Abstract
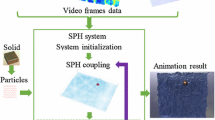
In this paper, we propose a hybrid (physical-stochastic) model of surface element (surfel) fluctuations for the visual simulation of an endlessly running water surface. This model comprises two main phases: preprocessing and endless animation phases. First, we simulate a physics-based method for a specific period of time during the preprocessing phase. We construct a stochastic vector field in the simulation, referred to as a Markov-Type Vector Field (MTVF), using only the surface values of the fluid flow. Next, we import the MTVF data into the main endless animation phase and create a surface fluctuation animation by surfels and temporary velocity field modeling of the MTVF using a random sample. In our approach, the surfel edges that cover the fluid flow domain are transferred simply via a temporary single velocity and the new flow surface is determined directly based on their positions. MTVF allows us to generate a water surface animation endlessly in real time without the time-consuming processes of solving the corresponding physical equations. We describe the MTVF construction method and the endless surface animation steps, as well as present the results of experiments that demonstrate the plausibility of our method.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burrell, T., Arnold, D., Brooks, S.: Advected river textures. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 20(2–3), 163–173 (2009)
Chentanez, N., Muller, M.: Real-time simulation of large bodies of water with small scale details. In: Proc. of ACM SIGGRAPH/EUROGRAPHICS Symposium on Computer Animation (2010)
Enright, D., Marschner, S., Fedkiw, R.: Animation and rendering of complex water surfaces. ACM Trans. Graph. 21, 736–744 (2002)
Foster, N., Fedkiw, R.: Practical animation of liquids. In: SIGGRAPH ’01: Proc. of the 28th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, pp. 23–30 (2001)
Glassner, A.S.: Duck! IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 22(4), 88–97 (2002)
Bridson, R., Houriham, J., Nordenstam, M.: Curl-noise for procedural fluid flow. ACM Trans. Graph. 26(3), 26 (2007)
Kipfer, P., Westermann, R.: Realistic and interactive simulation of rivers. In: Proc. of the Conference on Graphics Interface, vol. 137, pp. 41–48 (2006)
Koshizuka, S., Tamako, H., Oka, Y.: Particle method for incompressible viscous flow with fluid fragmentation. Comput. Fluid Dyn. J. 4, 29–46 (1995)
Koshizuka, S., Oka, Y.: Moving particle semi-implicit method for fragmentation of incompressible fluid. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 123, 421–434 (1996)
Marcelo, M.M., Fujimoto, T., Chiba, N.: Efficient animation of water flow on irregular terrains. In: GRAPHITE Uf06, pp. 107–115 (2006)
Monaghan, J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 30, 543–574 (1992)
Müller, M., Charypar, D., Gross, M.: Particle-based fluid simulation for interactive applications. In: Proceedings of the 2003 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. SCA ’03, pp. 154–159 (2003)
Neyret, F., Praizelin, N.: Phenomenological simulation of brooks. In: Proc. Eurographics Workshop on Computer Animation and Simulation, pp. 53–64 (2001)
Norris, J.R.: Markov Chains. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1998)
Nugjgar, P., Fujimoto, T., Chiba, N.: Markov-type velocity field designed for endless animation of water stream. In: Proceedings of CGI2011 Conf., Fluid and Effects Simulation Session, Paper No. 4, Ottawa University, Canada, June (2011)
Nugjgar, P., Fujimoto, T., Chiba, N.: Markov-type velocity field for efficiently animating water stream. Vis. Comput. 28(2), 219–229 (2012)
Perlin, K.: An image synthesizer. In: Proc. SIGGRAPH, pp. 287–296 (1985)
Premoze, S., Tasdizen, T., Bigler, J., Lefohn, A., Whitaker, R.T.: Particle-based simulation of fluids. Eurographics 22(3), 401–410 (2003)
Reeves, W.T.: Particle systems—a technique for modeling a class of fuzzy objects. Comput. Graph. 17(3), 359–376 (1983)
Shi, S., Ye, X., Dong, Z., Zhang, Y.: Real-time simulation of large-scale dynamic river water. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 15(6), 635–646 (2007)
Stam, J.: Stable fluids. In: SIGGRAPH ’99: Proc. of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, pp. 121–128 (1999)
Tessendorf, J.: Simulating ocean water. In: SIGGRAPH 2004 Course Notes 31 (2004)
Thon, S., Ghazanfarpour, D.: Real-time animation of running waters based on spectral analysis of Navier–Stokes equations. In: Proc. of Computer Graphics International, pp. 333–346 (2002)
Thürey, N., Rüde, U., Stamminger, M.: Animation of open water phenomena with coupled shallow water and free surface simulation. In: Proceedings of the 2006 Eurographics/ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Computer Animation. Eurographics Association, Goslar (2006)
Yu, Q., Neyret, F., Bruneton, E., Holzschuch, N.: Scalable real-time animation of rivers. Comput. Graph. Forum 28(2), 239–248 (2009)
Yu, Q., Neyret, F., Neyret, F., Steed, A.: Feature-based vector simulation of water waves. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 22, 91–98 (2011)
Yuksel, C., House, D.H., Keyser, J.: Wave particles. ACM Trans. Graph. 26 (2007)
Zhu, Y., Bridson, R.: Animating sand as a fluid. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 965–972 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nugjgar, P., Chiba, N. Markov-Type Vector Field for endless surface animation of water stream. Vis Comput 29, 959–968 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-013-0851-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-013-0851-z