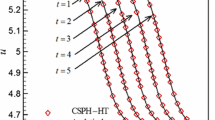
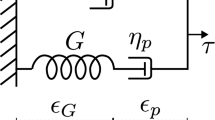
Abstract
We propose a particle-based hybrid method for simulating volume preserving viscoelastic fluids with large deformations. Our method combines smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) and position-based dynamics (PBD) to approximate the dynamics of viscoelastic fluids. While preserving their volumes using SPH, we exploit an idea of PBD and correct particle velocities for viscoelastic effects not to negatively affect volume preservation of materials. To correct particle velocities and simulate viscoelastic fluids, we use connections between particles which are adaptively generated and deleted based on the positional relations of the particles. Additionally, we weaken the effect of velocity corrections to address plastic deformations of materials. For one-way and two-way fluid-solid coupling, we incorporate solid boundary particles into our algorithm. Several examples demonstrate that our hybrid method can sufficiently preserve fluid volumes and robustly and plausibly generate a variety of viscoelastic behaviors, such as splitting and merging, large deformations, and Barus effect.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinci, N., Ihmsen, M., Akinci, G., Solenthaler, B., Teschner, M.: Versatile rigid-fluid coupling for incompressible SPH. ACM Trans. Graph. 31(4), 62:1–62:8 (2012)
Becker, M., Ihmsen, M., Teschner, M.: Corotated SPH for deformable solids. In: Proceedings of the Fifth Eurographics Conference on Natural Phenomena, pp. 27–34 (2009)
Becker, M., Teschner, M.: Weakly compressible SPH for free surface flows. In: Proceedings of the 2007 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 209–217 (2007)
Bender, J., Müller, M., Otaduy, M.A., Teschner, M.: Position-based methods for the simulation of solid objects in computer graphics. In: EUROGRAPHICS 2013 State of the Art Reports, pp. 1–22 (2013)
Bodin, K., Lacoursiere, C., Servin, M.: Constraint fluids. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 18(3), 516–526 (2012)
Chang, Y., Bao, K., Liu, Y., Zhu, J., Wu, E.: A particle-based method for viscoelastic fluids animation. In: Proceedings of the 16th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology, pp. 111–117 (2009)
Clavet, S., Beaudoin, P., Poulin, P.: Particle-based viscoelastic fluid simulation. In: Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 219–228 (2005)
Cummins, S.J., Rudman, M.: An SPH projection method. J. Comput. Phys. 152(2), 584–607 (1999)
Gerszewski, D., Bhattacharya, H., Bargteil, A.W.: A point-based method for animating elastoplastic solids. In: Proceedings of the 2009 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 133–138 (2009)
He, X., Liu, N., Li, S., Wang, H., Wang, G.: Local poisson SPH for viscous incompressible fluids. Comput. Graph. Forum 31(6), 1948–1958 (2012)
Ihmsen, M., Akinci, N., Becker, M., Teschner, M.: A parallel SPH implementation on multi-core CPUs. Comput. Graph. Forum 30(1), 99–112 (2011)
Ihmsen, M., Cornelis, J., Solenthaler, B., Horvath, C., Teschner, M.: Implicit incompressible SPH. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 20(3), 426–435 (2014)
Ihmsen, M., Orthmann, J., Solenthaler, B., Kolb, A., Teschner, M.: SPH fluids in computer graphics. In: EUROGRAPHICS 2014 State of the Art Reports, pp. 21–42 (2014)
Jones, B., Ward, S., Jallepalli, A., Perenia, J., Bargteil, A.W.: Deformation embedding for point-based elastoplastic simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 33(2), 21:1–21:9 (2014)
Macklin, M., Müller, M.: Position based fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 32(4), 104:1–104:5 (2013)
Macklin, M., Müller, M., Chentanez, N., Kim, T.Y.: Unified particle physics for real-time applications. ACM Trans. Graph. 33(4), 104 (2014)
Mao, H., Yang, Y.H.: Particle-based non-Newtonian fluid animation with heating effects. Tech. rep. (2006)
Miller, G., Pearce, A.: Globular dynamics: a connected particle system for animating viscous fluids. Comput. Graph. 13(3), 305–309 (1989)
Müller, M., Charypar, D., Gross, M.: Particle-based fluid simulation for interactive applications. In: Proceedings of the 2003 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 154–159 (2003)
Müller, M., Heidelberger, B., Hennix, M., Ratcliff, J.: Position based dynamics. J. Vis. Commun. Image Rep. 18(2), 109–118 (2007)
Müller, M., Heidelberger, B., Teschner, M., Gross, M.: Meshless deformations based on shape matching. ACM Trans. Graph. 24(3), 471–478 (2005)
Müller, M., Keiser, R., Nealen, A., Pauly, M., Gross, M., Alexa, M.: Point based animation of elastic, plastic and melting objects. In: Proceedings of the 2004 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 141–151 (2004)
Solenthaler, B., Pajarola, R.: Predictive-corrective incompressible SPH. ACM Trans. Graph. 28(3), 40:1–40:6 (2009)
Solenthaler, B., Schläfli, J., Pajarola, R.: A unified particle model for fluid-solid interactions. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 18(1), 69–82 (2007)
Steele, K., Cline, D., Egbert, P.K., Dinerstein, J.: Modeling and rendering viscous liquids. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 15(3–4), 183–192 (2004)
Takahashi, T., Fujishiro, I., Nishita, T.: A velocity correcting method for volume preserving viscoelastic fluids. In: Proceedings of the Computer Graphics International 2014 (2014)
Takahashi, T., Nishita, T., Fujishiro, I.: Fast simulation of viscous fluids with elasticity and thermal conductivity using position-based dynamics. Comput. Graph. 43, 21–30 (2014)
Takamatsu, K., Kanai, T.: A fast and practical method for animating particle-based viscoelastic fluids. Int. J. Virtual Real. 10, 29–35 (2011)
Tamura, N., Nakaguchi, T., Tsumura, N., Miyake, Y.: Spring-bead animation of viscoelastic materials. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 27(6), 87–93 (2007)
Terzopoulos, D., Platt, J., Fleischer, K.: Heating and melting deformable models. J. Vis. Comput. Animat. 2, 68–73 (1991)
Zhou, Y., Lun, Z., Kalogerakis, E., Wang, R.: Implicit integration for particle-based simulation of elasto-plastic solids. Comput. Graph. Forum 32(7), 215–223 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work has been partly supported by JST CREST. We would like to thank anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, T., Dobashi, Y., Fujishiro, I. et al. Volume preserving viscoelastic fluids with large deformations using position-based velocity corrections. Vis Comput 32, 57–66 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-014-1055-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-014-1055-x