cimrman R, Scopatz A (2017) SymPy: symbolic computing in Python. PeerJ Comput Sci 3:e103. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.103
van der Walt S, Colbert SC, Varoquaux G (2011) The NumPy array: a structure for efficient numerical computation. Comput Sci Eng 13(2):22–30
Hunter JD (2007) Matplotlib: a 2D graphics environment. Comput Sci Eng 9(3):90–95
Riegel J, Mayer W, van Havre Y (2001–2017). FreeCAD (Version 0.15.4671) [Software]. http://www.freecadweb.org
Ahrens J, Geveci B, Law C (2005) ParaView: an end-user tool for large data visualization. In: Visualization handbook. Elsevier, ISBN-13: 978-0123875822
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank the reviewers for their useful comments and suggestions towards improvement of the paper.
Funding
The author(s) received no funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oruç, Ö. A meshless multiple-scale polynomial method for numerical solution of 3D convection–diffusion problems with variable coefficients. Engineering with Computers 36, 1215–1228 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00758-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00758-5