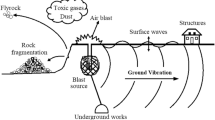
Abstract
The prediction model of blasting vibration has always been a hot and difficult topic because of the very complex nonlinear relationship between the blasting vibration and its influencing factors. A novel algorithm of Nested-ELM for predicting blasting vibration was proposed in this paper. Nested-ELM algorithm can quickly select the optimal input weights and biases of hidden nodes by setting MSE as the fitness function and combining with RWS method. And the algorithm can also quickly determine the optimal number of hidden nodes by setting its initial value according to the empirical formulas and selecting MAPE as the diffusion search index. The feasibility and superiority of Nested-ELM algorithm for predicting blasting vibration were proved by the application of Nested-ELM model on four different types of blasting vibration samples. This paper can provide a novel improved ELM algorithm for predicting blasting vibration with good performance in operation efficiency, prediction accuracy, generalization and sample-number independence.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hakan AK, Konuk Adnan (2008) The effect of discontinuity frequency on ground vibrations produced from bench blasting: a case study. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 28:686–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2007.11.006
Khandelwal M, Monjezi M (2013) Prediction of flyrock in open pit blasting operation using machine learning method. Int J Min Sci Technol 23:313–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2013.05.005
Armaghani DJ, Hajihassani M, Mohamad ET, Marto A, Noorani SA (2014) Blasting-induced flyrock and ground vibration prediction through an expert artificial neural network based on particle swarm optimization. Arab J Geosci 7:5383–5396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1174-0
Hasanipanah M, Monjezi M, Shahnazar A, Armaghani DJ, Farazmand A (2015) Feasibility of indirect determination of blast induced ground vibration based on support vector machine. Measurement 75:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2015.07.019
Hasanipanah M, Bakhshandeh Amnieh H, Khamesi H, Jahed Armaghani D, Bagheri Golzar S, Shahnazar A (2018) Prediction of an environmental issue of mine blasting: an imperialistic competitive algorithm-based fuzzy system. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:551–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1395-y
Cardu M, Coragliotto D, Oreste P (2019) Analysis of predictor equations for determining the blast-induced vibration in rock blasting. Int J Min Sci Technol 29:905–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2019.02.009
Hasanipanah M, Jahed Armaghani D, Khamesi H, Bakhshandeh Amnieh H, Ghoraba S (2016) Several non-linear models in estimating air-overpressure resulting from mine blasting. Eng Comput 32:441–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-015-0425-y
Bui X, Nguyen H, Le H, Bui H, Do N (2020) Prediction of blast-induced air over-pressure in open-pit mine: assessment of different artificial intelligence techniques. Nat Resour Res 29:571–591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09461-0
Asl PF, Monjezi M, Hamidi JK, Armaghani DJ (2018) Optimization of flyrock and rock fragmentation in the Tajareh limestone mine using metaheuristics method of firefly algorithm. Eng Comput 34:241–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0535-9
Rad HN, Hasanipanah M, Rezaei M, Eghlim AL (2018) Developing a least squares support vector machine for estimating the blast-induced flyrock. Eng Comput 34:709–717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0568-0
Hasanipanah M, Bakhshandeh Amnieh H (2020) A fuzzy rule-based approach to address uncertainty in risk assessment and prediction of blast-induced flyrock in a quarry. Nat Resour Res 29:669–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09616-4
Bian JQ, Bi JY, Wang HD (2019) Numerical simulation study on unsteady distribution law of dust in blasting roadway of inclined ditch mine. China Min Mag 28:269–274. https://doi.org/10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2019.S1.037
Zou CF, Deng YF (2019) Study on dust production law and dust reduction technology in blasting stope. Min Res Dev 39:34–37. https://doi.org/10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2019.08.007
Ghasemi Ebrahim (2017) Particle swarm optimization approach for forecasting backbreak induced by bench blasting. Neural Comput Appl 28:1855–1862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2182-2
Hasanipanah M, Bakhshandeh Amnieh H (2020) Developing a new uncertain rule-based fuzzy approach for evaluating the blast-induced backbreak. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00919-6
Khandelwal M, Saadat M (2015) A dimensional analysis approach to study blast-induced ground vibration. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48:727–735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-014-0604-y
Zhao HB, Long Y, Li XH, Lu L (2016) Experimental and numerical investigation of the effect of blast-induced vibration from adjacent tunnel on existing tunnel. KSCE J Civ Eng 20:431–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0130-9
Xu C, Deng CF (2016) Investigating spectral behavior of tunnel blast-induced vibration using wavelet analysis: a case study of a dam in China. J Civ Struct Health Monit 6:637–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13349-016-0183-6
Yang JH, Lu WB, Li P, Yan P (2018) Evaluation of rock vibration generated in blasting excavation of deep-buried tunnels. KSCE J Civ Eng 22:2593–2608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-0240-7
Zhou SR, Zhou JM, Wang HH, Ding XF, Ye JB, Zhao MS (2018) Analysis of blasting parameters optimization and blasting vibration effects of subway excavation. Blasting 35:85–89. https://doi.org/10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2018.02.015
Ma Q, Zhou FX, Zhang WY, Li YX (2019) An analytical study on blast-induced ground vibration with gravitational effect. Soil Mech Found Eng 56:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-019-09604-8
Xu SD, Li YH, Liu JP, Zhang FP (2019) Optimization of blasting parameters for an underground mine through prediction of blasting vibration. J Vib Control 25:1585–1595. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546319829938
Tian E, Zhang J, Soltani Tehrani M, Surendar A, Ibatova AZ (2019) Development of GA-based models for simulating the ground vibration in mine blasting. Eng Comput 35:849–855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-018-0635-1
Khandelwal M, Armaghani DJ, Faradonbeh RS, Yellishetty M, Majid MZA, Monjezi M (2016) Classification and regression tree technique in estimating peak particle velocity caused by blasting. Eng Comput 33:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0455-0
Hasanipanah M, Naderi R, Kashir J, Noorani SA, Qaleh AZA (2016) Prediction of blast produced ground vibration using particle swarm optimization. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0462-1
Fouladgar N, Hasanipanah M, Bakhshandeh Amnieh H (2017) Application of cuckoo search algorithm to estimate peak particle velocity in mine blasting. Eng Comput 33:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0463-0
Behzadafshar K, Mohebbi F, Soltani Tehrani M, Hasanipanah M, Tabrizi O (2018) Predicting the ground vibration induced by mine blasting using imperialist competitive algorithm. Eng Comput 35:1774–1787. https://doi.org/10.1108/EC-08-2017-0290
Nguyen H, Bui X, Bui H, Cuong DT (2019) Developing an XGBoost model to predict blast-induced peak particle velocity in an open-pit mine: a case study. Acta Geophys 67:477–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-019-00268-4
Nguyen H, Bui X, Tran Q, Mai N (2019) A new soft computing model for estimating and controlling blast produced ground vibration based on hierarchical K-means clustering and cubist algorithms. Appl Soft Comput 77:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.01.042
Monjezi M, Baghestani M, Faradonbeh RS, Saghand MP, Armaghani DJ (2016) Modification and prediction of blast-induced ground vibrations based on both empirical and computational techniques. Eng Comput 32:717–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0448-z
Wu X, Zhang YP, Guo QF (2017) Amplification and attenuation effect of blasting vibration on step topography. Explos Shock Waves 37:1017–1022. https://doi.org/10.11883/1001-1455(2017)06-1017-06
Dauji Saha (2018) New approach for identification of suitable vibration attenuation relationship for underground blasts. Eng J 22:147–159. https://doi.org/10.4186/ej.2018.22.4.147
Liu GP (2019) Prediction of blasting vibration velocity for large-section tunnel blasting. Blasting 36:129–136. https://doi.org/10.3963/j/issn.1001-487X.2019.03.020
Saheli R, Saha D (2019) Ground vibration attenuation relationship for underground blast: a case study. J Inst Eng (India) Ser A 100:763–775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-019-00382-y
Aawal H, Mishra AK (2019) Modified scaled distance regression analysis approach for prediction of blast-induced ground vibration in multi-hole blasting. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 11:202–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2018.07.004
Monjezi M, Ghafurikalajahi M, Bahrami A (2011) Prediction of blast-induced ground vibration using artifcial neural networks. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 26:46–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2010.05.002
Monjezi M, Hasanipanah M, Khandelwal M (2013) Evaluation and prediction of blast-induced ground vibration at Shur River Dam, Iran, by artificial neural network. Neural Comput Appl 22:1637–1643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-0856-y
Nguyen H, Bui X, Tran Q, Moayedi H (2019) Predicting blast-induced peak particle velocity using BGAMs, ANN and SVM: a case study at the Nui Beo open-pit coal mine in Vietnam. Environ Earth Sci 78:479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8491-x
Verma AK, Singh TN (2013) A neuro-fuzzy approach for prediction of longitudinal wave velocity. Neural Comput Appl 22:1685–1693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-0817-5
Dindarloo Saeid R (2015) Prediction of blast-induced ground vibrations via genetic programming. Int J Min Sci Technol 25:1011–1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.09.020
Bhagwat VP, Dey K (2016) Comparison of some blast vibration predictors for blasting in underground drifts and some observations. J Inst Eng (India) Ser D 97:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-015-0086-4
Himanshu VK, Roy MP, Mishra AK, Paswan RK, Panda D, Singh PK (2018) Multivariate statistical analysis approach for prediction of blast-induced ground vibration. Arab J Geosci 11:460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3796-8
Matidza MI, Zhang J, Huang G, Mwanggi AD (2020) Assessment of blast-induced ground vibration at Jinduicheng Molybdenum open pit mine. Nat Resour Res 29:831–841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09623-5
Hajihassani M, Jahed Armaghani D, Marto A, Mohamad ET (2015) Ground vibration prediction in quarry blasting through an artificial neural network optimized by imperialist competitive algorithm. Bull Eng Geol Environ 74:873–886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0657-x
Khandelwal M, Armaghani DJ, Faradonbeh RS, Yellishetty M, Majid MZA, Monjezi M (2017) Classification and regression tree technique in estimating peak particle velocity caused by blasting. Eng Comput 33:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0455-0
Samareh H, Khoshrou SH, Shahriar K, Saberi MM (2015) Seismic data classification using cluster analysis for predicting ground vibration caused by blast. Arab J Geosci 8:9679–9692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1923-3
Faradonbeh RS, Armaghani DJ, Abd Majid MZ, Tahir MD, Ramesh Murlidhar B, Monjezi M, Wong HM (2016) Prediction of ground vibration due to quarry blasting based on gene expression programming: a new model for peak particle velocity prediction. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:1453–1464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-0979-2
Hasanipanah M, Faradonbeh RS, Bakhshandeh Amnieh H, Armaghani DJ, Monjezi M (2017) Forecasting blast-induced ground vibration developing a CART model. Eng Comput 33:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0475-9
Hasanipanah M, Golzar SB, Larki IA, Maryaki MY, Ghahremanians T (2017) Estimation of blast-induced ground vibration through a soft computing framework. Eng Comput 33:951–959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0508-z
Hasanipanah M, Naderi R, Kashir J, Noorani SA, Qaleh AZA (2017) Prediction of blast-produced ground vibration using particle swarm optimization. Eng Comput 33:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0462-1
Eskandar H, Heydari E, Hasanipanah M, Jalil Masir M, Mahmodi Derakhsh A (2018) Feasibility of particle swarm optimization and multiple regression for the prediction of an environmental issue of mine blasting. Eng Comput 35:363–376. https://doi.org/10.1108/EC-01-2017-004
Arthur CK, Temeng VA, Ziggah YY (2020) Novel approach to predicting blast-induced ground vibration using Gaussian process regression. Eng Comput 36:29–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-018-0686-3
Zhang YN, Yang YW, Li W (2010) Neural network with direct weight determination method. Sun Yat-sen University Press, Guangzhou
Zhang ZX (2011) Neural networks control and Matlab simulation. Harbin Institute of Technology Press, Harbin
Monjezi M, Ahmadi M, Sheikhan M, Bahrami A, Salimi AR (2010) Predicting blast-induced ground vibration using various types of neural networks. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 30:1233–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2010.05.005
Zhao HB, Long Y, Liu HQ, Li XH, Zhong MS (2014) Application of neural networks to prediction of peak amplitude of blasting vibration velocity of urban tunnel. Eng Blasting 20:23–27. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2014.05.005
Ram Chandar K, Sastry VR, Hegde C (2017) A critical comparison of regression models and artificial neural networks to predict ground vibrations. Geotech Geol Eng 35:573–583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-016-0126-3
Shi JJ, Li QY, Zhang Q, Wei X, Wang H (2017) Forecast system for blasting vibration velocity peak based on Matlab and BP neural network. Explos Shock Waves 37:1087–1092. https://doi.org/10.11883/1001-1455(2017)06-1087-06
Taheri K, Hasanipanah M, Bagheri Golzar S, Abd Majid MZ (2017) A hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm-artificial neural network for forecasting the blast-produced ground vibration. Eng Comput 33:689–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0497-3
Ragam P, Nimaje DS (2018) Evaluation and prediction of blast-induced peak particle velocity using artificial neural network: a case study. Noise Vib Worldw 49:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1177/0957456518763161
Nguyen H, Bui X, Tran Q, Le T, Do N, Hoa LTT (2019) Evaluating and predicting blast-induced ground vibration in open-cast mine using ANN: a case study in Vietnam. SN Appl Sci 1:125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-018-0136-2
Ganguly S (2019) Development of a blast induced vibration prediction model using an artificial neural network. J S Afr Inst Min Metall 119:187–200. https://doi.org/10.17159/2411-9717/2019/v119n2a11
Ma HY, Zhang YP, Liu HY (2019) Prediction of blasting vibration velocity in underground stope based on BP neural network. Explos Mater 48:55–59. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2019.06.011
Nguyen H, Drebenstedt C, Bui X, Bui DT (2020) Prediction of blast-induced ground vibration in an open-pit mine by a novel hybrid model based on clustering and artificial neural network. Nat Resour Res 29:691–709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09470-z
Li YM (2019) Research and application of improved algorithm of classifier based on BP neural network. Dissertation, China University of Geosciences
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2004) Extreme learning machine: a new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2004 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN2004), Budapest, July 25-29, pp 985–990. https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2004.1380068
Huang GB, Ding XJ, Zhou HM (2010) Optimization method based extreme learning machine for classification. Neuro Comput 74:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2010.02.019
Xie ZG, Xu K, Liu LG, Xiong YS (2014) 3D shape segmentation and labeling via extreme learning machine. Comput Graph Forum 33:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/cgf.12434
Cao JW, Zhang K, Luo MX, Yin C, Lai XP (2016) Extreme learning machine and adaptive sparse representation for image classification. Neural Netw 81:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2016.06.001
Wang MJ, Chen HL, Li HZ, Cai ZN, Zhao XH, Tong CF, Li J, Xu X (2017) Grey wolf optimization evolving kernel extreme learning machine: application to bankruptcy prediction. Eng Appl Artif Intell 63:54–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2017.05.003
Lv FC, Liu Y, Qi YX, Yan YH, Zhang JT, Xie Q (2018) Short-term load forecasting based on optimized learning machine using improved genetic algorithm. J North China Electric Power Univ 45:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-2691.2018.06.01
Xu JQ, Wu WN, Sun W, Wang YN, Liang QK (2019) Optimized extreme learning machines and their application in decoupling of multi-component force information. Chin J Sens Actuators 32:1487–1492. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2019.10.010
Yin HH, Yang XW, Liu JM, Han X (2019) An extreme learning machine based on ant lion optimization. Comput Appl Softw 36:230–234. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2019.08.039
Fu B (2015) Passive target localisation algorithm based on optimizing extreme learning machine with PSO. Comput Appl Softw 32:325–328. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2015.11.076
Pang S, Yang XY, Lin XS (2017) Evolutionary extreme learning machine optimized by quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. J Syst Simul 29:2447–2458. https://doi.org/10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.201710028
Chu ZY, Ma Y, Cui J (2018) Adaptive reactionless control strategy via the PSO-ELM algorithm for free-floating space robots during manipulation of unknown objects. Nonlinear Dyn 91:1321–1335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3947-6
Li QW, Han F, Ling QH (2018) An improved double hidden-layer variable length incremental extreme learning machine based on particle swarm optimization. In: International conference on intelligent computing (ICIC 2018), Wuhan, August 15-18, pp 34–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95933-7_5
Zhang TH, Yu J, Ye ZL, Lin Y (2019) Classification model research of mixed kernel extreme learning machine based on particle swarm optimization. J Geomat Sci Technol 36:56–61. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2019.01.011
Zhao H, Zuo KW, Qin YZ (2016) Improved artificial bee colony optimize ELM classification model. Comput Meas Control 24:251–254. https://doi.org/10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2016.10.071
Wang Y, Wang A, Ai Q, Sun HJ (2017) A novel artificial bee colony optimization strategy-based extreme learning machine algorithm. Prog Artif Intell 6:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13748-016-0102-4
Wang XM, Wan XH, Zhu YY, Jiang ZL, Liu JX (2014) Prediction for building vibration velocity caused by blasting based on PSO-ELM. Sci Technol Rev 32:15–20. https://doi.org/10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2014.19.001
Jahed Armaghani D, Kumar D, Samui P, Hasanipanah M, Roy B (2020) A novel approach for forecasting of ground vibrations resulting from blasting: modified particle swarm optimization coupled extreme learning machine. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-00997-x
Li XB, Deng GD, Liu ZX (2015) On the predication for the blast vibration velocity based on SA-ELM. J Saf Environ 15:115–119. https://doi.org/10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2015.03.025
Wen TX, Chen XY, Shao LB, Dou R, Wei P (2017) Prediction on parameters optimized GA-ELM model for cast blasting in open-pit mine. J China Coal Soc 42:630–638. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2016.0572
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and application. Neurocomputing 70:489–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126
Huang GB, Wang DH, Lan Y (2011) Extreme learning machine: a survey. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 2:107–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-011-0019-y
Rao CR, Mitra SK (1971) Generalized inverse of matrices and its applications. Wiley, Baltimore
Serre D (2002) Theory and applications. Springer, New York
Wei B, Yu F, Xu X, Xie C (2014) Interactive evolutionary algorithm based on improved roulette wheel selection strategy. Comput Digit Eng 42:1763–1767. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2014.10.004
Xia GM, Zeng JC (2007) A stochastic particle swarm optimization algorithm based on the genetic algorithm of roulette wheel selection. Comput Eng Sci 29:51–54. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2007.06.016
Ma JY (2018) Research on chaotic firefly algorithm based on roulette wheel selection strategy. Dissertation, Xidian University
Zhu DQ, Shi H (2006) Theory and application of artificial neural network. Science Press, Beijing
Ma CD, Dong LJ, Zhou YN, Xu JC (2014) Nonlinear model for predicting characteristic parameters of blasting vibration and its application. Ming Metall Eng 34:1–4. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2014.06.001
Li B, Bi TH, Liu XW (2018) Influence factors of blasting vibration of shallow tunnel based on grey relational analysis. Eng Blasting 24:86–90. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2018.04.017
Guan XM, Nie QK, Li HW, An JY (2019) Research overview on dynamic response and damage of existing structure under tunnel blasting vibration. China Civ Eng J 52:151–158. https://doi.org/10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2019.s1.021
Singh CP, Agrawal H, Mishra AK, Singh PK (2019) Reducing environmental hazards of blasting using electronic detonators in a large opencast coal project-a case study. J Mines Met Fuels 67:345–350
Golafshani EM, Ashour A (2016) A feasibility study of BBP for predicting shear capacity of FRP reinforced concrete beams without stirrups. Adv Eng Softw 97:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.02.007
Gong SW, Ling TH (2009) Fuzzy neural networks model of peak particle vibration velocity forecast for blasting and its application. Ming Res Dev 29:95–97. https://doi.org/10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2009.02.031
Tang H, Shi YQ, Li HB, Li JR, Wang XW, Jiang PC (2007) Prediction of peak velocity of blasting vibration based on neural network. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 26:3533–3539. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.z1.145
Shi XZ (2007) Study of time and frequency analysis of blasting vibration signal and the prediction of blasting vibration characteristic parameters and damage. Dissertation, Central South University
Hasanipanah M, Jahed Armaghani D, Bakhshandeh Amnieh H, Majid MZZ, Tahir MMD (2017) Application of PSO to develop a powerful equation for prediction of flyrock due to blasting. Neural Comput Appl 28:1043–1050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2434-1
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51874123 and 51504082) and Open Project Foundation of Fujian Research Center for Tunneling and Urban Underground Space Engineering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, H., Chen, J., Zhu, J. et al. A novel algorithm of Nested-ELM for predicting blasting vibration. Engineering with Computers 38, 1241–1256 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01082-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01082-z